Professional diploma computerised accounts payroll equips you with the skills to master modern accounting and payroll systems. This comprehensive training delves into the intricacies of computerised accounting, highlighting the vital role of payroll software in today’s businesses. From understanding different software applications to navigating the ethical considerations of payroll management, this diploma offers a thorough and practical approach to the field.
The program covers everything from introductory concepts to advanced practical applications. You’ll learn about various software, explore case studies, and gain insight into the future of this dynamic industry. Data security and privacy are also key elements, emphasizing responsible and compliant practices.
Introduction to Computerised Accounts and Payroll
Computerised accounting systems have revolutionized how businesses manage their financial records. These systems offer significant advantages over manual methods, including increased accuracy, efficiency, and data accessibility. From tracking income and expenses to generating financial reports, computerised accounting provides a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health. This overview delves into the core principles of computerised accounting, highlighting the pivotal role of payroll software in modern business operations, and emphasizing the crucial role of professional training in this field.Modern businesses rely heavily on payroll software to manage employee compensation accurately and efficiently.
These systems automate tasks such as calculating salaries, deductions, and taxes, ensuring compliance with labour laws and reducing the risk of errors. Furthermore, payroll software often integrates with other accounting systems, streamlining the entire financial process.
Computerised Accounting Systems Overview
Computerised accounting systems leverage software applications to automate and streamline various accounting functions. These systems store and process financial data digitally, offering features like automated data entry, sophisticated reporting tools, and real-time access to information. This digital approach fosters improved accuracy and efficiency compared to manual methods, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on timely and precise financial data.
Role of Payroll Software in Modern Businesses
Payroll software plays a critical role in managing employee compensation and ensuring compliance with labor laws. Automation of tasks like calculating salaries, deductions, and taxes minimizes errors and saves valuable time. The integration with other accounting systems enhances data consistency and reduces the risk of discrepancies.
Importance of Professional Training
Professional training in computerised accounts and payroll is essential for developing expertise and staying abreast of industry best practices. This training equips individuals with the knowledge and skills to effectively manage financial records and payroll processes, ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Furthermore, training enhances the ability to adapt to evolving technological advancements and industry regulations.
Different Types of Computerised Accounting Software for Payroll
Understanding the diverse types of accounting software used for payroll is crucial for businesses to select the most appropriate system for their needs. This selection process should consider factors such as company size, specific requirements, and budget constraints. A well-chosen software solution will ensure accuracy, efficiency, and compliance with labor regulations.
| Software Type | Description | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud-Based Payroll Software | Accessed via the internet, typically subscription-based, offering flexibility and scalability. | Small to medium-sized businesses needing flexibility and accessibility. |
| On-Premise Payroll Software | Installed locally on a company’s server. | Larger businesses requiring greater control over data security and customization. |
| Integrated Accounting Software with Payroll Module | Combines accounting and payroll functions within a single platform. | Businesses requiring a holistic view of financial data and integrated management. |
Diploma Structure and Curriculum

A professional diploma in computerised accounts and payroll equips individuals with the essential skills and knowledge to excel in the field. This structured program provides a comprehensive understanding of accounting principles, payroll processing, and the application of computer software to these tasks. The curriculum is designed to be practical, emphasizing hands-on experience and real-world applications.This diploma program delves into the intricacies of managing financial records, processing employee compensation, and utilizing accounting software.
Graduates are well-prepared for entry-level positions in accounting and payroll departments, or for further advancements in their careers.
Typical Modules Covered, Professional diploma computerised accounts payroll
The curriculum typically includes modules focusing on fundamental accounting principles, bookkeeping, and financial reporting. Payroll processing, including calculations, deductions, and reporting, is a core component. Software proficiency is also vital, encompassing the use of specific accounting and payroll software packages. Many programs also incorporate modules on tax regulations and compliance, and potentially, advanced topics like budgeting and forecasting.
- Fundamental Accounting Principles: This module covers the core concepts of double-entry bookkeeping, the accounting equation, and the preparation of financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement). Understanding these principles is essential for accurate record-keeping and financial reporting.
- Bookkeeping and Financial Reporting: This module delves into the practical application of accounting principles. Students learn how to record transactions, prepare journals and ledgers, and generate various financial reports. Accuracy and meticulousness are paramount in this area.
- Payroll Processing: This module focuses on the calculation of salaries, wages, and deductions (e.g., taxes, benefits). Students learn about different payroll methods, tax regulations, and the importance of compliance. This module is crucial for efficient and accurate payroll management.
- Computerised Accounting Software: The use of accounting software like QuickBooks, Xero, or similar programs is a key element. This module trains students on data entry, report generation, and reconciliation procedures using these tools. Hands-on experience is emphasized.
- Tax Regulations and Compliance: This module covers current tax laws and regulations relevant to payroll processing and business operations. Compliance is vital for avoiding penalties and maintaining a legitimate business.
Key Skills Developed
This type of training develops a wide range of essential skills. These skills include:
- Data Entry and Analysis: Accuracy and speed in data input are critical for efficient record-keeping. Analysis of data is also crucial for identifying trends and patterns.
- Software Proficiency: The ability to use accounting and payroll software packages effectively is a key requirement in today’s business environment. Learning how to navigate and use these programs proficiently is essential.
- Financial Reporting: The creation of accurate and comprehensive financial reports is crucial for informed decision-making. The skill to present data effectively and clearly is essential.
- Problem Solving and Critical Thinking: Troubleshooting errors, resolving discrepancies, and identifying solutions are crucial in payroll and accounting. Logical reasoning and critical thinking are required to analyze problems and find solutions.
- Compliance and Ethics: Adhering to tax regulations and ethical accounting practices are essential to ensure legality and maintain a trustworthy reputation. Understanding the legal implications is critical.
Learning Outcomes
Graduates of a professional diploma in computerised accounts and payroll are expected to:
- Demonstrate a strong understanding of accounting principles and payroll processing.
- Effectively utilize accounting and payroll software to manage financial records and employee compensation.
- Prepare accurate and comprehensive financial reports, including income statements, balance sheets, and payroll records.
- Comply with relevant tax regulations and maintain accurate records.
- Analyze financial data to identify trends and make informed decisions.
Comparison of Diploma Programs
| Program | Duration | Curriculum Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Program A | 12 Months | Focuses on practical applications of accounting software and payroll processing. Emphasizes hands-on training with QuickBooks. |
| Program B | 18 Months | Offers in-depth modules on advanced accounting concepts, budgeting, and forecasting. Provides more advanced payroll management techniques. |
| Program C | 15 Months | Includes a strong emphasis on tax regulations and compliance. Includes specialized modules on international accounting standards. |
Software Applications and Tools
Choosing the right software is crucial for efficient computerised accounting and payroll. Different software packages offer varying features, impacting the accuracy, speed, and overall management of financial data. Understanding the common tools and their specific functionalities is key to optimizing workflow and ensuring compliance. This section explores the landscape of software used in computerised accounting and payroll, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Common Software for Computerised Accounting
Commonly used software for computerised accounting includes dedicated accounting packages like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage. These applications provide comprehensive tools for managing various aspects of financial transactions, from recording invoices and expenses to generating reports and financial statements. Each package boasts a range of features tailored for specific business needs, from small startups to larger corporations. Some features frequently encountered in these packages are automated accounting processes, bank reconciliation tools, and reporting functions.
Common Software for Computerised Payroll
Payroll software is essential for processing employee wages and deductions accurately. Leading payroll software providers include ADP, Paychex, and Gusto. These systems automate the payroll process, ensuring accurate calculations, tax withholdings, and compliance with local and federal regulations. Modern payroll software often includes features for managing employee information, tracking time and attendance, and integrating with other accounting software.
Features of Leading Payroll Software
Different payroll software solutions offer varying levels of functionality. Key features to consider include employee management, time and attendance tracking, tax calculation, and report generation. Features such as direct deposit integration, automated tax filings, and compliance reporting are also valuable considerations.
Comparison of Payroll Software Functionality
Payroll software solutions vary in their capabilities. Some focus on simplicity and ease of use for smaller businesses, while others cater to complex needs with extensive features for large corporations. The functionality of these software solutions impacts factors like processing speed, accuracy, and compliance. Comparing different software packages can be critical to finding the best fit for a business.
Key Features of Leading Payroll Software Applications
| Software Application | Employee Management | Time & Attendance Tracking | Tax Calculation & Reporting | Compliance Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADP | Comprehensive employee database with customizable fields; integration with HR systems. | Advanced time tracking options, including manual entries, clock-in/out, and PTO management. | Accurate calculation of federal, state, and local taxes, and reporting. | Compliance with various payroll regulations and automatic updates for tax changes. |
| Paychex | Centralized employee records, allowing for easy data management and updates. | Flexible time tracking methods, accommodating various work arrangements. | Automated tax calculations and reporting; support for complex tax scenarios. | Compliance tools for various payroll jurisdictions and proactive alerts for regulatory changes. |
| Gusto | Intuitive employee onboarding and management tools. | Simple and user-friendly time tracking interface. | Automated calculations and reporting for most common tax situations. | Automatic compliance updates and reporting on compliance status. |
Practical Application and Case Studies
Mastering computerised accounting and payroll goes beyond theoretical knowledge. Real-world application is crucial for effective implementation and problem-solving. This section dives into practical examples, case studies, and the setup process to solidify your understanding of these vital business functions.
Real-World Applications of Computerised Accounting and Payroll
Computerised accounting and payroll systems are ubiquitous in modern businesses. They streamline processes, enhance accuracy, and provide valuable insights into financial performance. From small startups to large corporations, these systems are essential for managing finances and employee compensation. For example, a small retail store can use computerised accounting to track sales, expenses, and inventory levels in real-time.
Large corporations use sophisticated systems to manage complex global operations, ensuring accurate reporting and compliance with various regulations.
A professional diploma in computerised accounts and payroll is a great stepping stone for a career in finance. Learning the intricacies of accounting software is crucial, but understanding the vulnerabilities in systems, like those exploited by the infamous Stuxnet worm ( stuxnet dissecting the worm ), also helps build a more robust understanding of data security. Ultimately, a solid grasp of computerised accounting and payroll principles is vital for any aspiring financial professional.
Case Study: Payroll Software Implementation in a Small Business
A small bakery, “Sweet Sensations,” struggled with manual payroll calculations. Errors were frequent, leading to delays in payments and compliance issues. They implemented a payroll software solution. The software automated tasks like calculating deductions, generating pay stubs, and processing payments. This resulted in significant time savings, improved accuracy, and enhanced employee satisfaction.
A professional diploma in computerised accounts and payroll is super valuable for future career success. Understanding the intricacies of payroll, accounts, and financial management is key, but a great manager also needs strong leadership skills, excellent communication, and the ability to motivate teams. Learning about leadership styles and decision-making processes is important, and I highly recommend checking out this insightful article on what makes a great manager to get a better perspective.
Ultimately, a solid foundation in computerised accounts and payroll, combined with managerial skills, will make you a highly sought-after professional in this field.
The software also enabled the bakery to comply with tax regulations effortlessly.
Setting Up a Payroll System in a Company
Setting up a payroll system involves several key steps. First, define the necessary data, including employee details, pay rates, deductions, and tax information. This step ensures the system accurately reflects the company’s payroll structure. Second, select appropriate software or a cloud-based solution. Third, implement the chosen system, including training employees and establishing procedures for data entry and verification.
Fourth, configure the system to meet specific legal requirements and internal policies. This step ensures compliance and efficiency.
Data Accuracy in Payroll Processing: A Case Study
Inaccurate payroll data can lead to severe consequences. A manufacturing company, “Precision Parts,” experienced a data entry error that resulted in incorrect tax withholdings. The error went unnoticed for several months, causing significant tax penalties. To avoid such situations, they implemented robust data validation procedures and established a double-entry system for payroll data. This approach significantly reduced errors, ensuring compliance and maintaining a positive relationship with the tax authorities.
Industry Trends and Future Developments
The field of computerised accounting and payroll is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for professionals in this sector to maintain relevance and adapt to the dynamic landscape. This section delves into the current trends, the impact of automation, predicted future developments, and emerging technologies shaping the future of payroll processing and accounting.
Current Trends in Computerized Accounting and Payroll
The current landscape of computerised accounting and payroll is marked by a strong emphasis on cloud-based solutions, automation, and data analytics. Businesses are increasingly migrating their accounting and payroll systems to cloud platforms for scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. This shift allows for real-time data access and collaboration, significantly improving efficiency. Additionally, automation is streamlining routine tasks, reducing manual errors, and freeing up staff for more strategic roles.
Impact of Automation and Technology
Automation tools, including robotic process automation (RPA), are significantly impacting the field. RPA automates repetitive tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and reconciliation, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. This frees up human resources to focus on higher-level tasks, such as financial analysis and strategic decision-making. Moreover, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is beginning to influence data analysis and predictive modelling in accounting and payroll, enabling proactive identification of potential issues and opportunities.
Future Developments and Challenges
Several key developments are anticipated in the coming years. The integration of blockchain technology in financial transactions promises enhanced security and transparency, especially in payroll management. Furthermore, the increasing demand for real-time reporting and analysis will require more sophisticated data visualization tools and dashboards. Businesses will face the challenge of adapting to these evolving technologies and ensuring data security and compliance in a constantly changing regulatory environment.
Examples include the growing importance of data privacy regulations like GDPR, which will necessitate careful handling and management of employee data.
Emerging Technologies Affecting Payroll Processing and Accounting
Several emerging technologies are impacting payroll processing and accounting. These include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are being used to automate tasks, detect anomalies, and provide predictive insights, potentially leading to improved fraud detection and more accurate payroll calculations.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based accounting and payroll solutions are becoming more prevalent, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness for businesses of all sizes. This also facilitates remote work and global collaboration.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s inherent security and transparency can enhance the integrity and traceability of payroll transactions, minimizing the risk of fraud and errors. It also improves transparency for both employers and employees.
- Big Data Analytics: Analyzing large datasets can provide valuable insights into employee behavior, productivity, and financial performance. This can help businesses make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
Examples of Current Applications
Many businesses are already leveraging these technologies. For instance, some companies utilize AI-powered tools to automatically categorize expenses, while others are implementing cloud-based payroll systems to improve efficiency and reduce administrative overhead. Real-time data analysis is also becoming more common, enabling businesses to respond quickly to financial trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
Data Security and Privacy in Payroll: Professional Diploma Computerised Accounts Payroll
Payroll processing involves handling highly sensitive financial data, making robust data security paramount. Protecting employee information, wages, and deductions is crucial to maintain trust and avoid legal repercussions. Failure to safeguard this data can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.Payroll data is a treasure trove of personal and financial details. From social security numbers to bank account information, these records are prime targets for malicious actors.
Compromised data can result in identity theft, fraudulent transactions, and significant financial hardship for employees. Implementing strong security measures is essential to mitigate these risks and maintain the integrity of the payroll system.
Importance of Data Security in Payroll Processing
Data security in payroll processing is not merely a best practice; it’s a fundamental necessity. A secure system protects employee data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This safeguards employees’ financial well-being, maintains the company’s reputation, and prevents legal issues arising from data breaches. The consequences of a data breach can be severe, ranging from hefty fines to lawsuits and reputational damage.
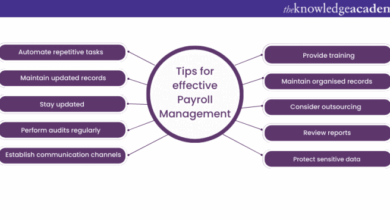
Measures to Protect Sensitive Payroll Data
Protecting sensitive payroll data requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes employing robust access controls, encrypting data both in transit and at rest, implementing regular security audits, and establishing clear data breach response plans. Furthermore, employee training on security awareness is critical. Employees must understand the importance of protecting sensitive data and adhere to security protocols.
- Strong Access Controls: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls restricts access to payroll data to authorized personnel only. This prevents unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive information. Restricting access to only necessary data for specific roles further reduces the potential impact of a security breach. For example, HR staff might need access to employee details, but not necessarily to salary information.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive payroll data both in transit and at rest protects it from unauthorized access even if a system is compromised. Encryption renders data unintelligible to unauthorized individuals, making it useless for malicious purposes. For example, using encryption for transferring payroll data between systems, and encrypting data stored in databases are essential.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits of the payroll system identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers. This proactive approach strengthens security measures and prevents potential breaches. Audits should cover access controls, data encryption, and security policies, among other areas.
- Data Breach Response Plan: A comprehensive data breach response plan Artikels procedures to follow in the event of a security incident. This includes steps to contain the breach, notify affected parties, and mitigate potential damage. The plan should also involve legal counsel to ensure compliance with regulations and handle potential legal repercussions.
- Employee Security Awareness Training: Training employees on security awareness helps them recognize and avoid phishing attempts, suspicious emails, and other security threats. This reduces the risk of human error leading to a data breach. Employees must be aware of the importance of password security, the dangers of clicking on unknown links, and the reporting of suspicious activities.
Compliance with Relevant Regulations and Laws
Payroll data is subject to various regulations and laws that mandate specific security measures. These regulations aim to protect employee privacy and financial data. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties. For example, GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and other local data privacy regulations must be adhered to. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial to maintaining compliance.
A professional diploma in computerised accounts and payroll is a great way to kickstart a career in finance. Learning the intricacies of managing accounts and payroll is a valuable skill in any business, but the future of these processes is likely to be significantly influenced by technological advancements like the new ‘DNA-like design’ concept that could lead to smaller faster microchips.
This innovative approach suggests a revolutionary change in microchip technology, and understanding these developments is important for professionals in the field, whether they’re learning the basics of payroll or refining advanced accounting techniques. Ultimately, a solid foundation in computerised accounts and payroll will always be relevant, even as technology evolves.
Data Security Best Practices for Payroll Systems
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Software Updates | Keeping software up-to-date patches known vulnerabilities, and enhances security. |
| Strong Passwords | Implementing strong, unique passwords for all accounts and regularly changing them. |
| Regular Backups | Creating regular backups of payroll data to restore in case of data loss. |
| Access Control Lists (ACLs) | Restricting access to payroll data based on roles and responsibilities. |
| Firewall Protection | Protecting the network from unauthorized access. |
| Monitoring and Logging | Monitoring system activity and logging all access attempts for auditing. |
| Security Awareness Training | Regular training for employees on data security best practices. |
Ethical Considerations in Payroll Management

Payroll management, a critical function in any organization, extends beyond simple calculations. It involves the ethical handling of sensitive employee data and the financial well-being of a workforce. A robust ethical framework is essential to ensure fairness, accuracy, and transparency in the entire process.Accurate and transparent payroll processing builds trust and fosters a positive work environment. Ethical considerations extend to all aspects of payroll, from data security to the treatment of employees’ compensation.
Accuracy and Transparency in Payroll Processing
Ensuring accuracy in payroll processing is paramount. Inaccurate calculations can lead to financial discrepancies, affecting both employees and the organization. Transparent procedures, clear communication, and readily accessible information for employees about their earnings, deductions, and benefits are crucial. Employees should have access to their pay stubs and understand how their deductions are calculated.
Potential Ethical Dilemmas in Payroll Management
Ethical dilemmas can arise in various payroll situations. One example is when an employee’s hours are misrecorded. This might be intentional or due to errors in timekeeping systems. Another dilemma is the handling of confidential information regarding salary discrepancies, bonuses, or performance-related incentives. Maintaining confidentiality and following established policies is crucial.
Solutions for Ethical Dilemmas
Several solutions can mitigate the risk of ethical dilemmas in payroll management. Implementing robust timekeeping systems, employing independent audits, and establishing clear communication channels can help prevent and resolve discrepancies. Regular training for payroll staff on ethical principles and policies is essential to ensure compliance. Establishing a system for reporting potential issues anonymously, without fear of retaliation, can be instrumental in uncovering and addressing ethical concerns early.
Employees should be encouraged to report any perceived irregularities or inconsistencies.
Maintaining Accurate Records
Accurate payroll records are essential for several reasons. They serve as legal documentation for tax purposes, providing a clear audit trail for compliance with regulations. Precise records help in resolving discrepancies promptly, and aid in forecasting future payroll needs. Maintaining detailed records also assists in identifying trends and patterns that might signal potential issues. Regular backups of data are also vital in preventing data loss and ensuring continuity.
Problem Solving and Troubleshooting
Navigating the complexities of computerised payroll is crucial for accuracy and compliance. Troubleshooting errors promptly and efficiently is vital for maintaining a smooth workflow and avoiding potential financial and legal issues. This section details common payroll problems, their resolution strategies, and the importance of continuous learning in this ever-evolving field.
Common Payroll Processing Problems
Troubleshooting payroll issues often involves a methodical approach. Identifying the root cause is paramount to implementing the correct solution. Common problems include incorrect data entry, missing or duplicated payments, calculation errors, and system malfunctions.
- Incorrect Data Entry: Mistakes in entering employee details, hours worked, or deductions can lead to inaccurate payroll calculations and payments. Data validation procedures and double-checking entries are essential to prevent these errors.
- Missing or Duplicated Payments: These errors can arise from system glitches or manual data processing issues. Regular system checks and manual reconciliation are crucial to catch these problems early.
- Calculation Errors: Complex calculations, such as overtime, taxes, and benefits, are prone to mistakes. Using built-in payroll software tools for these calculations and validating the results can minimise these errors.
- System Malfunctions: Technical glitches, software bugs, or hardware failures can disrupt payroll processing. Having backup systems, disaster recovery plans, and regular software updates can mitigate these risks.
Troubleshooting Steps
A systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential. Following a predefined procedure helps streamline the resolution process.
- Identify the Problem: Carefully review payroll reports, employee records, and system logs to pinpoint the specific issue. Detailed records and logging capabilities are invaluable for pinpointing the source of the problem.
- Isolate the Cause: Once the problem is identified, determine the underlying cause. Is it a data entry error, a software bug, or a system malfunction? Careful analysis is key to solving the problem effectively.
- Implement a Solution: Based on the identified cause, implement the appropriate solution. This may involve correcting data entries, updating software, or restoring system backups. Testing the solution before applying it to the entire payroll is recommended.
- Verify the Solution: After implementing the solution, double-check the payroll calculations and payments to ensure accuracy. Thorough verification helps prevent future recurrences of the same error.
Importance of Continuous Learning and Development
The payroll landscape is constantly evolving. Staying abreast of new technologies, regulations, and best practices is crucial. Continuous learning and development through training, certifications, and professional networks ensures you remain current and proficient in handling complex issues.
Example of a Complex Payroll Error and Resolution
Imagine an employee’s hours were incorrectly recorded in the system. This led to an underpayment. After reviewing the timesheet, the payroll manager identified the error in the input data. They corrected the hours in the system and recalculated the employee’s pay, ensuring accurate payment.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, a professional diploma in computerised accounts and payroll offers a robust pathway to a rewarding career. The program emphasizes practical skills, explores industry trends, and highlights ethical considerations. By mastering the intricacies of computerised accounting and payroll, graduates will be well-prepared to excel in this ever-evolving field.