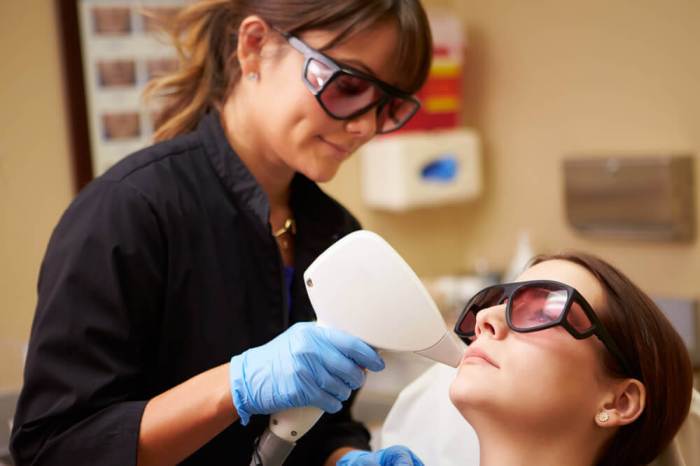
Working in medical aesthetics is a rapidly growing field offering exciting career paths. This guide delves into the world of non-surgical cosmetic enhancements, exploring the diverse roles, training requirements, and ethical considerations involved. From understanding the scope of procedures to navigating the market trends, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview for aspiring professionals and those seeking to expand their knowledge in this dynamic industry.
The field encompasses a range of procedures, each with its own techniques, tools, and patient considerations. This detailed exploration will highlight the necessary skills, education, and certifications required for various positions within medical aesthetics. We’ll also cover crucial elements such as patient consultations, informed consent, and the potential risks and benefits of different procedures.
Introduction to Medical Aesthetics
Medical aesthetics is a rapidly evolving field that blends medical expertise with cosmetic enhancements. It focuses on improving the appearance and well-being of patients through non-invasive and minimally invasive procedures. This field is increasingly popular due to the demand for safe and effective ways to address concerns about aging, skin imperfections, and body contouring.The scope of medical aesthetic procedures encompasses a wide range of treatments designed to address various concerns.
From rejuvenating the skin and improving facial contours to addressing body shaping and enhancing overall appearance, these procedures offer customized solutions for diverse patient needs. The procedures aim to enhance natural beauty and improve self-confidence.
Definition of Medical Aesthetics
Medical aesthetics encompasses procedures that combine medical knowledge and techniques with cosmetic goals. These procedures aim to improve the patient’s appearance, address specific concerns, and enhance their overall well-being. A key differentiator from purely cosmetic procedures is the integration of medical principles, safety protocols, and the use of FDA-approved products and techniques.
Scope of Medical Aesthetic Procedures
The scope of medical aesthetic procedures is extensive and includes a variety of treatments, targeted at specific areas of the body and addressed concerns. These procedures cover a wide spectrum of needs, from rejuvenating the skin to shaping the body. Examples include:
- Skin rejuvenation: Procedures like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser treatments, and fillers can improve skin texture, reduce wrinkles, and diminish the appearance of acne scars.
- Facial contouring: Dermal fillers, Botox, and other injectables can subtly reshape facial features, reducing wrinkles and adding volume to certain areas.
- Body contouring: Procedures like liposuction, laser treatments, and radiofrequency technologies can help patients achieve desired body shapes and reduce fat deposits.
- Hair restoration: Treatments like hair transplantation can address hair loss and promote healthy hair growth.
Historical Context of Medical Aesthetics
The history of medical aesthetics is deeply intertwined with the evolution of medical knowledge and cosmetic desires. Early forms of skin rejuvenation and body shaping techniques have existed for centuries, evolving alongside advancements in medicine and technology.
- Early Practices: Ancient civilizations employed various methods to improve appearance, including cosmetic surgery and skincare treatments. For example, ancient Egyptians used ingredients like henna for dyeing hair and cosmetics, while ancient Greeks and Romans valued beauty and sought to enhance their appearance.
- Modern Era: The development of modern medical aesthetics has been greatly influenced by breakthroughs in scientific research and the rise of cosmetic surgery. The introduction of new technologies like lasers, fillers, and injectables has revolutionized the field.
Evolution of Techniques and Technologies
The evolution of medical aesthetics has been marked by a constant refinement of techniques and a proliferation of innovative technologies.
- Advancements in Injectables: The development of more sophisticated fillers and botulinum toxin (Botox) has led to more precise and effective treatments for wrinkles, facial lines, and other aesthetic concerns. For example, the use of hyaluronic acid fillers has become increasingly common for facial volume restoration.
- Laser Technology: Laser treatments have revolutionized skin rejuvenation, offering targeted therapies for various skin conditions and concerns, including hair removal, skin resurfacing, and scar reduction. For example, fractional lasers can effectively treat wrinkles and acne scars while stimulating collagen production.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: The trend towards minimally invasive procedures has made aesthetic treatments safer and more accessible. The development of technologies like ultrasound-guided liposuction and non-surgical fat reduction techniques has minimized recovery time and potential risks.
Difference between Medical Aesthetics and Cosmetic Surgery
While both medical aesthetics and cosmetic surgery aim to enhance appearance, they differ significantly in their approach and scope.
| Characteristic | Medical Aesthetics | Cosmetic Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Non-invasive or minimally invasive | Invasive |
| Procedures | Fillers, Botox, lasers, peels | Rhinoplasty, breast augmentation, liposuction |
| Recovery Time | Generally shorter | Longer |
| Risks | Lower | Higher |
| Goals | Enhance natural beauty, address specific concerns | Transform or alter physical features |
Medical aesthetics focuses on subtle enhancements and improvements, while cosmetic surgery is more drastic, aiming for significant transformations. This distinction ensures that patients can choose the appropriate approach to meet their individual needs and goals.
Career Paths in Medical Aesthetics
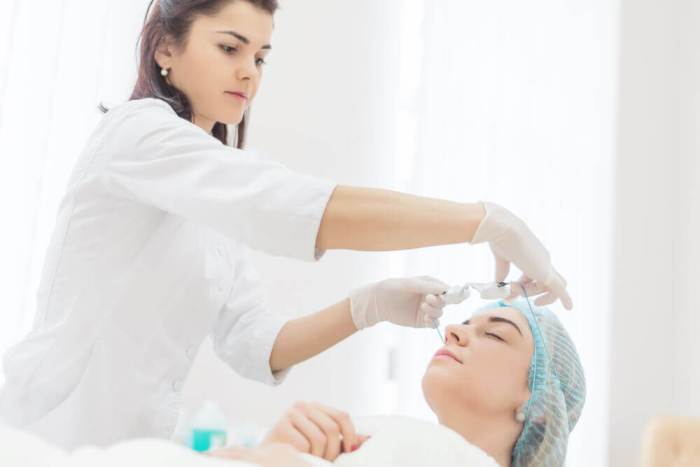
The medical aesthetics field offers a diverse range of career paths, catering to individuals with varying skill sets and interests. From technical procedures to patient interaction and business management, the opportunities are substantial. This diverse landscape allows individuals to specialize in areas that align with their passions and aspirations within the medical aesthetic industry.
Different Roles in Medical Aesthetics, Working in medical aesthetics
The medical aesthetics industry encompasses various roles, each with distinct responsibilities and skill requirements. These roles often require a blend of technical expertise, customer service skills, and business acumen. The roles are crucial for delivering high-quality patient care and running successful aesthetic practices.
Aesthetics Practitioner
Aesthetics practitioners perform a wide range of non-invasive and minimally invasive procedures. Their responsibilities include patient consultations, treatment planning, and administering procedures like Botox injections, dermal fillers, chemical peels, and laser treatments. They must possess strong knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and the specific products and techniques they utilize. Furthermore, effective communication and interpersonal skills are vital for building rapport with patients.
Medical Aesthetician
Medical aestheticians, often working under the supervision of a physician, assist in a variety of procedures. Their duties include preparing patients, sterilizing equipment, maintaining records, and providing aftercare instructions. A medical aesthetician typically possesses a strong understanding of skin anatomy and conditions, along with an understanding of medical safety protocols.
Nurse Practitioner/Physician Assistant
Nurse practitioners and physician assistants in medical aesthetics often oversee more complex procedures. Their responsibilities can include diagnosing conditions, administering medications, performing advanced aesthetic procedures, and managing patient care. A solid foundation in medical science and a comprehensive understanding of medical regulations are essential. These roles demand exceptional clinical judgment and decision-making skills.
Working in medical aesthetics is fascinating, constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in beauty and health. It’s about understanding not just the technical aspects but also the patient’s desires and expectations. This is very similar to the concept explored in the article “windows 8 and the perception game” windows 8 and the perception game , where the way something is presented significantly impacts how it’s perceived.
Ultimately, effective work in medical aesthetics relies on a nuanced understanding of both the procedures and the patient’s perspective.
Business Manager/Administrator
Business managers and administrators in medical aesthetics are responsible for the operational aspects of the practice. Their responsibilities range from scheduling appointments and managing inventory to overseeing financial operations and marketing efforts. Effective organizational skills, strong business acumen, and proficiency in relevant software applications are crucial.
Table of Common Career Paths and Qualifications
| Role | Responsibilities | Skills | Education/Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aesthetics Practitioner | Patient consultations, treatment planning, procedure administration | Strong knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and products/techniques; effective communication; interpersonal skills | Cosmetology license, specialized aesthetic training, possibly advanced certifications in specific procedures (e.g., Botox, fillers) |
| Medical Aesthetician | Preparing patients, sterilizing equipment, maintaining records, aftercare instructions | Strong understanding of skin anatomy and conditions; medical safety protocols; interpersonal skills | Cosmetology license, advanced medical aesthetic training, possibly medical assistant certification |
| Nurse Practitioner/Physician Assistant | Diagnosing conditions, administering medications, advanced aesthetic procedures, patient care management | Strong medical science foundation; comprehensive understanding of medical regulations; clinical judgment and decision-making skills | Registered Nurse (RN) or Physician Assistant (PA) certification, advanced training in aesthetic medicine |
| Business Manager/Administrator | Scheduling, inventory management, financial operations, marketing | Organizational skills; business acumen; proficiency in relevant software | Business administration degree or related certification, potentially medical office administration certification |
Training and Education
Embarking on a career in medical aesthetics demands rigorous training and adherence to strict regulatory standards. This ensures the safety and efficacy of treatments, ultimately benefiting clients and maintaining the integrity of the field. Comprehensive education is crucial for developing the necessary skills and knowledge to practice safely and effectively.The educational pathway for medical aesthetic professionals typically involves a structured curriculum that blends theoretical knowledge with practical application.
This multifaceted approach equips practitioners with the expertise to handle a diverse range of procedures and patient needs. The licensing and regulatory frameworks vary across jurisdictions, highlighting the importance of understanding local requirements before pursuing this career path.
Training Programs
Training programs for medical aesthetic professionals often encompass a combination of classroom learning, hands-on workshops, and supervised clinical experience. These programs are designed to provide a holistic understanding of the field, covering both the scientific underpinnings and the practical aspects of treatment delivery. Graduates should emerge with the capability to conduct a variety of aesthetic procedures, from injectables to laser treatments, while upholding the highest standards of patient care.
Curriculum Components
The curriculum typically includes a diverse range of subjects. Anatomy and physiology are fundamental to understanding the structure and function of the body, enabling practitioners to effectively target treatment areas and mitigate potential risks. Advanced knowledge of dermatology, pharmacology, and cosmetic products is essential to comprehend the science behind various aesthetic treatments and their impact on the skin.
Furthermore, programs incorporate essential aspects of patient consultation, treatment planning, and aftercare management. Hands-on training and supervised clinical experience are vital for developing practical skills and proficiency. This often involves working with standardized training models, and with the guidance of experienced mentors, developing expertise in administering various procedures under realistic scenarios.
Licensing and Regulatory Requirements
Licensing and regulatory requirements for medical aesthetic practitioners vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction. Each region has its own specific guidelines concerning qualifications, training, and the scope of practice. Practitioners must adhere to these regulations to ensure legal and ethical compliance. This typically involves obtaining relevant licenses and certifications, and in some cases, adhering to specific professional standards set by regulatory bodies.
Understanding these prerequisites is essential before initiating the educational process. A thorough investigation into the requirements of the target region is crucial to confirm compliance and avoid any potential legal issues.
Accredited Institutions
Accreditation of medical aesthetic training programs is a critical aspect of quality assurance. Reputable and accredited institutions provide a comprehensive educational experience, adhering to stringent standards set by relevant professional organizations. Choosing an accredited institution helps ensure that the program meets recognized standards of excellence, leading to the acquisition of highly valued qualifications. This often signifies adherence to rigorous quality control measures, fostering confidence in the legitimacy and reliability of the education provided.
Consult with professional associations and regulatory bodies for a list of accredited institutions.
Importance of Continuing Education
The medical aesthetic field is dynamic and constantly evolving. Continuing education is vital for practitioners to remain abreast of the latest advancements in techniques, technologies, and treatment modalities. This ongoing learning process allows practitioners to enhance their skills, adapt to emerging trends, and ensure they deliver the most effective and up-to-date care. Staying updated is essential for practitioners to adapt to new developments in treatment methodologies and technological advancements, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Patient Considerations: Working In Medical Aesthetics
Choosing a medical aesthetic professional is a significant decision, impacting the safety and effectiveness of your treatment. Understanding the factors involved in selecting a qualified practitioner, along with the importance of consultations, informed consent, and potential risks and benefits, is crucial for achieving desired outcomes while minimizing potential complications.Selecting the right practitioner involves more than just aesthetics; it hinges on expertise, experience, and a commitment to patient well-being.
A thorough understanding of these aspects allows patients to make informed choices, leading to positive experiences and results.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Medical Aesthetic Professional
Selecting a qualified medical aesthetic professional involves careful consideration. Factors such as the practitioner’s credentials, experience, and reputation play a vital role. Look for board certifications, relevant licenses, and memberships in professional organizations. A practitioner with a strong track record of successful treatments and positive patient feedback is also a valuable asset. Checking for malpractice claims or complaints is also crucial.
Moreover, consider the practitioner’s communication style and their ability to explain procedures clearly and address any concerns. A good rapport with your practitioner is vital for a positive experience.
Client Consultations and Assessments
Thorough consultations are essential for successful medical aesthetic treatments. These consultations provide an opportunity for patients to discuss their goals, concerns, and expectations with the practitioner. A comprehensive assessment evaluates the patient’s medical history, current health conditions, and any pre-existing skin conditions. This allows the practitioner to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and identify any potential contraindications.
The consultation process enables open communication and a shared understanding of the treatment plan, minimizing risks and maximizing the chances of achieving desired outcomes.
Importance of Informed Consent
Informed consent is a critical aspect of medical aesthetics. It’s a process where the practitioner provides comprehensive information about the procedure, including potential risks, benefits, alternatives, and expected outcomes. Patients must understand the procedure thoroughly and willingly consent to the treatment. This process ensures that patients make informed decisions based on a complete understanding of the involved factors.
The practitioner must document the consent process meticulously.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Different Procedures
Understanding the potential risks and benefits of various medical aesthetic procedures is paramount. Each procedure carries unique risks and benefits, depending on factors such as the patient’s individual characteristics, the chosen procedure, and the practitioner’s skill. It’s crucial for patients to be fully informed about the potential risks, complications, and long-term effects of a procedure. Benefits, such as improved appearance and self-confidence, must also be considered.
Working in medical aesthetics is fascinating, blending beauty with medical science. However, the constant need for high-quality tools and reliable technology is crucial. Just like the recent news about Google propelling the Chromebook Pixel into a blurry future here , we need to ensure the tech we use in aesthetics remains robust and cutting-edge to provide the best possible results for our clients.
Ultimately, staying ahead of the curve in medical aesthetics is essential.
Realistic expectations are key to a positive experience.
Procedure Comparison Table
| Procedure | Benefits | Risks | Ideal Candidates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dermal Fillers | Reduced wrinkles and folds, enhanced facial contours, lip augmentation | Possible bruising, swelling, infection, asymmetry, migration of filler | Individuals with moderate to severe facial wrinkles or volume loss, seeking subtle enhancements |
| Botox | Reduction of wrinkles and fine lines, smoothing facial expressions | Temporary weakness or drooping of muscles, allergic reactions, bruising | Individuals with moderate to severe dynamic wrinkles (those that appear with facial expressions) |
| Chemical Peels | Skin rejuvenation, reduction of acne scars, improvement of skin texture | Redness, swelling, peeling, potential for infection | Individuals with mild to moderate skin concerns, seeking to improve skin tone and texture |
| Laser Treatments | Skin resurfacing, reduction of scars, hair removal, pigmentation reduction | Burning, scarring, redness, skin discoloration, potential for infection | Individuals with various skin concerns, including wrinkles, acne scars, sun damage, and unwanted hair |
Procedure Overview
Diving deeper into the world of medical aesthetics, we now explore the diverse range of procedures available. Understanding the specifics of each procedure, the techniques employed, and the post-procedure care is crucial for both practitioners and patients. This section provides a comprehensive overview, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Common Medical Aesthetic Procedures
A multitude of procedures cater to various aesthetic concerns, from rejuvenating the skin to enhancing facial features. Each procedure targets specific issues and utilizes unique techniques. Factors like the patient’s individual needs, skin type, and desired outcome determine the most suitable approach.
Facial Procedures
Facial rejuvenation is a popular area of focus, with procedures designed to address wrinkles, fine lines, sagging skin, and other signs of aging. Dermal fillers, for example, can plump up facial contours, while chemical peels or laser treatments can resurface the skin. These procedures can significantly improve the appearance of the face, enhancing natural beauty and boosting self-esteem.
Body Contouring Procedures
Body contouring aims to reshape and refine specific areas of the body. Liposuction, for example, removes excess fat from targeted regions. Alternatively, non-surgical procedures like CoolSculpting use controlled cooling to eliminate fat cells. The techniques and tools vary based on the specific area being treated and the patient’s goals.
Skin Rejuvenation Procedures
These procedures are designed to address various skin concerns, from acne scars and hyperpigmentation to sun damage. Chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and laser treatments are examples of skin rejuvenation techniques. These procedures work by stimulating collagen production, improving skin texture, and reducing blemishes.
Hair Restoration Procedures
Hair loss is a common concern that can be addressed with medical aesthetic procedures. Hair transplantation, for instance, involves transferring hair follicles from a donor area to the recipient area. This procedure aims to restore hair density and fullness, offering a solution for those experiencing hair loss.
Table of Procedures by Body Area
| Body Area | Procedure | Description | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Face | Dermal Fillers | Injections of hyaluronic acid or other fillers to add volume and smooth wrinkles. | Reduced wrinkles, improved facial contours, enhanced volume. |
| Face | Chemical Peels | Application of chemical solutions to exfoliate the skin, revealing smoother, more even skin tone. | Improved skin texture, reduced acne scars, diminished hyperpigmentation. |
| Face | Laser Treatments | Use of lasers to target specific skin concerns, including wrinkles, pigmentation, and scars. | Reduced wrinkles, improved skin tone, diminished scars and blemishes. |
| Body | Liposuction | Surgical removal of excess fat from specific areas. | Reduced fat deposits, sculpted body contours. |
| Body | CoolSculpting | Non-surgical procedure using controlled cooling to eliminate fat cells. | Reduced fat deposits, sculpted body contours. |
| Body | Skin Tightening Treatments | Procedures to improve skin elasticity and firmness. | Improved skin tone and texture, reduced wrinkles and sagging. |
| Scalp | Hair Transplantation | Transferring hair follicles from a donor area to the recipient area. | Increased hair density, restoration of hair loss. |
Post-Procedure Care
Proper post-procedure care is essential for optimal results and minimizing complications. This typically involves following the practitioner’s instructions carefully, including specific medication regimens and lifestyle modifications. Patients should also be prepared for potential side effects, such as swelling, bruising, or discomfort, and be aware of how to manage them effectively.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The medical aesthetics industry is dynamic and ever-evolving, driven by consumer demand, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Understanding current trends and anticipating future developments is crucial for practitioners to adapt and thrive in this competitive landscape. This section explores the exciting future of medical aesthetics, highlighting key market trends and emerging technologies.The industry is characterized by a blend of established procedures and innovative approaches, fueled by a growing awareness of aesthetic enhancements and a desire for personalized solutions.
Working in medical aesthetics is fascinating, constantly evolving with new treatments and techniques. Juggling patient care, procedures, and staff management is a whirlwind, but incredibly rewarding. If you’re looking to elevate your career in this field, understanding the inner workings of a business, like the role of a chief of staff for ceo, can be invaluable. Chief of staff for CEO roles often involve strategic planning and operational efficiency, which are skills directly transferable to running a successful medical aesthetics practice.
Ultimately, mastering these principles can significantly enhance your leadership within the industry.
This creates a fertile ground for continued growth and diversification, promising exciting opportunities for professionals in the field.
Current Market Trends
The current market is experiencing a surge in demand for non-invasive and minimally invasive procedures. Patients are increasingly seeking natural-looking results, leading to a preference for subtle enhancements and personalized treatments. The rise of social media and online platforms has amplified the visibility of these procedures, creating a heightened awareness and demand for expertise in the field.
Growth and Development of the Industry
The medical aesthetics industry is experiencing robust growth, fueled by factors like an aging population, increased disposable income, and a rising awareness of aesthetic enhancements. The industry’s development is further facilitated by the increasing acceptance of aesthetic procedures as a legitimate health concern and an investment in one’s well-being. The demand for personalized treatments, customized to individual patient needs, is another key driver of industry growth.
The evolution of treatment options from invasive surgical procedures to minimally invasive, non-surgical options is also shaping the growth and development.
Projected Future Trends
Future trends in medical aesthetics will be shaped by the continued pursuit of natural-looking results, the incorporation of advanced technologies, and the increasing emphasis on patient safety and well-being. For instance, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics and treatment planning will personalize patient care and improve treatment outcomes. Emphasis on personalized medicine and patient-centric approaches will be a defining factor in the future of this field.
Emerging Technologies in Medical Aesthetics
Several emerging technologies are revolutionizing the field of medical aesthetics. These include:
- AI-powered diagnostics and treatment planning: AI algorithms can analyze patient data, predict treatment outcomes, and optimize treatment plans, leading to more precise and effective procedures.
- 3D printing of customized devices: 3D printing allows for the creation of highly personalized treatment devices and tools, improving precision and efficacy.
- Laser technology advancements: The development of new laser wavelengths and treatment modalities allows for more precise and targeted treatments with reduced side effects.
- Bio-regenerative medicine: This emerging field involves stimulating the body’s natural healing processes to promote tissue regeneration and rejuvenation, leading to improved long-term results.
Anticipated Impact on Career Opportunities
The emerging technologies and trends in medical aesthetics will significantly impact career opportunities. Professionals who possess a strong understanding of these advancements, coupled with practical skills and experience, will be highly sought after. The increasing demand for specialized expertise in areas like AI-assisted treatments, personalized medicine, and advanced laser techniques will create diverse career paths and opportunities for professionals to specialize in particular procedures or technologies.
For instance, specialists in AI-powered diagnostics and treatment planning are expected to be in high demand.
Ethical Considerations
The field of medical aesthetics, while offering transformative possibilities, demands a high level of ethical awareness. Practitioners must navigate complex situations with sensitivity and a commitment to patient well-being, ensuring procedures are performed safely and responsibly. Ethical considerations are not just a set of rules; they are the foundation upon which trust and credibility are built.Ethical standards in medical aesthetics are paramount to maintaining the integrity of the field and safeguarding patient safety.
These standards encompass a wide range of principles, from informed consent and confidentiality to conflict of interest and continuing education. Maintaining a high ethical standard promotes patient confidence and fosters a positive reputation for the entire profession.
Ethical Standards in Medical Aesthetics
Ethical standards in medical aesthetics are designed to protect patients and ensure that procedures are performed with the highest level of care and integrity. These standards often align with general medical ethics but have specific considerations related to the cosmetic nature of the procedures. This includes transparency about potential risks, realistic expectations, and avoiding exploitation of vulnerable patients.
Ethical Dilemmas and Challenges
Medical aesthetic practitioners face various ethical dilemmas, such as balancing patient desires with realistic expectations, determining appropriate treatment options, and handling situations where patient needs conflict with the practitioner’s personal values. Another challenge is maintaining confidentiality while complying with legal requirements. A further ethical concern arises when offering procedures that might be considered unnecessary or potentially harmful to the patient.
Role of Professional Organizations
Professional organizations play a crucial role in promoting ethical conduct within the medical aesthetic community. These organizations often develop and enforce codes of ethics, providing guidance for practitioners. They also offer educational resources and support to help practitioners navigate ethical dilemmas. By establishing and upholding these standards, professional organizations contribute significantly to maintaining high ethical standards and a positive public image for the profession.
Patient Safety and Well-being
Patient safety and well-being are paramount in medical aesthetics. Practitioners must prioritize thorough assessments, appropriate pre- and post-procedure care, and comprehensive communication with patients. It is vital to understand and address patient concerns and fears, ensuring informed consent and appropriate aftercare. This includes providing clear information about potential complications, risks, and alternatives.
Ethical Guidelines for Medical Aesthetic Professionals
Adherence to a strong ethical framework is essential for medical aesthetic professionals. These guidelines ensure patient safety, maintain professional integrity, and build trust within the community.
- Informed Consent: Thorough and comprehensive information about the procedure, including potential risks, benefits, alternatives, and potential complications, must be provided to the patient before any treatment. Consent must be freely given and documented.
- Patient Confidentiality: Patient information should be handled with the utmost confidentiality, adhering to all relevant privacy laws and regulations.
- Conflicts of Interest: Practitioners must disclose any potential conflicts of interest, such as financial incentives or personal relationships, that could compromise the objectivity of their recommendations or procedures.
- Continuing Education: Staying updated on the latest advancements, techniques, and safety protocols is essential. Practitioners must engage in ongoing education and training to maintain competency and deliver high-quality care.
- Realistic Expectations: Practitioners should ensure patients have realistic expectations about the outcomes of procedures. This includes discussing the limitations and potential for variation in results.
- Appropriate Treatment: Practitioners should only perform procedures for which they are qualified and certified. Procedures should be selected based on patient needs and not driven by financial gain.
- Avoiding Exploitation: Vulnerable patients, such as those with psychological issues or unrealistic expectations, must be identified and treated with extra caution and sensitivity. Practitioners must ensure that procedures are not being exploited for personal gain.
Business Aspects of Medical Aesthetics
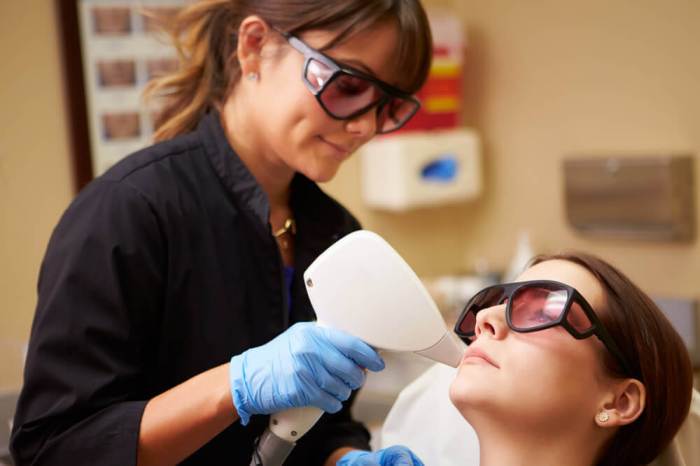
Turning a passion for beauty and health into a thriving medical aesthetics practice requires careful planning and execution. It’s more than just administering treatments; it’s a business built on customer relationships, strategic marketing, sound financial management, and unwavering adherence to regulations. Understanding these elements is crucial for long-term success and profitability.The medical aesthetics industry is dynamic and competitive.
Success hinges on a comprehensive understanding of business principles, not just technical skills. This involves creating a sustainable practice that attracts clients, manages costs, and ensures profitability.
Financial Aspects of the Business
Financial planning is fundamental to any business venture, and medical aesthetics is no exception. A detailed budget encompassing start-up costs, operating expenses, and projected revenue is essential. This includes expenses like rent, utilities, supplies, staff salaries, marketing, and insurance premiums. Understanding pricing strategies and calculating profitability margins are crucial. Analyzing historical data, if available, from similar practices, can offer insights into pricing and profitability.
Marketing and Advertising Strategies
Attracting clients in the competitive medical aesthetics market requires a robust marketing strategy. Building a strong online presence through a professional website, social media engagement, and online advertising is crucial. Content marketing, showcasing expertise through blog posts, articles, and educational videos, can also attract clients seeking knowledge and confidence in the practitioner.
Successful Business Models
Numerous successful business models exist in medical aesthetics. One model involves focusing on a specific niche, such as anti-aging treatments or cosmetic injectables, allowing the practice to specialize and build expertise. Another approach is building a multi-service practice encompassing various aesthetic procedures, attracting a wider range of clientele. Partnerships with complementary businesses, such as spas or wellness centers, can also broaden service offerings and client reach.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Adherence to industry regulations is non-negotiable. Understanding and meticulously following licensing requirements, HIPAA guidelines for patient privacy, and relevant state and local regulations are essential. This includes maintaining proper documentation, handling patient information securely, and adhering to ethical conduct standards. Failure to comply can lead to severe consequences, including legal action and reputational damage. Regular reviews and updates on regulatory changes are crucial to ensure continuous compliance.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, working in medical aesthetics presents a rewarding and dynamic career path. The industry’s growth and innovative advancements continue to shape the field, creating new opportunities for skilled professionals. From understanding the diverse procedures and patient needs to navigating the ethical and business aspects, this comprehensive guide provides a strong foundation for anyone interested in entering or advancing within this exciting field.
The journey of becoming a medical aesthetic professional involves meticulous training, a strong understanding of patient care, and a commitment to ethical practice. This overview highlights the crucial aspects to ensure a successful career.

