What is chief technology officer? This role is critical in today’s tech-driven world, shaping a company’s technological future. A CTO is more than just a technical expert; they’re strategic leaders who bridge the gap between innovation and business success. They define the tech roadmap, manage teams, and ensure the company stays ahead of the curve.
From defining the CTO role’s core responsibilities and historical evolution to understanding their interaction with other departments, this exploration covers the various aspects of the CTO’s function. The article will also examine the different types of organizations that employ a CTO and how the role might vary in each case, and then delve into the CTO’s essential duties, key metrics, and leadership skills.
This includes comparison with similar roles like CIO and VP of Engineering. The discussion also delves into skills and qualifications, strategic planning, team management, technological trends, budgeting, and problem-solving. In essence, we’ll uncover the multifaceted nature of the CTO role.
Defining the Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Role
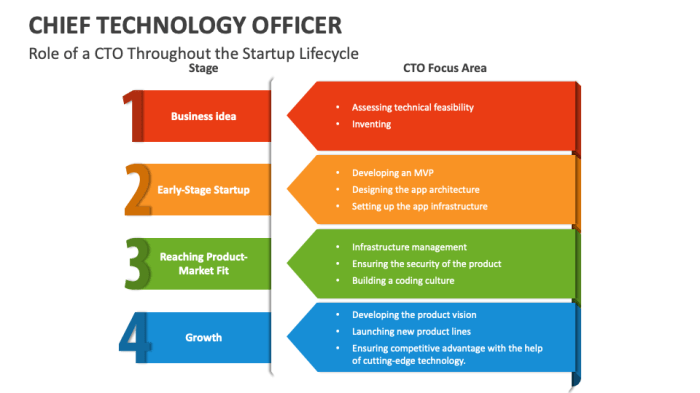
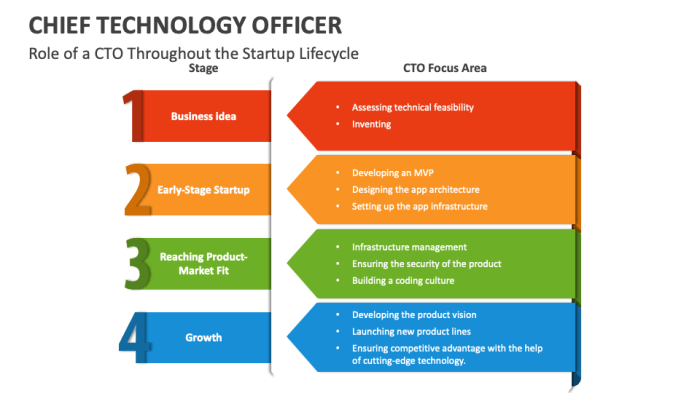
The Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is a pivotal executive in modern organizations, responsible for driving technological innovation and ensuring the effective use of technology to achieve business goals. Their role extends beyond simply managing IT infrastructure; it encompasses strategic planning, technological foresight, and collaboration with other departments to leverage technology for competitive advantage. The CTO’s influence is profound, impacting everything from product development to operational efficiency.The CTO’s responsibilities have evolved significantly over time.
Initially, the role focused primarily on maintaining and improving existing systems. Today, it encompasses a much broader scope, encompassing areas like emerging technologies, cybersecurity, and the development of innovative solutions. This evolution reflects the increasing importance of technology in all aspects of modern business.
CTO Core Responsibilities
The CTO’s responsibilities are multifaceted and encompass both strategic and operational aspects. They are accountable for defining the organization’s technology strategy, ensuring its alignment with business objectives, and overseeing its execution. This includes developing and implementing technology roadmaps, managing budgets, and overseeing the technology team. A crucial part of the role is fostering a culture of innovation and technological proficiency within the organization.
Historical Evolution of the CTO Role
The CTO role has evolved from a primarily operational function focused on maintaining IT infrastructure to a strategic leadership position responsible for driving innovation and technological advancement. Early CTOs were often embedded within the IT department, overseeing the day-to-day operations of computer systems. However, as technology’s importance grew, the role shifted to encompass broader strategic responsibilities. This transition reflects the growing understanding of technology’s critical role in achieving business objectives.
Today’s CTO is often a key player in shaping the company’s overall vision and strategy.
Organizational Structure and Interactions
The CTO typically reports to the CEO or a senior executive and often sits on the executive leadership team. Their role interacts closely with other departments, including product development, marketing, sales, and operations. Effective collaboration is crucial for ensuring that technology initiatives are aligned with business needs and contribute to the company’s overall success. For instance, the CTO might work closely with the product development team to ensure that new products leverage the latest technologies.
They also collaborate with marketing and sales to develop strategies for leveraging technology to increase customer engagement and revenue.
Types of Organizations Employing a CTO
The role of the CTO can differ depending on the size and type of organization. In a small startup, the CTO might be responsible for a broader range of tasks, including product development and engineering. In a large enterprise, the CTO’s responsibilities might be more focused on strategic planning and technology architecture. Even in a non-profit, a CTO can play a critical role in streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and delivering essential services.
Comparison of CTO Responsibilities Across Different Organizational Types
| Responsibility Area | Description | Impact on Company | Example Activities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Technology Planning | Defining the organization’s technology roadmap, ensuring alignment with business goals, and anticipating future technological trends. | Guides the company’s technological future, ensuring long-term competitiveness. | Developing technology roadmaps, conducting market research on emerging technologies, and identifying opportunities for technological innovation. |
| Technology Team Management | Leading, motivating, and developing the technology team, ensuring efficient and effective performance. | Ensures the team’s effectiveness and creates a positive work environment, leading to high-quality work. | Conducting performance reviews, providing mentorship, and recruiting talent. |
| Technology Budget Management | Managing the technology budget, ensuring resources are allocated effectively and efficiently. | Optimizes resource utilization and maintains financial health. | Preparing and presenting budget proposals, tracking expenditures, and identifying cost-saving opportunities. |
| Technology Infrastructure Management | Ensuring the availability and security of the organization’s technology infrastructure. | Guarantees smooth operations and protects the organization from security risks. | Managing servers, networks, and other infrastructure components, implementing security protocols, and ensuring disaster recovery plans are in place. |
Key Responsibilities and Duties
A Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is a pivotal role in any organization, especially those heavily reliant on technology. They bridge the gap between the technical vision and the overall business strategy, ensuring that technology investments align with company goals and drive innovation. This crucial role requires a deep understanding of both technology trends and the needs of the business.The CTO’s responsibilities extend far beyond simply managing the IT department.
They are architects of the company’s technological future, leading the charge in developing and implementing strategic technology initiatives. This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the company’s current and future technological landscape, enabling them to proactively address challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Essential Duties and Tasks
The CTO’s daily tasks encompass a broad spectrum of responsibilities, from overseeing the technical roadmap to fostering innovation within the organization. They are involved in strategic decision-making, technical planning, and operational execution. A core duty is defining the technology strategy and ensuring its alignment with business objectives. This includes identifying emerging technologies and assessing their potential impact on the company.
They must also be adept at managing resources, both human and financial, to effectively execute the technology strategy.
Key Metrics for CTO Success
Measuring the success of a CTO requires a multifaceted approach, going beyond simple metrics like cost savings. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should reflect the impact of technology on the business. These include metrics like project delivery time, quality of deliverables, adoption rates of new technologies, and the return on investment (ROI) of technology initiatives. Furthermore, the ability to attract and retain top engineering talent is a crucial factor in a CTO’s success, as it directly impacts the organization’s technical capabilities.
Comparison with Other Tech Roles
The CTO’s role differs significantly from that of a Chief Information Officer (CIO) or a Vice President of Engineering. While all three roles focus on technology, their scopes and priorities vary. A CIO typically focuses on managing IT infrastructure and operations, ensuring the smooth running of existing systems. A VP of Engineering, on the other hand, is more deeply involved in the day-to-day management of engineering teams and product development.
The CTO, however, sits at a higher level, overseeing the entire technology landscape and its strategic integration into the business. They are responsible for the long-term vision, whereas the CIO and VP of Engineering are more focused on the present and near-term execution.
Leadership Qualities for a Successful CTO
A successful CTO needs a unique blend of leadership qualities. Strong communication skills are essential for articulating the technical vision to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Strategic thinking and foresight are crucial for anticipating future technological trends and aligning them with business needs. Moreover, the ability to build and motivate high-performing teams is essential for driving innovation and achieving project goals.
The CTO needs to be decisive, adaptable, and a strong problem-solver.
Stakeholder Interactions
| Stakeholder | Needs |
|---|---|
| Executive Leadership | Strategic alignment of technology initiatives with business goals; clear articulation of the value proposition of technology investments. |
| Engineering Teams | Clear direction, support, and resources to deliver high-quality products; opportunities for professional development and advancement. |
| Product Management | Integration of technology into product development processes; efficient and reliable technology platforms. |
| Business Units | Support for their operational needs through effective technology solutions; rapid response to their technological challenges. |
| External Partners | Effective communication and collaboration; reliable and secure technology platforms for joint initiatives. |
Skills and Qualifications

The Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is a critical role in any organization, especially in today’s technology-driven world. Beyond technical proficiency, a successful CTO needs a unique blend of skills and experience to navigate the complexities of modern tech. They must be able to bridge the gap between technical innovation and business strategy, ensuring technology aligns with organizational goals.A CTO’s success hinges on their ability to lead and inspire a team, anticipate technological trends, and translate them into actionable strategies.
Their deep understanding of the technical landscape allows them to make informed decisions about resource allocation and technological investments.
Technical Expertise
A CTO needs a profound understanding of current and emerging technologies. This encompasses not only specific programming languages and frameworks, but also a broader knowledge of system architecture, cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data management. A comprehensive understanding of the technology stack, including hardware and software, is essential. Their technical expertise allows them to assess, evaluate, and implement technological solutions effectively.
Expertise in AI/ML, big data, and blockchain is increasingly valuable.
Essential Soft Skills
Leadership, communication, and strategic thinking are paramount for a CTO. A successful CTO must effectively communicate technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders, translate business needs into technical requirements, and motivate and mentor their team. Problem-solving abilities, adaptability to change, and a strong sense of vision are crucial to navigating the dynamic tech landscape. They need strong interpersonal skills to foster collaboration and build strong relationships with internal and external partners.
Strong negotiation skills are also important to secure resources and partnerships.
Educational Backgrounds and Certifications
A Master’s degree in Computer Science, Engineering, or a related field is common for CTOs. Specific certifications, such as those in cloud computing (AWS, Azure, GCP), project management (PMP), or cybersecurity (CISSP), can further enhance a candidate’s qualifications. A PhD in a relevant field can be a significant asset, particularly for CTOs involved in research and development. Formal education, however, is not the sole criterion; practical experience and demonstrable achievements are equally important.
Experience Levels and Career Path
CTO candidates often possess significant experience in software development, engineering, or related fields. A typical career path involves starting as a developer or engineer, progressing through roles like senior engineer, team lead, and director of engineering before transitioning into a CTO position. The specific experience requirements vary by industry and organization size, but a consistent track record of success and leadership is generally expected.
Industry-Specific Skill Sets
| Industry | Key Technical Skills | Key Soft Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech | Security, cryptography, compliance, financial modeling, regulatory knowledge | Risk management, compliance expertise, strong financial acumen |
| Healthcare Tech | Data privacy, HIPAA compliance, medical device integration, AI/ML in healthcare | Ethical considerations, patient privacy, data security, collaboration with healthcare professionals |
| E-commerce | Scalable architecture, high-availability systems, payment processing, supply chain management | Customer experience focus, data analysis, understanding of market trends |
Strategic Vision and Planning: What Is Chief Technology Officer
The Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is more than just a technical expert; they are a strategic architect, guiding the company’s technological trajectory. This role demands a deep understanding of the business’s overarching goals and the ability to translate those ambitions into tangible technology initiatives. A successful CTO anticipates future technological trends and leverages them to enhance the company’s competitive advantage.A CTO’s strategic planning extends beyond merely implementing existing technologies.
It encompasses identifying emerging technologies and assessing their potential to disrupt or improve existing processes. This foresight is crucial for staying ahead of the curve and capitalizing on opportunities that might otherwise be missed.
Strategic Planning in Relation to Business Goals
A CTO’s strategic planning should be intrinsically linked to the overall business strategy. This means aligning technology initiatives with financial targets, market positioning, and customer needs. For instance, if the business aims to expand into a new market, the CTO should develop a technology roadmap that supports this expansion. This could involve building a scalable cloud infrastructure, developing a new mobile application for customer engagement, or implementing a system for data analysis to better understand the new market.
Product Development and Innovation
The CTO plays a pivotal role in fostering product development and innovation. By leveraging technological expertise and industry insights, they can identify areas where technology can improve existing products or create entirely new offerings. A CTO might lead a team to develop a new feature for a software product, automate a manufacturing process, or design a novel user interface.
This can include using AI for product recommendations, leveraging IoT for predictive maintenance, or adopting machine learning for enhanced customer service.
Driving Technology Adoption and Implementation
Implementing new technologies across a company requires careful planning and execution. The CTO is responsible for ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the return on investment. This often involves developing training programs, creating clear implementation schedules, and monitoring the effectiveness of the new technologies. For example, a CTO might implement a phased approach for rolling out a new software system, providing ongoing support to users, and gathering feedback to continuously improve the system.
Identifying Emerging Technologies and Potential Applications
Staying abreast of emerging technologies is critical for a CTO. This involves attending industry conferences, subscribing to relevant publications, and networking with other industry professionals. For example, a CTO might investigate the potential of blockchain technology for supply chain management, explore the possibilities of augmented reality for customer interaction, or assess the implications of artificial intelligence for data analysis and automation.
The key is not just to identify these technologies, but to assess their potential impact on the company’s specific needs.
Technology Roadmap Development
A well-defined technology roadmap is essential for guiding the company’s technological direction. It serves as a blueprint for technology investments and provides a clear path for achieving strategic goals. This roadmap should be adaptable to changing market conditions and incorporate feedback from various stakeholders.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Define Objectives | Clearly articulate the business goals and how technology will contribute to achieving them. |
| 2. Assess Current State | Evaluate the existing technology infrastructure and its alignment with the objectives. |
| 3. Identify Opportunities | Analyze emerging technologies and their potential application to the business. |
| 4. Prioritize Initiatives | Evaluate the feasibility and impact of different initiatives based on strategic importance and resource availability. |
| 5. Develop Implementation Plan | Create detailed plans for each initiative, including timelines, budgets, and resource allocation. |
| 6. Monitor and Evaluate | Track progress, gather feedback, and adjust the roadmap as needed to maintain alignment with business objectives. |
Leading and Managing Teams
A CTO’s success hinges significantly on their ability to lead and manage a high-performing technical team. This involves more than just technical expertise; it demands strong interpersonal skills, strategic thinking, and the capacity to foster a collaborative and innovative environment. A skilled CTO understands the nuances of motivation and communication within a diverse technical landscape, ensuring the team’s collective efforts drive the company’s technological vision forward.Effective team leadership is crucial for a CTO.
They need to establish clear goals, delegate tasks effectively, and provide ongoing support and guidance. This leadership extends beyond direct supervision to encompass fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement. A CTO must create a supportive environment where team members feel empowered to contribute their unique skills and ideas.
A Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is essentially the tech visionary of a company, overseeing all things digital. They’re crucial for innovation and driving technological advancement. Silicon Valley, renowned for its groundbreaking ideas, has pioneered an innovative approach to creating American jobs, exemplified by its dynamic companies. This often involves fostering a culture of experimentation and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the tech world, as detailed in this insightful piece on the topic.
Ultimately, a CTO plays a pivotal role in shaping a company’s tech future, drawing on those kinds of creative solutions to make a real difference.
Motivating and Inspiring Teams
A CTO motivates their team by clearly articulating the project’s significance and its alignment with the company’s overall strategic goals. This involves demonstrating a genuine passion for the work and fostering a sense of shared purpose among team members. Recognition and appreciation for individual contributions are also key. Regular feedback sessions, both positive and constructive, help team members understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
Opportunities for professional development and skill enhancement contribute significantly to team morale and motivation. A supportive environment, free of micromanagement, allows team members to take ownership of their work and feel valued for their contributions.
Managing Diverse Technical Teams
Managing diverse technical teams requires a nuanced approach. Recognizing and respecting the varying backgrounds, perspectives, and communication styles of team members is essential. A CTO must be adept at creating an inclusive environment where everyone feels heard and valued. This includes actively seeking diverse viewpoints and ensuring equitable opportunities for all team members. Addressing potential biases and fostering empathy are crucial aspects of effective team management.
Conflict resolution strategies are essential tools for navigating disagreements and ensuring productive collaboration. Understanding the unique technical expertise and career aspirations of each team member allows for personalized mentorship and development plans, thereby creating a more engaged and productive workforce.
Communication and Collaboration
Clear and consistent communication is paramount in a CTO’s role. This involves not only technical discussions but also conveying strategic direction, project updates, and company news. Open communication channels, such as regular team meetings and informal check-ins, foster transparency and trust. Tools and platforms for seamless collaboration, such as project management software and shared document repositories, are crucial for efficient teamwork.
Effective communication strategies, including active listening and providing constructive feedback, create a supportive environment where team members feel empowered to share ideas and concerns. A CTO’s ability to translate complex technical concepts into easily understandable language for non-technical stakeholders is also a critical aspect of effective communication.
Leadership Styles and Team Performance
Different leadership styles impact team performance in varying ways. A transformational leader inspires and motivates team members to exceed expectations. A democratic leader encourages participation and input from all team members, fostering a sense of ownership and shared responsibility. A coaching leader provides guidance and support, helping team members develop their skills and capabilities. A supportive leader prioritizes team well-being and creates a positive and collaborative work environment.
The most effective leadership style for a CTO will depend on the specific needs and characteristics of the team.
Building a High-Performance Engineering Team
Building a high-performance engineering team involves a multi-faceted approach. It begins with attracting top talent through competitive compensation packages and opportunities for growth. A clear understanding of team roles and responsibilities is vital. A robust onboarding process helps new team members quickly integrate into the team’s workflow. Establishing clear processes for code reviews, testing, and deployment ensures quality and efficiency.
A Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is essentially the tech visionary of a company, overseeing all things related to technology. They’re responsible for the strategic direction of tech initiatives, ensuring alignment with business goals. This often includes innovation, like exploring cutting-edge advancements like mean and green next gen turbochargers , and making sure the company stays ahead of the curve.
Ultimately, a CTO is a crucial leader, driving technological progress for the betterment of the entire organization.
Regular performance evaluations and feedback sessions are essential for ongoing improvement. Promoting a culture of continuous learning and innovation ensures that the team stays ahead of industry trends. Investing in the latest technologies and tools empowers the team to tackle complex challenges and deliver cutting-edge solutions.
Technology Trends and Innovation
The Chief Technology Officer (CTO) role is constantly evolving, driven by the rapid pace of technological advancement. Staying ahead of the curve and adapting to emerging trends is crucial for CTOs to effectively lead their teams and drive innovation within their organizations. This section explores the key technological trends shaping the modern CTO role, emphasizing the importance of continuous learning and adaptation in this dynamic profession.
Current Trends Shaping the CTO Role
The technological landscape is in a state of constant flux, demanding a proactive and adaptable approach from CTOs. Cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are significantly reshaping how businesses operate and compete. CTOs must understand these trends and their implications to ensure their organizations remain competitive and resilient.
Examples of CTO Adaptation to New Technologies
CTOs are increasingly leveraging AI tools for tasks like automating routine processes, analyzing vast datasets, and identifying new opportunities. Cloud computing is enabling agile development cycles and faster deployment of applications, demanding CTOs to lead in cloud migration and optimization strategies. Furthermore, CTOs are now responsible for integrating IoT devices and data streams into business operations, fostering smart solutions and creating new revenue streams.
Importance of Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The CTO profession requires continuous learning and adaptation to stay relevant in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. CTOs must embrace lifelong learning, actively seeking out new knowledge and skills in emerging technologies. This includes attending conferences, workshops, and online courses to stay updated on the latest advancements and trends. Adapting to new tools and technologies is vital for effectively leading teams and ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
Emerging Technologies with Significant Impact, What is chief technology officer
Several emerging technologies are poised to disrupt various industries, and CTOs need to understand their potential impact. These include blockchain technology, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR), which are transforming how businesses interact with customers and operate internally. Furthermore, advancements in quantum computing and nanotechnology have the potential to revolutionize industries ranging from medicine to materials science.
Key Technological Trends and Their Potential Impact on Businesses
| Technological Trend | Potential Impact on Businesses |
|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | Increased agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness; enabling faster deployment of applications and services. |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Automation of tasks, improved decision-making through data analysis, and creation of new products and services; enhancing efficiency and productivity. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Creation of smart solutions, enhanced operational efficiency, and new revenue streams through data collection and analysis; enabling proactive maintenance and optimization of processes. |
| Blockchain | Improved security and transparency in transactions, supply chains, and other business processes; fostering trust and efficiency. |
| Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) | Enhanced customer experiences, new training and education models, and improved design and prototyping processes; enabling immersive and interactive interactions. |
| Quantum Computing | Potential to solve complex problems in various industries, such as drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling; leading to breakthroughs in scientific and technological advancements. |
| Nanotechnology | Development of new materials with unique properties, advanced manufacturing techniques, and improved medical treatments; driving innovation across various sectors. |
Budgeting and Resource Management
The Chief Technology Officer (CTO) plays a critical role in ensuring the effective allocation of resources for technology initiatives. This involves not only understanding the financial implications of different technological choices but also strategically aligning those choices with the overall business goals. The CTO must be adept at justifying technology investments, optimizing spending, and advocating for the resources needed to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge.The successful implementation of technology strategies depends heavily on the efficient management of budgets and resources.
A Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is essentially the tech visionary of a company, overseeing all things digital. Their role is crucial in driving innovation, and a unified European patent system, as discussed in this insightful article on unified european patent system could goose innovation , could dramatically impact the landscape for tech leaders like CTOs. Ultimately, a CTO’s job is to leverage the best technological solutions to propel the company forward.
This requires a proactive approach that anticipates potential challenges and allocates funds in a way that maximizes returns. A CTO’s expertise in forecasting technological needs and their financial impact is crucial for the company’s long-term success.
The CTO’s Role in Managing Technology Budgets
The CTO acts as a bridge between the technical vision and the financial realities of the company. They must understand the costs associated with different technologies, the long-term implications of investments, and how to present these effectively to stakeholders. This involves careful planning, precise estimations, and the ability to articulate the value proposition of technology investments.
Methods for Optimizing Technology Investments and Resource Allocation
Optimizing technology investments involves a multi-faceted approach. Prioritizing projects based on their alignment with strategic goals, considering the return on investment (ROI), and implementing cost-effective solutions are crucial. A detailed understanding of existing infrastructure and its potential for integration with new technologies is also essential. Regular performance reviews and adjustments based on actual outcomes help ensure resources are utilized efficiently.
Cost-Benefit Analysis in Technology Decisions
A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is essential for any significant technology decision. This analysis should consider not only the upfront costs but also the long-term benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced productivity, and increased market share. Quantifying the potential gains and comparing them to the associated costs allows for informed decision-making. For example, a new software implementation might have high initial costs but lead to significant reductions in operational expenses over time.
Advocating for Necessary Resources
The CTO must be a strong advocate for the resources needed to support the company’s technological goals. This requires a clear understanding of the technological needs and a persuasive presentation of the value proposition. Demonstrating how specific investments will contribute to achieving business objectives is key. The CTO should also highlight the potential risks and opportunities associated with various investment options.
This often involves presenting data, ROI projections, and competitor analyses to demonstrate the necessity of specific resources.
Types of Technology Budgets and Responsibilities
| Budget Type | Description | CTO Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Budget | Funds for major capital expenditures, such as new hardware, software licenses, or infrastructure upgrades. | Developing and justifying proposals, tracking expenditures, and ensuring alignment with strategic goals. |
| Operating Budget | Funds for day-to-day technology operations, including maintenance, support, and ongoing software subscriptions. | Monitoring operational expenses, identifying areas for optimization, and ensuring smooth functioning of technology systems. |
| Research and Development (R&D) Budget | Funds for exploring new technologies, developing innovative solutions, and staying ahead of industry trends. | Prioritizing research projects, managing R&D spending, and fostering a culture of innovation. |
Troubleshooting and Problem Solving
A CTO’s role is fundamentally about navigating complexities and finding solutions. Troubleshooting and problem-solving are crucial aspects of this leadership position, requiring a blend of technical expertise, strategic thinking, and a proactive approach. A CTO who can identify, diagnose, and resolve technical issues efficiently is invaluable to the success of any organization.
Importance of Problem Solving in the CTO Role
A CTO’s problem-solving skills are paramount. Technical roadblocks, unexpected system failures, and evolving technological landscapes constantly demand effective solutions. The ability to quickly and decisively address these challenges directly impacts the company’s productivity, efficiency, and overall bottom line. A CTO’s strategic thinking is vital in recognizing the potential for issues and mitigating them before they become major crises.
Approaching Technical Issues and Roadblocks
A methodical approach is key when dealing with technical problems. A CTO should first understand the problem’s scope and impact. This includes identifying the root cause, collecting relevant data, and consulting with affected teams. Once the issue is well-defined, potential solutions can be explored. This process should involve evaluating the feasibility, cost, and risk associated with each solution.
Prototyping and testing are essential for validating the efficacy of any proposed solution. Crucially, the CTO should foster a culture of collaboration and communication, ensuring all stakeholders are informed and involved in the problem-solving process.
Critical Thinking and Decision-Making in a CTO’s Role
Critical thinking is essential for evaluating the merits of various solutions. A CTO must analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each option, considering long-term implications. Data-driven decisions are vital. Quantifiable metrics should guide choices, leading to optimal outcomes. Weighing potential risks and benefits is crucial in making sound judgments.
Decisions should always align with the organization’s strategic goals.
Leveraging Data and Insights to Solve Problems
Data analysis plays a pivotal role in identifying patterns and trends that can pinpoint the root cause of a problem. Performance metrics, user feedback, and system logs are invaluable resources. Using this data, the CTO can gain insights into the efficiency of existing systems and anticipate future issues. Data-driven decisions are not just about fixing existing problems, but also about preventing future ones.
Common Technical Problems and Potential Solutions
Troubleshooting requires a wide range of problem-solving skills. A CTO must be prepared for various issues.
| Common Technical Problem | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| System Downtime | Identify the cause (hardware failure, software glitch, network outage). Implement a backup plan or redundant systems. Monitor system health proactively. |
| Software Bugs | Thorough testing and debugging. Use a version control system for tracking changes. Implement a bug reporting system for users to report issues. |
| Security Breaches | Implement robust security measures. Regular security audits. Employee training on security protocols. Develop an incident response plan. |
| Performance Bottlenecks | Analyze system logs and performance metrics. Optimize code or database queries. Consider hardware upgrades. |
| Data Loss | Implement data backup and recovery procedures. Establish a data retention policy. Train staff on data handling best practices. |
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the Chief Technology Officer is a multifaceted role that requires a blend of technical expertise, strategic vision, and strong leadership skills. They are vital for driving technological innovation, managing teams, and aligning technology with business goals. Understanding the CTO’s responsibilities, skillsets, and strategic approach is crucial for any organization looking to thrive in today’s competitive technological landscape.
This overview provides a comprehensive understanding of what it takes to excel in this demanding yet rewarding role.

