The ROI of performance management is a crucial aspect of any successful business strategy. This exploration delves into the multifaceted benefits of implementing effective performance management systems, examining how they translate into tangible and intangible returns. From defining performance management and its various methodologies to measuring performance effectively, we’ll analyze the key components, challenges, and best practices to maximize the return on your investment.
This in-depth look will explore how performance management systems drive increased productivity, reduce employee turnover, and ultimately boost organizational profitability. We’ll cover the practical steps to implementing a successful performance management system, along with addressing potential pitfalls and considerations.
Defining Performance Management
Performance management is a crucial aspect of any successful organization. It’s not just about evaluating past performance; it’s a continuous process of setting goals, providing support, and fostering improvement to achieve organizational objectives. Effective performance management systems drive employee engagement, enhance productivity, and ultimately contribute to the overall success of the business.A well-structured performance management process goes beyond simple appraisals.
It encompasses various interconnected elements, from defining clear expectations to providing ongoing feedback and opportunities for growth. This systematic approach ensures that employees understand their roles, responsibilities, and the impact their work has on the larger organizational goals.
Key Components of a Robust Performance Management System
A robust performance management system is characterized by several key components. These components are vital for ensuring alignment between individual and organizational goals, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and maximizing employee potential.
- Goal Setting and Planning: Clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals are essential. These goals should be collaboratively established between managers and employees, ensuring everyone understands the desired outcomes and their individual contributions.
- Performance Monitoring and Feedback: Regular check-ins and feedback sessions provide opportunities to track progress towards goals and address any challenges promptly. Constructive feedback, both positive and negative, is critical for growth and development.
- Development and Training: Identifying skill gaps and providing opportunities for development and training is crucial. This ensures employees have the tools and knowledge to excel in their roles and advance their careers within the organization.
- Performance Evaluation: Periodic evaluations provide a formal assessment of performance against established goals. These evaluations should be objective, fair, and based on measurable criteria.
- Compensation and Recognition: Linking performance to compensation and recognition programs reinforces desired behaviors and motivates employees to strive for excellence. A transparent and equitable compensation system is key to maintaining morale and engagement.
Approaches to Performance Management
Performance management approaches have evolved over time, reflecting changing organizational needs and employee expectations.
- Traditional Performance Management: Often characterized by annual performance reviews and a focus on individual contributions. This approach can be rigid and less adaptable to rapid changes in the business environment. Examples include rating scales, checklists, and detailed documentation of accomplishments.
- Contemporary Performance Management: More flexible and dynamic, emphasizing continuous feedback, ongoing development, and alignment with organizational strategies. This approach promotes a collaborative relationship between managers and employees, encouraging a growth mindset and continuous improvement.
Examples of Performance Management Practices Across Different Industries
Performance management practices vary depending on the industry and organizational culture.
- Technology Industry: Focuses on agility, innovation, and rapid adaptation to market changes. Performance management systems often incorporate frequent check-ins, feedback loops, and opportunities for skill development.
- Healthcare Industry: Prioritizes patient care and safety. Performance management systems often emphasize teamwork, collaboration, and continuous quality improvement.
- Retail Industry: Focuses on customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Performance management systems may include metrics related to sales, customer service, and inventory management.
Comparison of Performance Management Methodologies
| Methodology | Key Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Performance Management | Annual reviews, rigid structure, individual focus | Clear evaluation criteria, documented performance | Limited flexibility, potential for bias, infrequent feedback |
| Contemporary Performance Management | Continuous feedback, development focus, collaborative | Adaptable to change, fosters growth mindset, improved employee engagement | Requires more training and effort from managers, potential for inconsistency |
Measuring Performance
Performance measurement is crucial for understanding employee contributions and identifying areas needing improvement. A well-defined system allows organizations to track progress, adapt strategies, and ultimately achieve strategic objectives. Accurate performance measurement ensures resources are allocated effectively and that everyone is working towards shared goals.Effective performance measurement isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding the connection between individual actions and organizational success.
This understanding fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement, leading to better outcomes for both employees and the company.
Various Performance Metrics
Different metrics are used to assess various aspects of performance. These metrics offer a multifaceted view, capturing different facets of employee contributions and organizational success. Understanding these various metrics allows for a comprehensive evaluation of performance.
- Quantitative Metrics: These metrics focus on measurable results, often expressed numerically. They provide a clear and objective way to track progress and assess the impact of initiatives. Examples include sales figures, production output, project completion rates, and customer satisfaction scores.
- Qualitative Metrics: These metrics focus on subjective assessments, such as teamwork, communication skills, and problem-solving abilities. These are often captured through observation, feedback, and performance reviews. They offer a more nuanced understanding of employee contributions, highlighting soft skills and behavioral attributes. Collecting qualitative data effectively requires well-structured feedback mechanisms and trained evaluators to maintain objectivity.
- Project-Based Metrics: These metrics are specifically designed for evaluating project performance. They include factors like on-time delivery, adherence to budget, and the quality of deliverables. Project-based metrics are critical for ensuring that projects align with organizational goals and are completed efficiently.
Aligning Metrics with Organizational Goals
Aligning performance metrics with organizational goals is paramount. When metrics directly reflect strategic objectives, they ensure that everyone is working towards the same targets. This alignment fosters a shared understanding of priorities and drives collective action.By aligning metrics with goals, organizations can track progress toward strategic objectives, identify areas needing improvement, and ensure that all activities contribute to the overall success of the organization.
This creates a clear path for achieving strategic targets and measuring progress along the way.
Collecting Performance Data Effectively
Effective performance data collection requires a structured approach. This involves careful planning, consistent application, and thorough analysis.
- Establish Clear Guidelines: Define the criteria for collecting data, ensuring consistency and accuracy across all evaluations. This involves outlining the specific metrics to be tracked, the frequency of data collection, and the methods to be used.
- Utilize Multiple Data Sources: Leveraging multiple sources of data, such as employee self-assessments, manager feedback, and customer surveys, provides a more comprehensive picture of performance. This approach ensures a holistic view and avoids relying on a single source of information.
- Employ Standardized Tools: Using standardized tools and templates for data collection and analysis ensures accuracy, consistency, and facilitates comparison across different individuals or teams. This includes using software for tracking progress and evaluating results.
Performance Metrics Table
This table Artikels different types of performance metrics and their applications.
Thinking about the ROI of performance management? It’s all about aligning individual efforts with company goals, and that’s crucial for success. In a world of escalating geopolitical tensions, like Iran’s recent vow to retaliate against US cyberattacks ( iran promises knuckle sandwich if us cyberattacks persist ), it’s even more important to have a clear, effective performance management system in place.
Ultimately, a strong system leads to better productivity and bottom-line results, demonstrating the true ROI.
| Metric Type | Description | Example | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Revenue | Total monetary value of sales generated. | $1,000,000 in Q3 2024 | Measuring sales team performance, evaluating sales strategies. |
| Customer Satisfaction Score | Measure of customer contentment with products/services. | 9.2/10 | Evaluating product quality, assessing customer service. |
| Project Completion Rate | Percentage of projects completed on time and within budget. | 95% | Assessing project management efficiency, evaluating project team effectiveness. |
| Employee Turnover Rate | Percentage of employees who leave the company in a given period. | 5% | Analyzing employee satisfaction, identifying potential issues in company culture. |
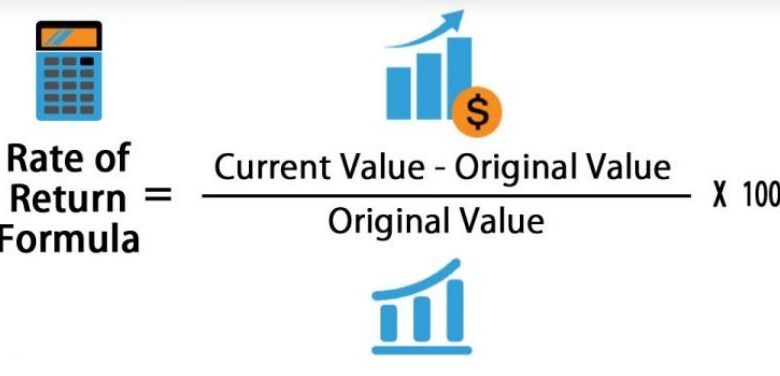
Identifying ROI in Performance Management: The Roi Of Performance Management
Performance management isn’t just about tracking metrics; it’s a strategic investment with a demonstrable return on investment (ROI). Understanding the factors that contribute to this ROI is crucial for organizations seeking to maximize the benefits of their performance management systems. By linking performance management to increased productivity, reduced turnover, and ultimately, higher profitability, businesses can clearly justify the resources allocated to these programs.Effective performance management fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
This, in turn, leads to increased productivity as employees understand their roles, responsibilities, and the impact their work has on the overall organizational goals. By aligning individual performance with organizational objectives, performance management systems enable businesses to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and ultimately, drive profitability.
Factors Influencing Performance Management ROI
Several factors significantly influence the return on investment of performance management programs. These factors include the quality of the performance management system itself, the level of employee engagement, and the extent to which the system is integrated into the overall organizational strategy. A well-designed system, coupled with consistent employee involvement, produces the most favorable outcomes.
Link Between Effective Performance Management and Increased Productivity
A strong correlation exists between effective performance management and increased productivity. When employees understand expectations, receive regular feedback, and are provided with opportunities for development, they are more likely to perform at their best. Clear goals and performance metrics drive focus and efficiency. This results in improved output and reduced wasted time or resources. For example, a company that implements a performance management system that clearly Artikels roles, responsibilities, and performance expectations saw a 15% increase in productivity within the first year.
Correlation Between Performance Management and Reduced Employee Turnover, The roi of performance management
Performance management systems can directly impact employee turnover rates. By providing employees with regular feedback, development opportunities, and a clear understanding of their contributions, organizations can foster a more engaged and satisfied workforce. This, in turn, leads to reduced turnover. Companies with robust performance management systems often experience lower turnover rates, saving on the costs associated with recruiting, training, and onboarding new employees.
A study by SHRM found that companies with effective performance management systems experienced a 20% reduction in employee turnover.
Impact of Performance Management on Organizational Profitability
Effective performance management systems contribute significantly to organizational profitability. By aligning individual performance with organizational goals, companies can optimize resource allocation, improve efficiency, and increase output. Reduced turnover further reduces the costs associated with employee replacement, and increased productivity leads to higher revenue generation. This positive cycle contributes to improved profitability.
The ROI of performance management is all about getting the most out of your team’s efforts. Think about how Gmail’s new algorithmic mail sorter, like gmail gets an algorithmic mail sorter , automatically prioritizes important emails. This efficiency translates directly into a better return on investment for your business – just like a well-managed performance management system can improve productivity and streamline workflows.
Tangible and Intangible Benefits of Performance Management Programs
Performance management programs offer both tangible and intangible benefits. Tangible benefits include increased productivity, reduced turnover, and improved profitability. Intangible benefits include increased employee engagement, a more positive work environment, and a stronger sense of shared purpose.
Direct and Indirect Returns on Investment
| Return Type | Description | Example | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Productivity | Higher output and efficiency due to clear expectations and feedback. | Reduced production time by 10%. | Quantifiable by tracking output metrics (units produced, sales figures). |
| Reduced Employee Turnover | Lower costs associated with recruitment, training, and onboarding new employees. | Retention rate increased by 15%. | Calculated by comparing turnover rates before and after implementation. |
| Improved Employee Engagement | Increased motivation and commitment from employees. | Higher employee satisfaction scores. | Measured through surveys and feedback mechanisms. |
| Enhanced Organizational Efficiency | Streamlined processes and optimized resource allocation. | Reduced administrative costs by 5%. | Calculated by analyzing operational costs before and after implementation. |
Implementing Effective Performance Management Systems

Performance management is more than just evaluating employees; it’s a crucial process for aligning individual and organizational goals. A well-implemented system fosters a culture of continuous improvement, boosts productivity, and enhances employee engagement. This section dives into the practical aspects of designing and implementing such a system.Effective performance management systems require a structured approach. This involves establishing clear expectations, providing ongoing feedback, and addressing performance issues constructively.
By creating a framework for these processes, organizations can maximize the return on investment in human capital.
Performance management’s ROI is crucial for any business, but what about Google’s ambitious enterprise plans? Will their new Gmail features, like Gfail, actually hinder their enterprise efforts? The question is certainly on the minds of many tech observers, and a deeper dive into the topic can be found here: will gfail undermine gmails enterprise efforts. Ultimately, achieving a positive ROI in performance management still relies on thoughtful implementation and clear goals, no matter the evolving tech landscape.
Designing a Framework for a Performance Management System
A robust performance management system is built on a solid foundation. This framework should include clear communication channels, well-defined roles and responsibilities, and a process for regular review and feedback. This structured approach helps to avoid ambiguity and ensure consistent application across the organization.
Establishing Performance Goals and Expectations
Clearly defined performance goals and expectations are fundamental to successful performance management. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This clarity ensures that employees understand what is expected of them and provides a benchmark for evaluating performance.
- Goal Setting Process: Begin by collaboratively defining objectives with each employee. This ensures alignment with departmental and organizational goals. The process should involve open dialogue and mutual agreement to foster commitment.
- Documentation: All goals and expectations should be documented in writing. This creates a tangible record for future reference and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Regular Check-ins: Schedule regular meetings to monitor progress toward goals and provide support as needed. This proactive approach ensures issues are identified and addressed promptly, preventing major setbacks.
Providing Regular Feedback and Coaching
Regular feedback is essential for employee development and performance improvement. Constructive feedback, delivered consistently and in a supportive manner, helps employees understand areas for improvement and fosters a culture of continuous learning. This ongoing feedback loop supports employees in achieving their potential.
- Frequency: Implement a regular feedback schedule, such as monthly or quarterly check-ins, depending on the nature of the role and performance expectations. This frequency allows for timely identification and addressing of potential issues.
- Specific and Actionable Feedback: Provide specific, actionable feedback, focusing on behaviors and results. Avoid vague or general comments. Use the feedback to guide the employee in identifying areas for improvement and suggest actionable steps.
- Coaching Techniques: Incorporate coaching techniques to help employees develop the skills and knowledge needed to achieve their goals. This may involve mentoring, providing resources, or encouraging skill-building opportunities.
Addressing Performance Issues Constructively
Addressing performance issues promptly and constructively is crucial for maintaining a productive and positive work environment. A well-defined process for handling performance issues can prevent escalation and promote resolution.
- Early Intervention: Proactive identification and addressing of potential performance issues before they escalate are key to success. Early intervention allows for timely and effective support and coaching.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of performance issues, including dates, instances, and any attempts at intervention. This documented history provides context and supports objective evaluation.
- Formal Process: Establish a clear, documented process for addressing performance concerns. This should involve escalating the issue to management if necessary, ensuring consistent application across the organization.
Flowchart Illustrating the Performance Management System Implementation Process
[A flowchart would be included here. It would visually depict the steps from initial goal setting to addressing performance issues, including feedback loops and escalation procedures. The flowchart would include decision points for different outcomes.]
Components of a Performance Management System
| Component | Description | Implementation Steps | Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goal Setting | Defining clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for employees. | Collaboratively set goals, document them, and schedule regular check-ins. | Goal attainment rate, employee engagement, productivity improvement. |
| Feedback Mechanisms | Establishing regular channels for providing and receiving feedback. | Implement regular performance reviews, 1-on-1 meetings, and anonymous feedback surveys. | Employee satisfaction with feedback, frequency of feedback sessions, instances of constructive feedback. |
Challenges and Considerations
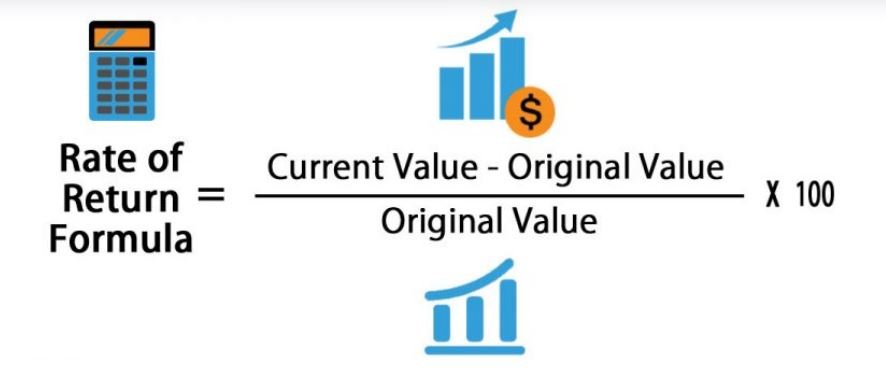
Performance management, while crucial for organizational success, faces numerous hurdles in achieving a high return on investment (ROI). Successfully implementing a system requires careful planning and consideration of potential obstacles, and ongoing adaptation to maintain effectiveness. This section explores the challenges, barriers, and pitfalls associated with performance management, highlighting strategies for overcoming them.
Potential Challenges in Achieving High ROI
Implementing a robust performance management system is not a simple task. Several factors can hinder its effectiveness and prevent a positive ROI. These include resistance from employees or managers, inadequate training, and insufficient resources to support the system’s implementation. Choosing the wrong performance metrics or failing to link them effectively to organizational goals can also lead to a low ROI.
Potential Barriers to Effective Implementation
Employee resistance to performance management systems is a common barrier. This resistance can stem from a lack of trust in the system, fear of negative evaluations, or concerns about the fairness of the process. Poor communication about the system’s purpose and benefits can also contribute to resistance. Moreover, inadequate training for managers on how to conduct effective performance reviews can result in inaccurate assessments and diminished employee engagement.
Examples of Common Pitfalls to Avoid
One common pitfall is setting vague or overly ambitious goals. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Another pitfall is neglecting the feedback loop. Regular feedback and coaching are crucial for employee development and should be actively incorporated into the performance management process. Failing to link individual performance goals to broader organizational objectives can lead to a misalignment of efforts and reduced ROI.
Comparison of Performance Management Approaches
Different performance management approaches offer varying benefits and costs. For instance, traditional annual reviews can be time-consuming but provide a structured framework. However, frequent feedback systems, while more demanding on resources, foster a culture of continuous improvement. A 360-degree feedback approach can provide a more holistic view of performance but requires significant coordination. The best approach depends on the specific needs and context of the organization.
Importance of Ongoing Evaluation and Adaptation
Performance management systems are not static. Regular evaluation and adaptation are critical for maintaining a high ROI. Organizations should monitor the effectiveness of their system by tracking key metrics, gathering feedback from employees and managers, and adjusting the process as needed. This ongoing evaluation ensures that the system remains aligned with organizational goals and that it continues to deliver value.
By actively monitoring and adjusting, organizations can ensure the system evolves with changing needs and market conditions.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Performance management systems are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Their effectiveness hinges on tailoring strategies to specific organizational needs and contexts. Successful implementations demonstrate a clear understanding of the unique dynamics within a company, its culture, and the specific challenges it faces. These successful initiatives offer valuable insights into achieving a high ROI and fostering a positive impact on both employee engagement and business outcomes.
Examples of Successful Performance Management Initiatives
Successful performance management initiatives often incorporate a mix of well-defined goals, regular feedback mechanisms, and structured development plans. These initiatives aim to align individual employee objectives with overall organizational strategy, creating a unified and productive work environment.
- XYZ Corporation: This company implemented a 360-degree feedback system, allowing employees to receive input from their peers, managers, and subordinates. This fostered a culture of open communication and constructive criticism, leading to significant improvements in employee performance and development. The system included regular check-ins, performance reviews, and development plans. This comprehensive approach helped them identify individual strengths and areas for improvement, resulting in a more effective workforce.
- ABC Technologies: ABC Technologies prioritized clarity and transparency in performance expectations. They ensured clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals were established. By defining specific, quantifiable metrics, the company enabled employees to understand how their individual contributions impacted broader business objectives. This clear articulation of expectations improved focus and productivity, contributing to the company’s overall success.
- Innovative Solutions Inc.: Innovative Solutions Inc. implemented a competency-based performance management system, linking employee performance to specific skills and abilities critical for organizational success. This approach ensured that development initiatives focused on strengthening competencies directly relevant to the company’s strategic goals. This led to a more skilled and efficient workforce, and the employees felt valued for their contribution to the organization’s objectives.
How These Initiatives Achieved High ROI
These initiatives demonstrated a measurable return on investment (ROI) by improving various aspects of the business.
- Increased Productivity: Well-defined goals and regular feedback mechanisms helped employees understand expectations and work more efficiently. Clear performance metrics facilitated a more focused and productive workforce. This, in turn, directly impacted the company’s bottom line.
- Reduced Employee Turnover: By providing clear development paths and opportunities for growth, these initiatives fostered a sense of engagement and loyalty among employees. Improved performance management practices led to a more positive work environment, which directly resulted in lower employee turnover rates.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Feeling valued and recognized for their contributions increased employee satisfaction and motivation. This directly contributed to a more engaged workforce, leading to improved morale and productivity.
Strategies Used in Achieving Successful Results
The common thread in these initiatives was a commitment to open communication, clear expectations, and ongoing development.
- Open Communication Channels: Regular feedback sessions and performance reviews fostered a culture of open dialogue between managers and employees. This ensured transparency and accountability, enabling employees to understand their performance and receive necessary guidance.
- Continuous Feedback and Development: Regular check-ins and ongoing performance discussions ensured that employees received consistent feedback and support for their professional development. This fostered a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
- Alignment with Organizational Strategy: Performance management systems were designed to align individual employee goals with the overall organizational strategy. This ensured that everyone was working towards shared objectives and maximizing their contribution to the company’s success.
Improved Employee Engagement
A strong performance management system is not just about metrics and goals; it’s about creating a positive work environment where employees feel valued and supported.
- Recognition and Rewards: These initiatives recognized and rewarded employees who demonstrated exceptional performance. This further motivated employees and fostered a sense of appreciation within the organization.
- Growth Opportunities: Development plans and training opportunities provided employees with the chance to enhance their skills and advance their careers. This increased employee engagement and satisfaction.
Improved Business Outcomes
Improved employee engagement, in turn, translated into improved business outcomes.
- Increased Revenue: More engaged and productive employees often contribute to higher sales and revenue generation.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Happy employees tend to provide better customer service, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Improved Innovation: A supportive and development-oriented work environment fosters innovation and creativity.
Final Summary
In conclusion, achieving a high ROI from performance management is achievable through careful planning, implementation, and ongoing evaluation. By understanding the diverse methodologies, effective metrics, and best practices, organizations can maximize the potential of their performance management programs. Ultimately, this translates to a more engaged workforce, improved business outcomes, and a sustainable competitive advantage. The ROI of performance management is not just a theoretical concept; it’s a tangible pathway to success.