Peer to peer insurance – Peer-to-peer insurance is a novel approach to risk-sharing, where individuals pool resources and share insurance needs within a community. It offers a dynamic, potentially more transparent, and accessible alternative to traditional insurance models. By sharing risks among peers, premiums can be lower and access to coverage potentially wider.
This model leverages technology and community bonds to create a unique insurance ecosystem. Different types of arrangements exist, from community-based schemes to subscription-based platforms. Key features often include shared risk pooling, dynamic pricing based on individual risk, and enhanced transparency.
Introduction to Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance, a rapidly evolving sector, is reshaping traditional insurance models by leveraging the power of online platforms and community-based risk sharing. It allows individuals to pool their risks and share the costs of insurance, potentially leading to more affordable and personalized coverage. This innovative approach is driven by the desire for greater transparency, control, and customization in insurance.This model shifts the traditional insurance paradigm by placing individuals at the center of the risk management process.
It allows for dynamic pricing, potentially lowering costs and enhancing the overall insurance experience for participants.
Peer-to-Peer Insurance Models
Peer-to-peer insurance models function on the principle of shared risk and collective responsibility. Various structures exist, each tailored to specific needs and risk profiles. One prevalent model is the use of online platforms that facilitate the connection between individuals who want to share risk. Another model involves groups of individuals pooling their resources to cover potential losses.
This sharing approach creates a collective risk pool, where the costs of potential losses are distributed among all participants.
Types of Peer-to-Peer Insurance Arrangements
Several types of peer-to-peer insurance arrangements are emerging. These arrangements vary based on the specific risks being insured and the mechanisms used for risk pooling. For example, some arrangements focus on specific types of risks, like car accidents, or they may be more general, covering a range of eventualities. Other arrangements might incorporate incentives or rewards for safe behavior, thereby promoting responsible risk management.
Core Principles of Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance is fundamentally based on a few core principles. These principles include transparency and trust amongst participants, with clear communication and shared understanding of risks and responsibilities. A significant component is the idea of shared responsibility. Each participant recognizes that they contribute to the pool and are accountable for ensuring the financial stability of the group.
Finally, the concept of community is crucial. Participants in peer-to-peer insurance arrangements often share common interests or characteristics, which fosters a sense of community and strengthens the platform’s ability to manage risk effectively.
Distinguishing Peer-to-Peer Insurance from Traditional Insurance
Traditional insurance relies on large, centralized institutions to manage risk. Peer-to-peer insurance, in contrast, decentralizes risk management. A fundamental difference lies in the risk pooling mechanism. Traditional insurance companies collect premiums from a large customer base, forming a massive risk pool. Peer-to-peer arrangements, on the other hand, aggregate risk among a smaller group of individuals, potentially leading to more personalized and dynamic pricing.
This approach emphasizes transparency and control over one’s risk, a characteristic often lacking in traditional insurance models.
Comparison of Peer-to-Peer and Traditional Insurance
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Insurance | Traditional Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Pooling | Shared among peers | Shared by a large insurer |
| Pricing | Dynamic, based on individual risk | Fixed premiums |
| Transparency | High | Low |
| Access | Potentially wider | Limited to insurer’s network |
Benefits and Advantages of Peer-to-Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance models offer a refreshing approach to traditional insurance, promising benefits for everyone involved. This innovative system fosters a collaborative environment where individuals share risks and rewards, leading to potentially lower costs and greater transparency. The potential for community building and increased access to insurance is also significant.
Peer-to-peer insurance is definitely an interesting concept, offering a potentially more accessible and affordable way to insure things. However, the challenges in scaling such systems are real, just like the hurdles facing Obama’s ambitious space vision, as he prepares to defend his plan against mounting criticism, here. Ultimately, peer-to-peer insurance could reshape how we think about risk-sharing, potentially bringing more people into the fold and making insurance more dynamic.
Benefits for Policyholders
Peer-to-peer insurance models can offer significant advantages for policyholders. Shared risk allows for the potential of lower premiums, compared to traditional insurance. This is because the risk pool is often larger and more diversified, reducing the overall cost of insurance for each individual. Additionally, policyholders gain greater transparency into how their premiums are calculated, fostering trust and accountability.
This level of insight allows policyholders to make informed decisions and potentially tailor their coverage to their specific needs. Increased access to insurance options is another significant benefit. Existing traditional insurance markets may not always cater to specific needs, or may be inaccessible due to various factors. Peer-to-peer models can provide alternatives and potentially open up the insurance market to previously underserved populations.
Advantages for Insurers
Insurers in a peer-to-peer environment can benefit from reduced administrative overhead. The collaborative nature of the model often simplifies the claims process, reducing the need for complex internal procedures. Furthermore, peer-to-peer models can potentially improve the risk assessment process. By analyzing the characteristics and behaviors of a specific community, insurers can develop more accurate risk profiles, leading to more precise premium calculations.
This, in turn, can enhance the financial stability and sustainability of the insurance program. In addition, peer-to-peer insurance can create new revenue streams through innovative service offerings.
Advantages from a Societal Perspective
Peer-to-peer insurance models can bring numerous benefits to society as a whole. The increased access to insurance can improve financial stability for individuals and families. This is particularly relevant in communities where traditional insurance may be unavailable or unaffordable. Further, the collaborative nature of peer-to-peer insurance fosters a sense of community and shared responsibility. This can lead to stronger social bonds and a more supportive environment.
In essence, peer-to-peer insurance models can be a catalyst for positive social change.
Key Benefits Summarized
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Lower Costs | Potentially lower premiums due to shared risk and reduced administrative overhead. For example, a shared-risk model for pet insurance might see lower premiums compared to traditional pet insurance because of a larger and more diversified risk pool. |
| Increased Access | More options for policyholders, including those who may have been previously excluded from traditional insurance markets due to factors such as age or health conditions. |
| Greater Transparency | Policyholders can see how their premiums are calculated, fostering trust and accountability in the insurance process. |
| Community Building | Encourages collaboration and community engagement, strengthening social bonds and mutual support. |
Challenges and Limitations of Peer-to-Peer Insurance: Peer To Peer Insurance
Peer-to-peer insurance, while promising, faces significant hurdles in its implementation. The decentralized nature of this model, while attractive, necessitates careful consideration of potential issues and limitations. A robust understanding of these challenges is crucial for successful development and adoption of this innovative insurance approach.
Trust and Reputation
Establishing trust between peers is paramount in peer-to-peer insurance. The lack of a centralized entity to mediate disputes and guarantee payouts creates a critical reliance on the trustworthiness of individuals participating in the system. This necessitates rigorous vetting processes to assess the reliability and financial stability of potential peers. Without this, the system’s integrity is compromised, leading to uncertainty and potentially fraudulent activities.
Risk Assessment, Peer to peer insurance
Accurate risk assessment is another significant challenge. Traditional insurance models rely on large datasets and sophisticated actuarial techniques to predict and price risks. In peer-to-peer systems, risk profiles are inherently more varied and often less well-defined, making it challenging to accurately assess the potential losses associated with each peer. Developing advanced risk modeling techniques that can adapt to the unique characteristics of individual peers and their potential risk exposure is essential.
This includes considering factors such as demographics, location, lifestyle, and past claims history.
Peer-to-peer insurance is all about connecting individuals directly, fostering a sense of community. It’s a bit like how amazing managers prioritize one-on-one time with their team members, why amazing managers do one on ones , to build trust and understand individual needs. This direct connection is key to the success of peer-to-peer insurance models, ensuring everyone is fairly covered and supported.
Regulation
Navigating the regulatory landscape is a significant hurdle for peer-to-peer insurance. Existing regulations are often tailored to traditional insurance models and may not adequately address the unique features of peer-to-peer systems. Understanding and adapting to the regulatory environment is crucial for compliance and sustainability. This includes staying informed about evolving regulatory changes and working with policymakers to establish appropriate frameworks.
Peer-to-peer insurance is definitely a fascinating concept, offering potentially lower costs and more tailored policies. It’s interesting to see how new technologies are influencing different sectors, like the recent news that AT&T is planning to start selling the Samsung Galaxy camera. This move could open up some exciting possibilities for consumers, especially if they offer more affordable plans than traditional providers.
Ultimately, peer-to-peer insurance might just be the next big thing in the industry, giving more control to individuals and offering a more personalized approach to coverage.
Operational Complexity
The decentralized nature of peer-to-peer insurance can lead to complex operational challenges. Managing claims, payouts, and dispute resolutions across a large network of peers can be logistically difficult and costly. Effective communication channels, dispute resolution mechanisms, and payment processing systems are essential to ensure smooth operation and maintain the trust of participants.
Scalability
Scaling peer-to-peer insurance systems to handle a large volume of transactions and participants can present significant challenges. Maintaining efficiency and security as the system grows is vital for long-term success. The platform needs to be robust enough to manage increasing demands while preserving its integrity and efficiency. This requires robust technological infrastructure, scalable data management systems, and a clear understanding of future needs.
Table of Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
| Challenge | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Trust and Reputation | Difficulty in verifying the reliability of peers | Implement rigorous vetting processes, including background checks and credit scoring |
| Risk Assessment | Accurately assessing the risk profiles of peers | Develop advanced risk modeling techniques, utilizing machine learning and data analytics to evaluate individual risk profiles. |
| Regulation | Navigating regulatory hurdles | Stay informed about regulatory changes and engage in proactive dialogue with regulatory bodies. |
| Operational Complexity | Managing claims, payouts, and dispute resolutions across a large network of peers | Develop efficient claim processing systems, establish clear dispute resolution mechanisms, and utilize secure payment platforms. |
| Scalability | Handling a large volume of transactions and participants | Employ scalable technology solutions, utilize cloud-based infrastructure, and establish clear protocols for growth and expansion. |
Peer-to-Peer Insurance Models and Platforms
Peer-to-peer insurance, a relatively new concept, is revolutionizing the insurance industry by empowering individuals to share risk and create customized insurance solutions. This shift from traditional insurance models opens exciting possibilities for more accessible and potentially more affordable coverage. Different models and platforms cater to diverse needs and preferences, allowing for personalized experiences.Understanding these models and platforms is key to appreciating the potential and challenges of peer-to-peer insurance.
It’s not just about connecting individuals; it’s about creating efficient and effective systems for managing risk in a collaborative environment.
Different Peer-to-Peer Insurance Models
Different peer-to-peer insurance models address specific needs and risk profiles. These models allow for flexibility and customization that traditional insurance often lacks. This allows users to select coverage that aligns with their individual circumstances and preferences.
- Community-Based Models: These models often focus on a shared risk pool within a specific community, such as a neighborhood, professional association, or hobby group. Strong community ties and shared values play a crucial role in establishing trust and encouraging participation.
- Subscription-Based Models: These models provide access to the platform’s tools, community engagement features, and potential discounts to members who pay a recurring subscription fee. This model often offers more comprehensive resources and support for users.
- Event-Based Models: These models focus on specific events or activities. For example, an event-based model might cover the risk of a shared activity like a hiking trip, enabling participants to pool their resources for potential expenses.
Examples of Successful Peer-to-Peer Insurance Platforms
Several platforms have emerged and demonstrated the potential of peer-to-peer insurance. These platforms illustrate different approaches and success factors. These platforms offer diverse options for users.
- Example 1: A platform focused on shared carpooling arrangements, where members pool resources to cover potential accidents or damages related to carpooling activities. This model addresses the shared risk of carpooling and encourages safer practices.
- Example 2: A platform for homeowners in a specific neighborhood, enabling them to share risks associated with potential damages to their properties, such as fire or storms. This model strengthens community bonds and offers cost-effective solutions to insurance needs.
- Example 3: A platform for freelancers, offering a peer-to-peer model to address issues like income protection or professional liability insurance. This model recognizes the unique needs of freelancers in a changing work environment.
Key Elements of Peer-to-Peer Insurance Platforms
Successful peer-to-peer insurance platforms require several key components. These components ensure trust, transparency, and effective risk management.
Key features include a secure platform for peer interactions, risk assessment tools, and transparent pricing mechanisms.
These elements contribute to a user-friendly and reliable experience.
Different Types of Peer-to-Peer Insurance Platforms
Different platforms cater to various needs and preferences. This table summarizes the key characteristics of community-based and subscription-based platforms.
| Platform Type | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Community-Based | Focuses on shared risk within a specific community, fostering trust and shared responsibility. | Strong community ties, shared values, and a focus on local risk assessment. |
| Subscription-Based | Members pay for access to the platform’s tools, community engagement features, and potential discounts. | Access to tools, community engagement, potential discounts, and a platform-wide risk pool. |
Future Trends and Developments in Peer-to-Peer Insurance
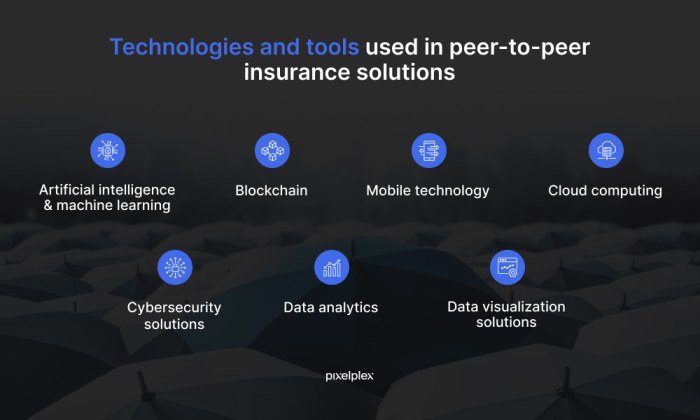
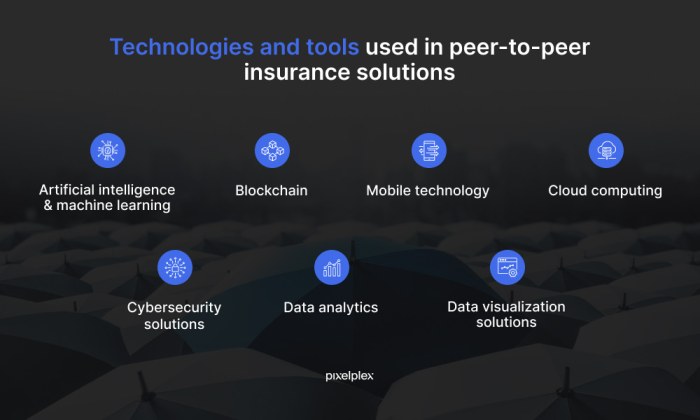
Peer-to-peer insurance is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. The future of this innovative approach to risk sharing promises exciting developments, potentially reshaping the traditional insurance landscape. This evolution hinges on the ability to leverage technology to improve efficiency, personalize coverage, and enhance the overall customer experience.The next phase of peer-to-peer insurance will likely see greater integration with existing technologies, fostering a more seamless and user-friendly experience for participants.
This will include improved data analysis, more sophisticated risk assessment models, and increased accessibility via mobile applications and other user-friendly interfaces. The ability to quickly access and process data will empower individuals and communities to participate more effectively in the sharing economy.
Predictive Modeling and Risk Assessment
Sophisticated algorithms and data analytics are crucial for accurately assessing risk and pricing premiums in peer-to-peer insurance models. This evolution will involve the development of more complex risk assessment models, incorporating a wider range of factors beyond traditional data points. For instance, predictive models can incorporate lifestyle data, health metrics, and even environmental factors to provide a more personalized and accurate risk profile for each participant.
Such advancements can lead to fairer pricing, as well as the identification of previously overlooked risk factors. This will lead to a more accurate reflection of individual risk profiles, improving the accuracy of premium calculations and reducing potential biases.
Integration of Technology and Platforms
The development of user-friendly platforms will be a key driver of growth in peer-to-peer insurance. Mobile applications, online portals, and streamlined data sharing systems will make it easier for individuals to access, manage, and participate in insurance networks. Integration with existing financial technologies, such as blockchain and cryptocurrency, will enhance transparency, security, and efficiency. The ease of access will be a major factor in driving broader adoption.
Personalized Insurance Products
Personalized insurance products will become increasingly common in peer-to-peer insurance, tailoring coverage to specific needs and preferences. This personalization will be driven by the ability to collect and analyze individual data points, such as driving habits, medical history, and even lifestyle choices. This approach will lead to more affordable and relevant coverage for individuals, reducing over- or under-insurance.
The potential exists for tailored products based on unique needs and circumstances.
Expanding Coverage and Applications
Peer-to-peer insurance models are likely to expand beyond traditional coverage areas. This will include coverage for niche markets, such as pet insurance, small business insurance, and even specialized professional liability coverage. As these models become more sophisticated, they will enable the creation of more specialized products to address unique insurance needs that aren’t adequately addressed by traditional insurance providers.
Impact on the Insurance Industry
The rise of peer-to-peer insurance will challenge the existing insurance industry to adapt and innovate. Traditional insurers will need to embrace new technologies and models to compete effectively. This will lead to a more dynamic and competitive insurance market, potentially resulting in more affordable premiums and enhanced customer service. The emergence of peer-to-peer models is set to revolutionize the way people access and manage insurance.
Concluding Remarks
Peer-to-peer insurance presents a fascinating alternative to traditional models, offering potential benefits like lower costs and increased access. However, challenges like trust, risk assessment, and regulation must be carefully considered. The future of this innovative approach will likely see continued evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing societal needs. Whether it truly gains traction will depend on overcoming these challenges and fostering trust among participants.

