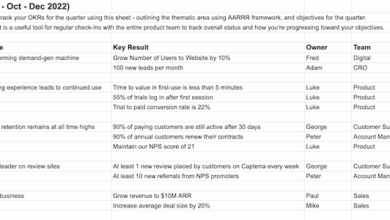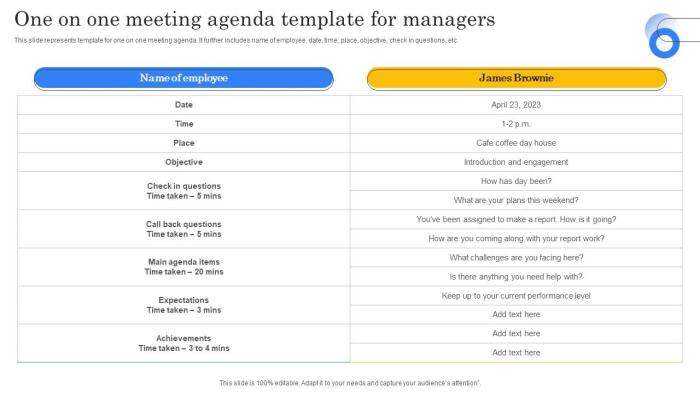
One on one meeting agenda is your roadmap to productive and impactful conversations. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential elements of crafting effective agendas, from defining the purpose to structuring the meeting for different objectives. We’ll explore various meeting types, offering templates and examples to help you navigate every scenario, from performance reviews to onboarding sessions.
Understanding the importance of clear expectations and goals is crucial for a successful one-on-one meeting. We’ll analyze common pitfalls to avoid, ensuring your meetings are not just productive but also efficient. By understanding the structure, common agenda items, and the use of effective visual representations, you’ll be well-equipped to lead and participate in valuable conversations.
Defining the Purpose of a One-on-One Meeting Agenda

A well-structured one-on-one meeting agenda is a roadmap for productive conversations. It clarifies expectations, ensures efficient use of time, and fosters a focused exchange of information between individuals. It acts as a guide, ensuring the meeting stays on track and achieves its objectives. A clear agenda sets the stage for meaningful discussions and tangible outcomes.A well-defined agenda is crucial for a successful one-on-one meeting.
It provides a framework for addressing key issues, sharing updates, and collaboratively working towards common goals. It ensures that both parties are prepared and can effectively participate, leading to more productive and insightful conversations.
Defining a One-on-One Meeting Agenda
A one-on-one meeting agenda is a pre-defined plan outlining the topics and objectives for a meeting between two individuals. It serves as a guide to ensure the meeting is focused and productive. This structured approach maximizes the meeting’s effectiveness, ensuring time is utilized efficiently and key issues are addressed.
Key Objectives of a Well-Structured Agenda
The key objectives of a well-structured one-on-one meeting agenda are multifaceted. They include: clarifying expectations, maximizing time efficiency, and facilitating focused communication. A well-structured agenda fosters open communication and helps both parties understand the other’s perspective, which leads to better collaboration.
Different Types of One-on-One Meetings and Their Agendas
Different types of one-on-one meetings require varying agenda structures. For example, performance review meetings necessitate a structured approach to evaluating past performance and setting goals for the future. These meetings will usually involve a discussion of accomplishments, areas for improvement, and development plans.
- Performance Reviews: This type of meeting requires a comprehensive agenda to cover past performance, identify areas for improvement, and set future goals. The agenda should include a review of key performance indicators (KPIs), a discussion of accomplishments and challenges, and the establishment of clear objectives and action plans for the next review period. This structure ensures the meeting is productive and provides a roadmap for future development.
- Check-in Meetings: A check-in meeting focuses on addressing current concerns, providing updates, and establishing next steps. The agenda might include a quick overview of recent projects, a discussion of any roadblocks, and an Artikel of priorities for the coming week. This agenda prioritizes efficiency and allows for timely identification of issues.
- Problem-Solving Meetings: A problem-solving meeting aims to identify and resolve specific issues. The agenda should be focused on the problem, possible solutions, and a plan of action. It might include defining the problem, brainstorming potential solutions, evaluating options, and creating a decision-making process.
Basic One-on-One Meeting Agenda Template
This template provides a framework for a standard one-on-one meeting.
| Time | Topic | Action Items |
|---|---|---|
| 0:00-0:15 | Introductions and Catch-up | Welcome and brief discussion of current projects |
| 0:15-0:45 | Project Updates | Review progress on key projects, discuss roadblocks |
| 0:45-1:00 | Next Steps and Action Items | Assign tasks, schedule follow-up meetings |
Planning Effective One-on-One Meeting Agendas: One On One Meeting Agenda
Crafting a productive one-on-one meeting agenda is crucial for maximizing efficiency and achieving specific outcomes. A well-structured agenda acts as a roadmap, guiding both you and your colleague through the meeting, ensuring that key topics are covered and decisions are made effectively. It fosters a focused and productive interaction, allowing for a more meaningful exchange of ideas and insights.A well-defined agenda provides a clear structure for the discussion, enabling a focused and productive conversation.
It is a critical tool for ensuring that the meeting stays on track and addresses the agreed-upon objectives. A clear agenda sets expectations and helps both parties prepare accordingly, reducing wasted time and improving overall outcomes.
My one-on-one meeting agenda is looking pretty packed today. We’ve got a lot to cover, from project updates to potential roadblocks. It’s important to stay on top of things, especially with recent news of malware affecting PCs, like the recent Energizer Jolts PCs with Malware incident. This incident highlights the importance of robust security measures. Thankfully, I’ve already outlined a few preventative steps on the agenda.
Now, back to that meeting!
Essential Items for a One-on-One Meeting Agenda
A comprehensive one-on-one meeting agenda should include key elements to ensure a focused and productive interaction. These elements are designed to cover all relevant aspects and provide a structure for the discussion.
- Meeting Purpose/Objectives: Clearly state the purpose and objectives of the meeting. This should align with the overall goals of the project or task at hand. For example, “Review progress on the Q3 sales report” or “Discuss strategies for improving customer satisfaction.” This ensures both parties are aware of the meeting’s intention from the start.
- Review of Previous Meeting Action Items: Address any outstanding action items from the previous meeting. This demonstrates accountability and ensures that tasks are being completed efficiently.
- Discussion Points: Artikel the key topics or issues to be discussed. This helps to structure the conversation and keep it focused. For instance, “Review current sales figures,” “Analyze customer feedback,” or “Brainstorm new marketing strategies.” This ensures all necessary points are addressed.
- Time Allocation: Allocate specific time slots for each discussion point. This helps to manage time effectively and prevents the meeting from going off-track. For example, “15 minutes for reviewing sales data,” “20 minutes for discussing customer feedback,” and “15 minutes for brainstorming new strategies.” This approach maintains meeting efficiency.
- Action Items & Deadlines: Clearly define any action items that need to be completed following the meeting. Include specific deadlines for each action. This promotes accountability and ensures that agreed-upon tasks are completed within a defined timeframe.
- Next Steps & Meeting Follow-up: Determine the next steps and how to follow up on the discussed points. This will keep momentum going. For example, “Schedule a follow-up meeting in two weeks,” or “Assign John to draft a report summarizing the discussed strategies.” This ensures continuity and actionable outcomes.
Best Practices for Creating a Productive Agenda
Creating a productive one-on-one agenda requires adherence to specific best practices. These practices enhance clarity and efficiency, maximizing the value derived from the meeting.
- Keep it Concise: Avoid overwhelming the agenda with excessive detail. Focus on the key points that need to be addressed.
- Collaborate with the Colleague: Involve your colleague in the agenda-setting process to ensure their input and agreement on the meeting’s scope. This collaborative approach ensures buy-in and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
- Prioritize Critical Issues: Identify the most critical issues and allocate more time for those. This helps ensure that critical topics are given the attention they deserve.
- Focus on Outcomes: Frame each discussion point in terms of the desired outcomes. This helps to maintain focus and ensure that the discussion stays on track.
- Use a Clear and Consistent Format: Employ a consistent format for presenting the agenda, making it easy to read and understand. This enhances clarity and predictability.
Different Methods for Planning One-on-One Meeting Agendas
Several methods can be employed for planning one-on-one meeting agendas. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses.
Planning one-on-one meeting agendas can be tricky, but it’s crucial for productivity. I’ve been looking at how mobile operating systems are evolving, and it’s fascinating to see how Android is becoming Flash Mobile’s first best friend, android becomes flash mobiles first bff. This close partnership could unlock some exciting possibilities, and ultimately, streamlining our one-on-one meetings to maximize output.
- Pre-Meeting Email: Send a detailed agenda in an email prior to the meeting. This allows the recipient to review the topics and prepare accordingly.
- Shared Document: Use a shared document (e.g., Google Docs, Microsoft Word) to collaboratively develop the agenda. This enables real-time input and allows for flexibility during the planning process.
- Meeting Notes App: Employ a meeting notes app for recording discussion points and follow-up actions. This provides a centralized repository for the meeting’s content.
Setting Clear Expectations and Goals in the Agenda
Defining clear expectations and goals within the agenda is essential. This sets the stage for a productive meeting.
- Expected Outcomes: Clearly articulate the desired outcomes from the meeting. This ensures both parties are aligned on the meeting’s objectives.
- Role Expectations: Define the roles and responsibilities of each participant to maintain clarity and avoid ambiguity. For example, “John will present the sales data,” or “Maria will lead the discussion on customer feedback.”
Potential Pitfalls to Avoid
Several pitfalls can hinder the effectiveness of a one-on-one meeting agenda. Understanding these pitfalls can help to avoid them.
- Overloading the Agenda: Avoid packing too many items into a single agenda. This can lead to rushed discussions and incomplete action items.
- Lack of Prioritization: Failing to prioritize discussion points can lead to irrelevant topics dominating the meeting.
- Missing Follow-up Actions: Not outlining clear follow-up actions can result in incomplete tasks and lost momentum.
Structuring the Agenda for Different Meeting Types
Crafting effective agendas is crucial for maximizing the value of one-on-one meetings. A well-structured agenda ensures that the meeting stays focused, productive, and achieves its objectives. Tailoring the agenda to the specific type of meeting is key to a successful outcome. Different meeting types require different approaches to structuring the agenda.By understanding the nuances of each meeting type, you can create an agenda that guides the discussion, facilitates collaboration, and ensures the desired outcomes are met.
This section provides examples of structured agendas for various one-on-one meeting types.
Performance Review Meeting Agenda
A performance review meeting should focus on evaluating past performance, identifying areas for improvement, and setting goals for the future. The agenda should be designed to foster a constructive dialogue, enabling both the manager and employee to actively participate in the review process.
- Review of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Discuss the employee’s accomplishments against their established KPIs. Quantify achievements wherever possible to demonstrate progress and impact. Acknowledge challenges encountered and explore strategies for overcoming them.
- Feedback Session: Provide constructive feedback on both strengths and areas needing development. Use the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to provide specific examples. Encourage the employee to share their perspective on their performance and areas they’d like to improve.
- Goal Setting for the Next Review Period: Establish clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for the next review period. Discuss how these goals align with departmental and organizational objectives.
- Action Planning and Follow-up: Artikel the steps needed to achieve the set goals, including timelines and responsibilities. Schedule a follow-up meeting to track progress and address any issues.
Mentoring Session Agenda
A mentoring session should foster a supportive environment where the mentee can gain insights and guidance from the mentor. The agenda should focus on active listening, open communication, and shared learning.
- Review of Mentee’s Goals and Aspirations: Discuss the mentee’s career aspirations, challenges, and learning objectives for the session. Identify specific areas where the mentor can provide support and guidance.
- Discussion of Challenges and Solutions: Explore the mentee’s current challenges and brainstorm potential solutions together. Encourage the mentee to take ownership of the problem-solving process.
- Skill Development and Knowledge Sharing: Provide practical advice and insights based on the mentor’s experience. Share relevant resources, articles, or examples to illustrate concepts.
- Action Planning and Next Steps: Define actionable steps the mentee can take to address their challenges and develop their skills. Schedule the next mentoring session and establish a clear follow-up plan.
Project Update Meeting Agenda
A project update meeting should keep stakeholders informed about the progress of a project and address any roadblocks. The agenda should be concise and focused on delivering essential updates and making crucial decisions.
- Project Overview: Briefly recap the project’s objectives and current status. Present a visual overview, such as a project timeline or progress chart, to clearly illustrate the progress.
- Progress Report: Detail the completed tasks, outstanding tasks, and any significant milestones achieved. Address any deviations from the project plan and explain the reasons behind them.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Discuss any identified risks and potential solutions. Focus on proactive measures to mitigate identified risks.
- Action Items and Next Steps: Assign responsibilities for outstanding tasks and define the next steps in the project. Establish a clear timeline for completing these tasks.
Goal-Setting Meeting Agenda
A goal-setting meeting should focus on defining clear objectives and developing strategies to achieve them. The agenda should be designed to foster a collaborative environment, ensuring all parties are aligned on the desired outcomes.
- Review of Current Goals and Performance: Assess past performance against established goals. Identify areas where progress has been made and areas where improvements are needed.
- Brainstorming Potential Goals: Engage in a brainstorming session to generate a list of potential goals for the upcoming period. Encourage diverse perspectives and ideas.
- Prioritization and Selection: Evaluate the generated goals based on factors such as feasibility, impact, and alignment with organizational objectives. Select the most important goals to focus on.
- Action Planning and Timelines: Artikel the steps required to achieve the chosen goals. Establish realistic timelines and assign responsibilities.
Problem-Solving Session Agenda
A problem-solving session should focus on identifying the root cause of a problem and developing effective solutions. The agenda should encourage open communication and collaborative problem-solving.
- Problem Definition: Clearly define the problem being addressed, ensuring all parties have a shared understanding of the issue.
- Data Gathering and Analysis: Collect relevant data and analyze the problem to identify the root cause. Use various analytical methods, such as SWOT analysis, to understand the problem’s context.
- Brainstorming Solutions: Generate a wide range of potential solutions to address the problem. Encourage creative thinking and out-of-the-box ideas.
- Evaluation and Selection: Evaluate the proposed solutions based on their feasibility, cost, and effectiveness. Select the most suitable solution to implement.
Content Examples and Methods for Agendas
Crafting effective one-on-one meeting agendas requires a thoughtful approach to ensure productive outcomes. A well-structured agenda acts as a roadmap, guiding both you and your team member through the discussion. This section delves into practical examples, methods, and strategies for creating impactful agendas.A strong agenda provides clarity and focus, preventing wasted time and fostering a sense of accomplishment.
It allows for a structured conversation that addresses critical points and facilitates progress on key objectives.
Specific Discussion Points for Meeting Types
Different meeting types require different discussion points. For example, a performance review meeting will center on past achievements, future goals, and areas for improvement. A project update meeting will focus on the current status of the project, challenges encountered, and next steps. A mentoring meeting will concentrate on career development, skill enhancement, and networking opportunities.
- Performance Review Meeting: Review past performance against established goals, discuss areas for improvement, set new goals, and identify resources needed for future success. Examples of discussion points include: “Quantifiable achievements in the last quarter,” “Areas where performance could be enhanced,” and “Development plans for the next quarter.”
- Project Update Meeting: Review the current project status, assess any roadblocks or challenges, and discuss action plans. Example discussion points: “Project progress report,” “Current challenges and solutions,” “Timeline updates and adjustments.”
- Mentoring Meeting: Discuss career goals, skill development, and networking opportunities. Examples: “Career aspirations and how the mentor can help,” “Skill gaps and how to fill them,” and “Networking opportunities and strategies.”
Methods for Documenting Action Items and Decisions, One on one meeting agenda
Clearly documenting action items and decisions is crucial for follow-up and accountability. A well-organized method ensures everyone is on the same page and understands their responsibilities.
- Action Item Log: A dedicated log, whether digital or physical, helps track action items, assigned individuals, deadlines, and completion status. This can be a simple spreadsheet or a dedicated project management tool.
- Decision Matrix: A table or chart format that documents the decision, rationale, assigned owner, and expected outcome. This is particularly helpful for complex decisions that require multiple stakeholders.
- Minutes of Meeting: A written record of the meeting’s key discussions, decisions, and action items. These minutes should be concise and well-organized, with clear definitions for each action item.
Steps for Incorporating Feedback and Follow-Up Tasks
Gathering and addressing feedback, and setting up follow-up tasks are essential to the success of one-on-one meetings. Feedback loops ensure the meeting isn’t a one-time event but a continuous improvement process.
- Active Listening and Feedback Collection: Actively listen to the feedback provided. Create a safe space for open and honest dialogue. Summarize the feedback to ensure clarity and understanding.
- Action Item Assignment and Prioritization: Assign specific individuals responsibility for action items. Prioritize tasks based on urgency and importance. Establish clear deadlines for each item.
- Follow-up Communication: Regularly check in with individuals to track progress on action items. Provide support and resources as needed. Address any roadblocks or challenges that arise.
Incorporating Open-Ended Questions into the Agenda
Open-ended questions encourage deeper discussion and foster a more collaborative environment. They allow for a wider range of responses, helping to uncover insights and potential issues.
- Example Open-Ended Questions: Instead of asking “Did you complete the project on time?”, try “What were the key challenges you faced during the project, and how did you overcome them?”. This type of question encourages a more detailed and insightful response.
- Strategic Placement: Incorporate open-ended questions into the agenda where appropriate. For example, after a project update, you could ask, “What are the next steps to prevent similar issues in the future?”.
Time Slots for Each Agenda Item
Assigning specific time slots for each agenda item ensures the meeting stays on track and addresses all necessary topics.
- Time Management: Allocate specific time slots for each agenda item to ensure the meeting stays focused and on schedule. This will help avoid rushing through important topics.
- Flexibility: While allocating time, allow for some flexibility. Some topics may take less time than anticipated, while others might require more discussion time.
Visual Representation of Agendas
Visualizing your one-on-one meeting agenda can significantly enhance its effectiveness. A clear, well-structured agenda allows for a focused discussion, ensuring that all crucial points are addressed and action items are clearly assigned. This visual representation also promotes a smoother meeting flow, making the process more efficient for both participants.A well-designed agenda serves as a roadmap, guiding the conversation and keeping everyone on track.
Visual aids such as tables and charts provide a concise and easily digestible overview of the meeting’s objectives and tasks, allowing participants to quickly grasp the meeting’s purpose and anticipated outcomes.
Key Sections of a One-on-One Meeting Agenda
A well-structured agenda lays out the meeting’s purpose and expected outcomes. A table illustrating the key sections will be beneficial for organizing the information.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Meeting Purpose | Clearly states the objective of the meeting. |
| Review of Previous Action Items | Summarizes completed tasks and outstanding items from previous meetings. |
| Discussion Points | Artikels the specific topics to be discussed. |
| Action Items | Identifies tasks and their assigned owners. |
| Next Steps/Meeting Follow-Up | Specifies action steps and scheduling for future meetings. |
Action Items and Owners
Action items are essential for tracking progress and ensuring tasks are completed. A table that demonstrates action items and their assigned owners is provided below.
Planning one-on-one meeting agendas can be tricky, but it’s crucial for productivity. While brainstorming, it’s worth noting the latest tech trends, like Dell’s colourful new netbook, designed for the creative set. Considering innovative products like this can spark fresh ideas for your own team’s projects, and help refine your agenda further.
| Action Item | Description | Owner |
|---|---|---|
| Finalize Project Proposal | Compile all project documents and prepare for review. | Project Manager |
| Schedule Team Meeting | Coordinate meeting dates and times with team members. | Project Coordinator |
| Prepare Presentation Slides | Create visuals for the upcoming presentation. | Marketing Team |
Meeting Styles and Agendas
Different meeting styles require different agendas. The table below compares and contrasts various styles and their corresponding agendas.
| Meeting Style | Agenda Focus | Typical Content |
|---|---|---|
| Problem-Solving Meeting | Identifying and resolving issues. | Defining the problem, brainstorming solutions, prioritizing solutions, and assigning action items. |
| Strategic Planning Meeting | Setting long-term goals and objectives. | Analyzing market trends, defining strategic initiatives, and outlining action plans. |
| Project Review Meeting | Evaluating project progress. | Assessing project milestones, identifying roadblocks, and adjusting plans. |
Common Agenda Items for Different Team Roles
The following table Artikels typical agenda items for various team roles.
| Team Role | Common Agenda Items |
|---|---|
| Project Manager | Project status updates, risk assessment, resource allocation. |
| Marketing Team | Campaign progress, lead generation, social media analysis. |
| Sales Team | Sales targets, lead qualification, customer relationship management. |
Detailed Meeting Agenda Format
This table presents a comprehensive format for structuring a one-on-one meeting agenda.
| Section | Example Content |
|---|---|
| Meeting Purpose | Review progress on Q3 goals and plan for Q4. |
| Review of Previous Action Items | Action item 1: Complete market research report. (Status: Complete) |
| Discussion Points | Q3 performance analysis, Q4 goals alignment, potential roadblocks. |
| Action Items | Action item 2: Schedule Q4 kickoff meeting. (Owner: Project Manager) |
| Next Steps/Meeting Follow-Up | Schedule follow-up meeting in two weeks to review action items. |
Illustrative Examples of Meeting Agendas
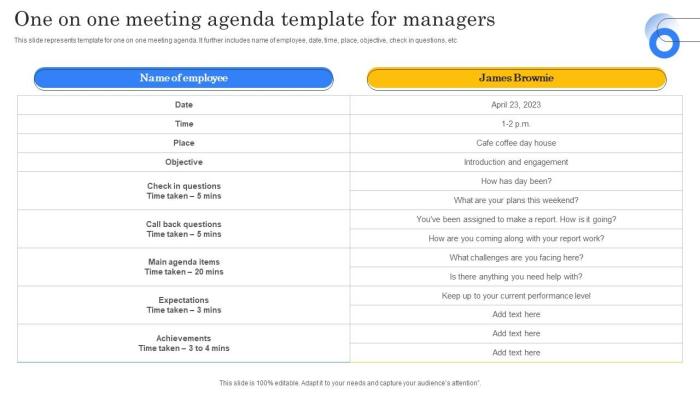
A well-structured one-on-one meeting agenda is crucial for maximizing efficiency and achieving desired outcomes. A clear framework ensures focused discussions, prevents tangents, and helps both parties leave the meeting feeling productive. Conversely, a poorly organized agenda can lead to wasted time and frustration. This section provides illustrative examples to demonstrate the impact of effective and ineffective agenda design.
Scenario of Improved Outcome
A software engineer, Sarah, was consistently struggling with meeting deadlines on complex projects. Her manager, David, scheduled a one-on-one meeting with a meticulously crafted agenda. The agenda focused on identifying the root cause of the delays, brainstorming potential solutions, and creating a realistic action plan with clear deadlines and responsibilities. By outlining specific tasks and timelines, they effectively addressed Sarah’s concerns and established a path forward.
The meeting resulted in a tangible plan, complete with documented action items, assigned owners, and a clear timeline for completion. This structured approach allowed Sarah to feel supported and empowered, leading to improved project performance and a more positive working relationship.
Scenario of Wasted Time
A marketing associate, Emily, had a one-on-one with her supervisor, Mark, for feedback on a recent campaign. The agenda was unstructured and lacked specific objectives. The meeting drifted from the campaign’s performance to broader company strategies, and then to personal anecdotes about Mark’s weekend. The lack of a clear focus led to a lack of concrete takeaways and actions for Emily to improve.
The meeting ended without a clear plan for moving forward, leaving Emily feeling frustrated and unsure of how to proceed with future campaigns.
Agenda for a Struggling Team Member
This agenda is designed for a one-on-one meeting with a team member experiencing difficulties with a project.
- Review of Project Progress: Discuss the current status of the project, identify specific tasks causing challenges, and explore the reasons behind these difficulties.
- Brainstorming Solutions: Encourage collaborative problem-solving. Generate potential solutions to overcome obstacles. Encourage the team member to actively participate in brainstorming and propose ideas.
- Action Plan Development: Establish a clear action plan with specific steps, deadlines, and assigned responsibilities. Ensure the team member understands their role in the action plan.
- Resource Allocation: Identify any necessary resources or support the team member needs to complete the project effectively. This might include additional training, tools, or mentorship.
- Follow-up Meeting: Schedule a follow-up meeting to review progress, address any new challenges, and adjust the action plan as needed.
Agenda for New Employee Onboarding
This agenda Artikels the key components of a new employee onboarding session.
- Company Introduction: Provide an overview of the company’s mission, values, and culture. This includes an introduction to key personnel and departments.
- Departmental Overview: Introduce the new employee to their team, their role, and the departmental structure.
- Role-Specific Training: Deliver training on the specific tasks and responsibilities of the new employee’s role, including software and tools usage.
- Company Policies: Review essential company policies, including code of conduct, employee benefits, and safety procedures.
- Q&A Session: Allow time for questions and clarification from the new employee.
Agenda for a One-on-One with a Senior Manager
This agenda focuses on a one-on-one with a senior manager, emphasizing strategic planning and career development.
- Review of Recent Performance: Discuss recent projects, accomplishments, and areas for improvement. Focus on quantifiable results and key performance indicators.
- Strategic Goals Alignment: Align individual goals with departmental and company objectives. Discuss how the employee’s work contributes to the broader strategic plan.
- Development Opportunities: Discuss opportunities for skill development, professional growth, and advancement within the organization.
- Feedback and Guidance: Seek feedback on performance and career trajectory. Discuss specific steps for skill enhancement and career advancement.
- Action Items and Next Steps: Document action items, assign responsibilities, and schedule follow-up meetings.
Common Agenda Items and Their Importance
Crafting a productive one-on-one meeting agenda hinges on carefully selecting and prioritizing agenda items. A well-structured agenda ensures that the meeting achieves its intended purpose, fostering clarity and efficiency. This section delves into common agenda items, their significance, and how they contribute to positive outcomes.
Common Agenda Items for Team Meetings
A comprehensive team meeting agenda typically includes items related to project updates, problem-solving, and team building. These items are crucial for keeping the team aligned, informed, and motivated. The inclusion of these elements fosters a collaborative environment and drives progress.
- Project Updates: This item ensures everyone is aware of the current status of projects. It helps identify roadblocks early, facilitating proactive problem-solving. For example, if a team member reports a delay in a critical project milestone, the team can address the issue immediately and avoid larger problems later.
- Problem Solving: This item allows the team to address challenges collectively. By focusing on specific problems and brainstorming solutions, teams can find creative solutions and improve overall efficiency. For instance, a recurring issue with software integration can be resolved through a dedicated team discussion and the implementation of a new protocol.
- Team Building Activities: These activities foster stronger relationships among team members. Icebreakers or shared learning opportunities can increase communication and understanding. This improves teamwork, which is crucial for projects demanding collaboration.
- Action Item Review: A crucial component for ensuring follow-through on agreed-upon actions. This item ensures accountability and tracks progress toward goals. A review of previous action items allows the team to address any outstanding issues and adjust plans accordingly. It is important to discuss any unforeseen complications.
Importance of Including Specific Agenda Items
The inclusion of specific agenda items is vital for a successful meeting. Each item contributes to the meeting’s overall purpose. The specific agenda items should align with the meeting’s objectives. This ensures that time is used effectively, and relevant topics are discussed thoroughly. This can lead to improved decision-making, higher productivity, and a stronger sense of shared responsibility.
- Focus and Direction: The agenda guides the meeting’s direction, preventing it from veering off track. This ensures that the meeting stays focused on the defined objectives. Clear direction allows the team to efficiently allocate their time.
- Actionable Outcomes: Specific agenda items lead to tangible outcomes. The team can create action plans and track progress. This leads to a sense of accomplishment and improved team performance.
- Measurable Results: By establishing specific metrics for each item, the team can measure the effectiveness of the meeting. This ensures that the meeting serves a purpose and is not a mere formality.
- Enhanced Communication: A well-defined agenda fosters open and transparent communication. Team members feel more comfortable sharing their perspectives, ideas, and concerns. This leads to a more inclusive and collaborative atmosphere.
Agenda Items Crucial for a Particular Meeting Type
The selection of agenda items depends on the type of meeting. A project kickoff meeting will require different agenda items than a team performance review. Understanding the purpose of the meeting is crucial to selecting the right items. This leads to a more focused and efficient use of time.
- Project Kickoff Meetings: Crucial items include project scope, timeline, team assignments, and initial goals. This ensures everyone understands their role and expectations. This can lead to a more cohesive project start-up.
- Performance Review Meetings: The agenda must include a review of past performance, identification of strengths and weaknesses, and setting goals for improvement. This provides a platform for constructive feedback and mutual understanding.
Ensuring All Relevant Topics are Covered
To ensure all relevant topics are covered, it is essential to create a comprehensive agenda. This requires anticipating potential discussion points and incorporating them into the agenda. This leads to a thorough and comprehensive discussion of all relevant issues.
- Brainstorming Sessions: Brainstorming sessions should be designed to generate as many ideas as possible, and the agenda should be flexible to accommodate new ideas that arise during the session.
- Detailed Planning: Detailed planning requires careful consideration of all potential issues. It is essential to have a detailed plan that accounts for all possible scenarios.
- Regular Check-ins: Regular check-ins can help anticipate potential problems and adjust the agenda as needed.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, a well-structured one on one meeting agenda is the cornerstone of effective communication and collaboration. By following the tips and examples provided, you can significantly improve the outcomes of your one-on-one meetings. From clarifying objectives to ensuring all relevant topics are covered, we’ve provided a practical approach to planning and executing productive dialogues. Remember, a thoughtful agenda is the key to maximizing the value of every interaction.