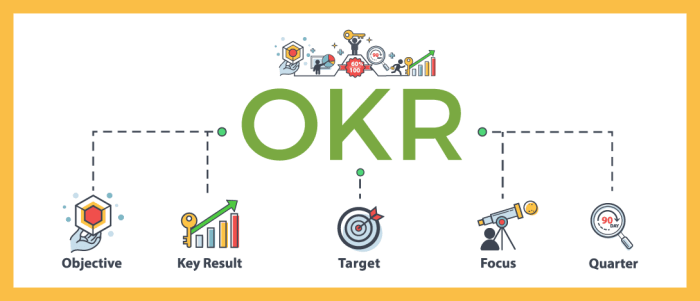
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) are a powerful framework for setting and achieving ambitious goals. This in-depth exploration dives into the core principles of effective OKRs, from defining clear objectives to measuring progress and adapting strategies. We’ll cover everything from the fundamental concepts to practical applications in various contexts, including marketing, sales, and product development. Get ready to unlock the secrets of successful goal setting!
The Artikel meticulously breaks down the OKR process into actionable steps. We’ll start by understanding the core concepts and defining the difference between goals, objectives, and key results. Then, we’ll explore how to establish objectives, define key results, and link them effectively. The importance of measuring progress and adapting to changing circumstances will also be highlighted. The ultimate goal is to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to implement OKRs effectively within your own teams or organizations.
Defining Objectives and Key Results
OKRs, or Objectives and Key Results, are a strategic management framework used to set ambitious goals and track progress toward achieving them. They provide a structured approach to aligning teams and individuals around common objectives, fostering a sense of shared purpose and driving tangible results. This framework is particularly effective in helping organizations focus on what truly matters and measure the impact of their efforts.Effective OKRs rely on a clear understanding of the desired outcomes and measurable metrics to track progress.
They promote a proactive and results-oriented culture, moving beyond simply identifying problems to actively seeking solutions and achieving tangible outcomes. This approach emphasizes ambitious yet attainable goals, motivating individuals and teams to strive for excellence.
Defining OKRs
OKRs are a goal-setting framework that helps teams define ambitious objectives and track their progress toward achieving them using measurable key results. They are designed to foster a shared understanding of the desired outcomes and drive accountability.
Core Principles of Effective OKRs
The effectiveness of OKRs hinges on adhering to key principles. These include clarity, ambition, measurability, and alignment. Objectives should be clearly defined, ambitious yet achievable, and directly tied to strategic priorities. Key results should be measurable, time-bound, and contribute directly to the achievement of the objective. Alignment ensures everyone is working toward the same overarching goals, maximizing impact.
Importance of Alignment
Alignment between objectives and key results is crucial for maximizing the impact of OKRs. When teams and individuals understand how their work contributes to the overall objectives, they are more likely to be motivated and focused on achieving desired results. This alignment creates a shared understanding and a sense of collective responsibility, leading to better collaboration and more efficient resource allocation.
Examples of Well-Defined Objectives and Key Results
A well-defined objective focuses on a specific area for improvement, while key results provide concrete, measurable ways to track progress toward achieving that objective. For example, an objective might be “Increase customer satisfaction.” Key results could include “Increase Net Promoter Score (NPS) by 15%,” “Reduce customer support tickets by 10%,” or “Increase customer feedback ratings by 10%.”
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Setting OKRs
Common pitfalls in setting OKRs include setting objectives that are too broad, key results that aren’t measurable, or objectives and key results that lack alignment with overall strategic goals. Specificity, measurability, and alignment are crucial elements of effective OKRs. For instance, instead of “Improve marketing efforts,” a more effective objective would be “Increase website traffic by 20%.”
Comparison of Goals, Objectives, and Key Results
| Element | Goal | Objective | Key Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad, overarching aspirations. | Specific, time-bound targets that contribute to the goal. | Measurable steps toward achieving the objective. |
| Specificity | General | Specific | Specific, measurable |
| Measurability | Not directly measurable | Not directly measurable | Measurable and quantifiable |
| Timeframe | Long-term | Medium-term | Short-term, usually within a quarter |
| Example | Increase company profitability | Increase revenue by 15% in Q3 | Close 10 new large contracts |
Establishing Objectives
Defining objectives is a crucial step in any strategic planning process. It’s the foundational layer upon which key results are built, ensuring alignment with overarching goals. A well-defined objective provides a clear direction for the team, fostering a shared understanding of what needs to be accomplished. Effective objectives are not just aspirations; they are concrete, measurable targets that drive tangible results.Clearly articulated objectives provide a roadmap for achieving desired outcomes.
They serve as a benchmark for progress, enabling continuous monitoring and adjustments as needed. Objectives, when coupled with measurable key results, become a powerful tool for tracking success and identifying areas requiring further attention.
Identifying Appropriate Objectives
Objectives should stem directly from strategic goals. They should be specific, focused, and relevant to the overall organizational direction. For example, if a strategic goal is to increase market share, a corresponding objective might be “Increase customer acquisition by 15% in the next quarter.” This objective is tied to the strategic goal and provides a quantifiable target.
Identifying appropriate objectives requires a deep understanding of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis).
Objectives and key results are crucial for focusing your efforts, but sometimes, the digital world throws curveballs. Like those pesky Snapchat videos that refuse to self-destruct, those spicy Snapchat vids don’t self-destruct , leaving a trail of unexpected consequences. Regardless of the digital hiccups, strong objectives and key results are still vital for effective planning and achieving your goals.
Examples of Effective Objectives
Effective objectives are ambitious yet achievable, balancing aspiration with realism. An objective like “Become the leading provider of sustainable energy solutions within the next three years” is ambitious but lacks the necessary specifics for effective tracking. A more effective objective would be “Increase the market share for solar panel installations by 20% within the next year.” This is measurable and aligned with the strategic goal.
Other examples include: “Improve customer satisfaction scores by 10%,” or “Reduce operational costs by 5%.”
Importance of Ambitious Yet Achievable Objectives
Objectives should push the boundaries while remaining attainable. Ambitious objectives motivate teams and encourage innovation. However, they must be grounded in realistic projections and resources. Achievability ensures that progress is demonstrable and that setbacks are not demoralizing. A carefully considered objective, balanced with a realistic timeline, provides a sense of progress and achievement.
Clarity and Measurability in Objectives
Clear objectives are easily understood by all stakeholders. They avoid ambiguity and ensure everyone is working towards the same goal. Measurable objectives allow for progress tracking and evaluation. For instance, instead of “Improve employee engagement,” a measurable objective is “Increase employee satisfaction scores by 15% within the next quarter, measured by employee surveys.” Measurability ensures accountability and allows for adjustments to be made as needed.
Questions to Ask When Setting Objectives
The following questions should be considered when setting objectives:
- What are the specific strategic goals that this objective supports?
- What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will track progress towards this objective?
- What resources are needed to achieve this objective?
- What is the realistic timeframe for achieving this objective?
- Who is responsible for achieving this objective?
These questions help to ensure that the objective is aligned with the overall strategy, measurable, and achievable.
Comparing Various Types of Objectives
| Objective Type | Description | Example | Measurable Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Objectives | Focus on financial performance | Increase revenue by 10% | Revenue figures, profit margins |
| Operational Objectives | Focus on internal processes | Reduce customer service wait times by 15% | Average wait times, customer service resolution rates |
| Customer Objectives | Focus on customer satisfaction and loyalty | Increase customer retention rate by 5% | Customer churn rate, customer lifetime value |
| Market Objectives | Focus on market share and growth | Increase market share in target segment by 15% | Market share data, market penetration rate |
This table provides a concise overview of different objective types, highlighting their characteristics, examples, and measurable metrics. By considering these diverse categories, organizations can effectively align their objectives with their strategic goals.
Defining Key Results
Defining Key Results is a crucial step in the OKR process. It’s where the aspirational objectives translate into concrete, measurable actions. Effective key results are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This section dives into the methods for creating strong key results, emphasizing their importance in driving tangible progress.Defining key results involves moving beyond abstract goals and translating them into quantifiable outcomes.
This transformation ensures that progress towards objectives can be tracked and measured, providing clear visibility into the success of the initiatives.
Method for Defining Specific and Measurable Key Results
Defining key results requires a meticulous approach, starting with a deep understanding of the objective. Each key result should directly contribute to achieving the objective. A key result is not just a task, but a measurable outcome. It needs to be specific enough that progress can be tracked and measured objectively. For example, instead of “Improve customer satisfaction,” a key result might be “Increase customer satisfaction scores by 15% as measured by the Net Promoter Score (NPS) survey.” This level of detail allows for precise tracking of progress.
Role of Time-Bound Key Results
Time-bound key results are essential for maintaining focus and momentum. They provide a clear timeframe within which to achieve the desired outcomes. This timeframe fosters a sense of urgency and encourages proactive planning and execution. For example, “Increase website traffic by 20% within the next quarter” sets a specific time frame for achieving the result. Without a time constraint, the key result becomes less actionable and less likely to be accomplished within the designated timeframe.
Importance of Verifiable Key Results
Verifiable key results are critical for accountability and transparency. They need to be based on data that can be objectively validated. This allows for transparent reporting on progress, enabling stakeholders to understand the effectiveness of initiatives and adjust strategies as needed. For example, “Reduce customer support tickets by 10% by implementing a new FAQ section” is verifiable because the number of support tickets can be tracked.
Objectives and key results (OKRs) are a fantastic framework for setting ambitious goals. It’s fascinating to see how these translate into real-world outcomes, like the recent news of researchers pulling out a $1 million Netflix victory in the last half hour researchers pulled out 1m netflix victory in last half hour. Clearly, well-defined OKRs can drive significant achievements.
This just reinforces the power of focusing on quantifiable results.
Examples of Effective Key Results
Effective key results demonstrate a clear link between the objective and the desired outcome. They are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example:
- Objective: Increase brand awareness. Key Result: Increase social media followers by 15% in Q3.
- Objective: Improve conversion rates. Key Result: Increase website conversion rate by 10% within the next two months.
- Objective: Enhance customer experience. Key Result: Reduce customer support response time by 25% in the next month.
These examples illustrate how clear objectives translate into specific and measurable results.
Comparison and Contrast of Different Types of Key Results
Key results can vary based on the nature of the objective. For example, key results related to sales might focus on revenue targets, while those related to marketing might focus on lead generation or brand awareness. The specific type of key result depends on the objective being pursued. While the fundamental principles of specificity and measurability remain consistent, the specific metrics used to measure progress may differ depending on the context.
Characteristics of Well-Defined Key Results
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Specific | Clearly defined and unambiguous, leaving no room for misinterpretation. |
| Measurable | Quantifiable and trackable, allowing for progress to be measured objectively. |
| Achievable | Realistic and attainable within the given timeframe. |
| Relevant | Directly aligned with the objective and contributes to its achievement. |
| Time-Bound | Clearly defined timeframe for achieving the result. |
Linking Objectives and Key Results
Connecting objectives and key results (OKRs) is crucial for ensuring alignment and progress toward strategic goals. A strong link clarifies the direct impact of each key result on the overarching objective, enabling teams to focus their efforts and track success effectively. Without this connection, OKRs risk becoming disconnected initiatives, potentially hindering overall progress.A well-defined link between objectives and key results provides a roadmap for action, guiding decision-making and resource allocation.
This clarity allows teams to prioritize tasks and measure the impact of their work in relation to the larger strategic vision. It fosters a shared understanding of the desired outcomes and the steps required to achieve them.
Strategies for Establishing a Clear Link
Establishing a clear connection between objectives and key results requires meticulous planning and a focus on quantifiable metrics. This involves articulating how each key result directly contributes to the overall objective. A common mistake is to list key results without considering their relationship to the objective, creating a disconnect in the strategy.
Examples of Demonstrating the Connection
Consider a company aiming to increase brand awareness. The objective might be “Boost brand recognition by 20%.” Key results could include: “Increase social media followers by 15,000” and “Secure 100 new brand mentions in relevant publications.” The connection is evident; increasing social media followers and media mentions directly supports achieving the overall objective of boosting brand recognition.
Significance of Quantifiable Metrics in Key Results
Quantifiable metrics in key results are essential for tracking progress and demonstrating impact. Using metrics like percentages, numbers, or specific dates allows for objective measurement of success. Qualitative data, while valuable, doesn’t provide the same level of clarity for assessing progress. For instance, instead of “improve customer satisfaction,” a more quantifiable key result would be “Increase customer satisfaction scores by 10% as measured by the Net Promoter Score (NPS).”
Potential Challenges in Aligning Objectives and Key Results
Challenges can arise from miscommunication, unclear definitions, or a lack of buy-in from all stakeholders. For example, differing interpretations of the objective or key result can lead to misaligned efforts. Furthermore, an insufficient understanding of the specific tasks required to achieve the key results can cause delays or setbacks. Another challenge is the lack of consistent monitoring and adjustments to the plan, potentially leading to deviations from the intended path.
Best Practices for Connecting Objectives and Key Results
Clear and concise language is paramount. Each key result should directly contribute to the objective, not merely relate to it in a general sense. Use specific and measurable terms to define the desired outcomes. Regular communication and review meetings are vital for ensuring alignment and addressing any emerging challenges. Finally, flexibility and adaptability are crucial.
Objectives and key results are not static; they should be reviewed and adjusted as needed.
Table Outlining Steps Involved in Linking Objectives and Key Results
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Define the Objective | Clearly articulate the desired outcome. |
| 2. Identify Key Areas for Improvement | Determine specific areas where improvement is needed to support the objective. |
| 3. Define Key Results | Specify measurable targets for each key area. |
| 4. Establish the Link | Articulate how each key result contributes to the objective. |
| 5. Monitor Progress | Track progress towards achieving key results. |
| 6. Adjust as Needed | Review and adapt the strategy based on progress and feedback. |
Measuring Progress and Adapting
Staying on track with your Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) requires constant monitoring and adaptation. This phase isn’t about perfection, but rather about responsiveness. Effective OKR management involves regularly assessing progress, identifying areas needing improvement, and making necessary adjustments to maintain alignment with your strategic goals. This allows you to maximize your chances of achieving desired outcomes.Monitoring progress towards key results is crucial for staying on track and making informed adjustments.
Regular check-ins and data analysis allow for proactive problem-solving and course correction. This iterative approach is vital to ensuring your efforts remain focused and impactful.
Monitoring Progress Towards Key Results
Regular tracking of key result progress is essential. It helps identify trends, pinpoint potential roadblocks, and adjust strategies accordingly. This proactive approach prevents setbacks and ensures that resources are utilized effectively.
Effective Methods for Tracking Progress, Objectives and key results
Various methods can be employed to track progress effectively. These include regular meetings, progress reports, and visual dashboards. Choosing the right method depends on the complexity of your key results and the preferences of your team.
- Regular Meetings: Scheduled meetings allow for real-time updates, discussions, and identification of potential issues. These meetings facilitate collaboration and provide a platform for team members to share insights and concerns.
- Progress Reports: Formal reports, whether weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, offer a structured overview of progress. They document key achievements, challenges, and next steps, promoting accountability and transparency.
- Visual Dashboards: Visual representations of key result data provide a clear overview of progress at a glance. These dashboards allow for easy identification of trends and deviations from expected outcomes.
Analyzing Data and Identifying Areas for Improvement
Data analysis is paramount for identifying areas needing improvement. It helps determine if your strategies are working as planned or if adjustments are necessary. This data-driven approach allows for informed decisions, maximizing the effectiveness of your efforts.
- Trend Analysis: Identifying trends in key result data provides insights into the overall progress and allows for proactive identification of potential problems. Examining data over time can reveal patterns and predict future performance.
- Variance Analysis: Analyzing the difference between predicted and actual results helps pinpoint areas of deviation. This analysis highlights specific aspects requiring attention or adjustment.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigating the underlying causes of performance issues, rather than just the symptoms, is essential for effective problem-solving. This involves identifying the root causes to implement targeted solutions.
Importance of Regular Reviews and Adjustments
Regular reviews and adjustments are vital for maintaining alignment with strategic goals. They provide opportunities to adapt strategies based on performance data and ensure that efforts remain relevant and effective.
Adapting Objectives and Key Results Based on Performance
Adapting OKRs based on performance is an essential component of effective OKR management. It allows for responsiveness and ensures that objectives remain relevant to the evolving context.
| Method | Description | Frequency | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Meetings | Team discussions about progress, challenges, and solutions. | Weekly/Bi-Weekly | Reviewing sales targets, discussing marketing campaigns, and identifying roadblocks. |
| Progress Reports | Formal documentation of key achievements, challenges, and next steps. | Weekly/Monthly | Detailed account of completed tasks, issues encountered, and projected timelines. |
| Visual Dashboards | Visual representations of key result data for quick overview. | Daily/Weekly | Real-time graphs illustrating website traffic, sales conversions, or customer satisfaction. |
OKRs in Different Contexts: Objectives And Key Results
OKRs, or Objectives and Key Results, are a powerful framework for aligning teams and individuals towards common goals. Their flexibility allows them to be adapted and implemented in various contexts, from bustling corporate environments to non-profit organizations. This adaptability is crucial for achieving optimal results and driving meaningful change. This exploration delves into the diverse applications of OKRs, demonstrating their versatility and effectiveness across different sectors.Understanding the nuances of applying OKRs across various business functions, organizational structures, and even non-profit models is key to maximizing their impact.
This involves recognizing how strategic goals translate into actionable objectives and key results, tailored to specific team needs and organizational dynamics.
OKRs in Marketing
Marketing teams often use OKRs to define specific campaign goals and measure their success. For instance, a marketing team might set an objective to increase brand awareness by 15% within the next quarter. Key results might include a target number of social media followers, a specific number of website visits, or an increase in lead generation. This allows for measurable progress tracking and ensures that marketing efforts are aligned with broader business objectives.
OKRs in Sales
Sales teams can use OKRs to focus on key performance indicators (KPIs). A sales team might set an objective to increase revenue by 20% in the next fiscal year. Key results could include a target number of new clients, average deal size, or sales cycle length. These metrics provide clear targets and help sales teams refine their strategies for maximum impact.
OKRs in Product Development
Product development teams use OKRs to define and deliver specific product features and improvements. For example, a product team might set an objective to improve user engagement by 10% within the next quarter. Key results could include metrics like user retention, daily active users, or in-app purchases. This process ensures that product development efforts are aligned with user needs and business goals.
Objectives and key results are crucial for any project, outlining what you want to achieve and how you’ll measure success. Samsung’s Galaxy Note series, aiming to blur the lines between phones and tablets, is a prime example of how a company can define objectives that drive innovation. For instance, Samsung Galaxy Note aims to harmonize phones with tablets , highlighting a clear focus on user experience and bridging the gap between mobile device categories.
This approach to product development, which aligns perfectly with the concept of key results, demonstrates the power of setting clear goals.
Adaptation of OKRs for Different Organizational Structures
Different organizational structures require slight adjustments to the OKR framework. In a hierarchical structure, objectives might be set at the top level, with teams breaking them down into specific, measurable key results. In flatter organizations, teams might have greater autonomy in defining their objectives and key results, while still aligning with broader organizational goals.
OKRs in Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations can use OKRs to track their progress toward achieving their mission. For example, a non-profit dedicated to supporting homeless individuals might set an objective to increase access to affordable housing by 25% over the next year. Key results could include the number of applications processed, the number of individuals housed, or the amount of funding raised.
Tailoring OKRs to Team/Department Needs
Effective OKRs are tailored to the specific needs of a team or department. Factors like existing resources, skill sets, and potential challenges should be considered when defining objectives and key results. This customization ensures that OKRs are realistic and achievable, fostering motivation and engagement.
Translating Strategic Goals into Actionable OKRs
Translating strategic goals into actionable OKRs requires careful consideration. Strategic goals should be broken down into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. This process helps ensure that OKRs are clearly defined and measurable, facilitating effective progress tracking.
Comparison of OKR Usage in Different Sectors
| Sector | Typical Objective Focus | Typical Key Result Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Marketing | Brand awareness, lead generation, customer acquisition | Website traffic, social media engagement, conversion rates |
| Sales | Revenue growth, customer retention, deal closure | New customer acquisition, average deal size, sales cycle length |
| Product Development | User engagement, product adoption, feature implementation | User retention, daily active users, in-app purchases |
| Non-profit | Mission fulfillment, resource mobilization, impact generation | Program participation, beneficiaries reached, funding secured |
Communicating and Aligning
OKRs are powerful tools for driving organizational alignment, but their effectiveness hinges on clear and consistent communication. This crucial step ensures that everyone understands the goals, how their work contributes, and how progress will be measured. Without proper communication, OKRs can become mere documents, failing to ignite the collective drive needed for success.Effective communication of OKRs is a multifaceted process.
It requires a strategic approach that goes beyond simply posting the objectives and key results. Stakeholders need to not only understand
- what* the OKRs are but also
- why* they are important and
- how* they impact their individual roles. This understanding fosters engagement and a shared sense of purpose.
Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication of OKRs involves tailoring the message to the specific audience. A senior executive will receive a different level of detail than a team member. Conciseness and clarity are paramount. Avoid jargon and complex language, prioritizing simple, direct language.
Clear and Concise Communication Examples
Present OKRs in a visual format like a slide deck or a dashboard. Use short, impactful statements. For example, instead of “Increase customer satisfaction scores by 15% within the next quarter,” use “Boost customer satisfaction to 4.5 stars by Q3.” These clear, concise statements ensure everyone understands the objective at a glance.
Regular Progress Updates
Regular progress updates are vital for maintaining momentum and addressing potential roadblocks. Weekly or bi-weekly updates, ideally in short meetings, allow teams to track their progress, discuss challenges, and adjust strategies as needed. This proactive approach keeps everyone informed and allows for timely interventions. For example, if a team is falling behind on a key result, the update allows for identification of the issue and quick action to get back on track.
Transparency and Shared Goals
Transparency is fundamental to building trust and fostering collaboration. Openly sharing progress, both successes and setbacks, promotes a culture of accountability and shared responsibility. This fosters a collaborative environment where everyone feels empowered to contribute and actively participate in achieving the common goals. This transparency ensures that any roadblocks or opportunities are recognized early and addressed promptly.
Fostering a Culture of Accountability
Accountability is a critical component of any successful OKR implementation. Regular reviews, individual check-ins, and public recognition of achievements are crucial. This builds a culture where individuals feel responsible for contributing to the overall success of the team and organization. This ensures everyone is aware of their responsibilities and the impact their work has on achieving the objectives.
Communication Channels for OKR Updates
| Communication Channel | Description | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|
| Team Meetings | Short, focused meetings for progress updates and discussion. | Daily/weekly progress tracking, issue resolution. |
| Email Newsletters | Regular updates summarizing progress and key achievements. | Broader audience updates, less detailed discussions. |
| Project Management Tools | Visual dashboards, progress trackers for real-time visibility. | Tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, assigning tasks. |
| Intranet/Internal Communication Platforms | Centralized hub for announcements, progress reports, and Q&A. | Company-wide updates, announcements, and clarifications. |
| One-on-One Check-ins | Individual discussions for feedback and guidance. | Addressing specific concerns, providing tailored support. |
Case Studies and Examples
OKRs are not just a theoretical framework; they’re a practical tool used by organizations worldwide to achieve ambitious goals. Understanding how successful companies have implemented OKRs provides valuable insights into their application and effectiveness. This section explores real-world examples, highlighting the strategies that led to significant achievements and the lessons learned along the way.Successful OKR implementations often involve a cultural shift within the organization.
Adopting OKRs isn’t just about setting goals; it’s about fostering a culture of accountability, transparency, and continuous improvement. This section examines how OKRs have shaped organizational cultures and fostered a collaborative environment.
Successful OKR Implementation at Google
Google, a pioneer in using OKRs, demonstrates the power of this framework. Their implementation wasn’t without challenges, but they consistently demonstrated how well-defined OKRs can drive significant progress. Google’s approach emphasizes clarity, alignment, and a commitment to measuring progress. Their focus on quantifiable results and iterative adjustments helped them achieve substantial milestones.
Examples of OKRs Leading to Significant Achievements
Numerous companies have seen remarkable success by leveraging OKRs. Consider a software development company aiming to improve user engagement. Their OKR might be:
- Objective: Increase user engagement by 25%.
- Key Result 1: Increase daily active users by 15%.
- Key Result 2: Reduce app abandonment rate by 10%.
- Key Result 3: Achieve a 10% increase in average session duration.
By focusing on measurable metrics and adapting strategies based on progress, the company could potentially achieve its objective and see a significant rise in user engagement. Another example could be an e-commerce company striving to enhance customer satisfaction. Their OKRs could target reducing customer support tickets and increasing positive customer reviews.
Lessons Learned from Successful Implementations
Key elements in successful OKR implementation include:
- Clear Communication: Ensuring everyone understands the objectives and key results is critical. Open dialogue and transparent communication are essential.
- Regular Check-ins: Consistent monitoring of progress is vital for course correction. Regular check-ins help teams adapt strategies and maintain momentum.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The ability to adjust OKRs based on evolving circumstances is crucial. Rigid adherence to initial plans can hinder progress.
- Focus on Measurable Results: OKRs must be quantifiable to track progress effectively. This allows for accurate evaluation of success and areas needing improvement.
These elements are fundamental to achieving meaningful results with OKRs.
Key Takeaways from Successful OKR Applications
- Improved Focus and Alignment: OKRs ensure everyone in the organization is working towards the same objectives.
- Increased Accountability: Clear goals and metrics create accountability for individual and team performance.
- Enhanced Transparency: Regular progress reports foster transparency and open communication within the organization.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Measurable results allow for data-driven decision-making and adjustments based on real-time progress.
Impact on Organizational Culture
OKRs can positively influence organizational culture by:
- Promoting Collaboration: Working towards shared objectives fosters teamwork and collaboration.
- Encouraging Innovation: Setting ambitious goals encourages creative problem-solving and innovative approaches.
- Fostering a Growth Mindset: Regular feedback and progress reviews help teams adapt and learn from their experiences.
The impact of OKRs extends beyond achieving specific goals; it cultivates a dynamic and forward-thinking organizational culture.
Summary of Key Takeaways from Case Studies
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Communication | Clear and frequent communication is crucial for successful implementation. |
| Accountability | OKRs foster a culture of accountability, ensuring individuals and teams are responsible for achieving their goals. |
| Adaptability | Flexibility and adaptability are essential for adjusting to changing circumstances and maintaining progress. |
| Measurability | Quantifiable key results allow for tracking progress and data-driven decision-making. |
| Culture | OKRs can transform organizational culture by promoting collaboration, innovation, and a growth mindset. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) offer a robust system for setting ambitious goals, driving progress, and fostering alignment within teams and organizations. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, equipping readers with the essential knowledge and practical strategies to successfully implement OKRs. By understanding the principles of defining objectives, creating measurable key results, linking them effectively, and continuously measuring progress, you can optimize your performance and achieve remarkable outcomes.
Embrace the power of OKRs to transform your goals into tangible achievements.