Navigating the essentials of payroll management is crucial for any business, big or small. This guide dives deep into the complexities of the payroll process, from understanding compensation types and tax regulations to managing data accurately and ensuring compliance. We’ll explore everything from the initial stages of employee data collection to the final reporting and compliance steps, highlighting key aspects and best practices along the way.
This comprehensive guide provides a practical framework for understanding and implementing efficient payroll procedures, focusing on accuracy, compliance, and automation. Learn how to navigate common challenges and build a strong, reliable payroll system that ensures your business runs smoothly.
Introduction to Payroll Management
Payroll management is the systematic process of calculating, recording, and distributing employee compensation. It encompasses all financial transactions related to employee wages, salaries, deductions, and benefits. A robust payroll system ensures accurate and timely payments, complying with legal regulations and internal policies. This is crucial for maintaining a positive employer-employee relationship and avoiding potential legal issues.Effective payroll management is essential for the smooth operation of any organization.
It fosters employee satisfaction, builds trust, and contributes significantly to financial stability. Accurate and timely payments demonstrate respect for employees’ hard work and dedication. Moreover, compliant payroll practices protect the organization from legal penalties and reputational damage.
Payroll Cycle Stages
The payroll cycle is a series of steps that must be followed in order to process employee compensation. Understanding these stages is crucial for ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
- Employee Time and Attendance Recording: This stage involves accurately recording the hours worked by each employee. Methods can range from manual time sheets to automated timekeeping systems. This data forms the basis for calculating gross pay.
- Payroll Data Input and Calculation: Inputting the recorded hours into the payroll system, along with relevant employee data like pay rates, deductions, and benefits, is critical. The system then calculates gross pay, net pay, and various deductions (taxes, insurance, etc.). Accurate input is paramount for avoiding errors.
- Payroll Processing and Review: This stage involves generating the payroll register and checking for errors. Payroll software often automates this process, reducing manual intervention and minimizing potential mistakes. Thorough review by a payroll specialist is crucial for verifying calculations and ensuring accuracy.
- Payroll Payment and Distribution: This step involves distributing payments to employees, which can be done through direct deposit, checks, or other methods. Ensuring timely payment is essential for maintaining good employee relations. Proper documentation and record-keeping are vital for audit purposes.
- Payroll Reporting and Reconciliation: Generating reports to track payroll data and reconcile the payroll system with other financial records is crucial for identifying potential issues. Payroll reports are used for budgeting, financial analysis, and ensuring compliance with regulations. This process ensures accurate financial records and minimizes the risk of errors.
Roles and Responsibilities in a Payroll Department
A well-structured payroll department plays a vital role in an organization’s financial stability. Understanding the different roles and responsibilities within this department is essential for effective management.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Payroll Administrator | Processing payroll data, calculating employee wages, ensuring compliance with regulations, managing employee records, and preparing payroll reports. |
| Payroll Specialist | Reviewing payroll data, identifying errors, resolving discrepancies, and providing support to employees and managers. |
| Payroll Manager | Supervising the payroll department, managing payroll processes, ensuring compliance, and developing strategies to improve payroll efficiency. |
| Accounting Clerk | Assisting with payroll tasks, processing transactions, maintaining records, and supporting the overall payroll function. |
Understanding Payroll Essentials
Payroll management is crucial for any business, ensuring employees are compensated fairly and accurately. A strong understanding of payroll essentials is vital for both employer and employee. This section delves into the different compensation types, payroll methods, deductions, and regulations, providing a comprehensive overview of the process.
Compensation Types
Various compensation structures exist, each with its own nuances. Understanding these types is essential for accurate payroll calculations.
- Salary: A fixed amount paid periodically, typically monthly or bi-weekly, regardless of the number of hours worked. This is common for salaried employees in managerial or professional roles.
- Hourly: Compensation based on the number of hours worked. This is prevalent for employees in various industries, like retail or construction, where tasks are time-dependent.
- Commission: Pay calculated as a percentage of sales or revenue generated. This structure is prevalent in sales roles, motivating performance-based output.
Payroll Methods
Choosing the right payroll method affects efficiency and accuracy. Both direct deposit and check printing have their own advantages and disadvantages.
- Direct Deposit: A secure and efficient method of transferring funds directly into employee bank accounts. It eliminates the need for physical checks and often reduces processing time.
- Check Printing: A traditional method involving printing paper checks for employee compensation. While it might be less secure and more time-consuming, it’s still a viable option for some businesses.
Payroll Deductions
Payroll deductions encompass various amounts subtracted from an employee’s gross pay. These deductions are crucial for various financial obligations.
Payroll deductions can include taxes, benefits, and other employer- or employee-directed withholdings. These deductions are vital to meet financial obligations, such as tax payments, insurance premiums, and loan repayments.
Common Payroll Deductions
Understanding the common deductions is essential for both employers and employees.
| Deduction Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Federal Income Tax | Tax levied by the federal government. |
| State Income Tax | Tax levied by individual states. |
| Social Security Tax | A mandatory contribution for social security benefits. |
| Medicare Tax | A mandatory contribution for Medicare healthcare benefits. |
| Health Insurance | Employee contributions to healthcare plans. |
| Retirement Contributions | Contributions to retirement accounts (401k, etc.). |
| Union Dues | Payments to labor unions. |
Payroll Tax Regulations
Payroll tax regulations vary based on jurisdiction. Employers must comply with these regulations to avoid penalties.
Federal, state, and local governments have specific regulations concerning payroll taxes. These regulations vary significantly based on factors such as location and employee status. Non-compliance can result in substantial penalties.
Payroll Process for Specific Employee Situations
Different employee situations require tailored payroll processes.
- Part-time Employees: Payroll calculations for part-time employees are adjusted based on their work hours. Calculations are proportionally reduced based on the number of hours worked.
- Overtime Employees: Employees working beyond their regular hours are entitled to overtime pay. Overtime pay is typically calculated at a higher rate than regular pay.
- Employees with Multiple Pay Types: Employees with a combination of salary, hourly, and commission compensation require careful calculation. Each component must be calculated separately and added together for the total compensation.
Managing Payroll Data
Accurate payroll management hinges on meticulous data handling. Incorrect or incomplete data can lead to significant errors, affecting both employees and the organization. This section dives into the crucial aspects of collecting, recording, validating, and securely storing payroll data.Payroll data accuracy is paramount. Errors can result in underpayments, overpayments, legal issues, and damage to employee trust. Robust procedures and systems are essential to ensure the integrity of this critical information.
Collecting and Recording Employee Data
Gathering accurate employee data is fundamental to a smooth payroll process. This includes details like employee names, addresses, tax information, and bank account details. Ensuring this information is up-to-date is vital. Timely updates are crucial to avoid discrepancies and maintain compliance. Regularly checking for changes, like address updates or marital status alterations, is a proactive step.
The collection process should be systematic and standardized, minimizing the potential for human error. Using standardized forms and data entry templates streamlines the process, ensuring accuracy and consistency. Timesheets, crucial for calculating hours worked, should be clear, concise, and easily understood. Pay rates should be meticulously documented, adhering to legal requirements and employee contracts.
Data Accuracy and Integrity
Data accuracy and integrity are the cornerstones of reliable payroll. The impact of inaccurate data extends beyond financial discrepancies. Inaccurate payroll data can lead to legal issues, employee dissatisfaction, and reputational damage. To maintain accuracy, it’s critical to establish robust verification processes. These processes should include cross-referencing employee information against various sources.
The use of internal controls is also essential to limit errors and ensure accountability.
Validating Employee Information and Ensuring Compliance
Validating employee information is essential for ensuring compliance with tax regulations and labor laws. This process should involve cross-referencing employee details against government databases and relevant records. For example, verifying employee social security numbers and tax withholdings against official government records is crucial. Employing automated systems can streamline this process and enhance accuracy. Maintaining a detailed audit trail of all data modifications is also critical.
This allows for easy tracking and resolution of any discrepancies.
Common Payroll Data Entry Errors
| Error Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Time Entry | Inaccurate recording of hours worked. | Recording 8 hours when only 7 were worked. |
| Incorrect Pay Rate | Using the wrong pay rate for an employee. | Using a new pay rate without updating the system. |
| Missing Deductions | Failing to include required deductions. | Forgetting to include health insurance premiums. |
| Data Entry Errors | Typographical or numerical mistakes. | Typing “1200” instead of “120”. |
| Missing or Inaccurate Tax Information | Using outdated or incorrect tax withholding information. | Using previous year’s tax rate instead of the current one. |
These errors can lead to significant problems, including penalties and legal issues. Thorough review procedures are crucial to minimizing these errors.
Secure Data Storage and Handling
Secure data storage and handling are paramount for protecting sensitive employee information. Employing encrypted storage methods, access controls, and data backups are crucial for maintaining confidentiality. Restricting access to payroll data to authorized personnel is critical. Regular security audits help identify vulnerabilities and maintain a robust security posture.
Payroll Management Systems and Tools
Payroll management software and spreadsheet tools are available to streamline the process. Software solutions offer automation, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency. Spreadsheets can be used for simpler tasks, but the potential for errors is higher. Choosing the right tool depends on the organization’s size, complexity, and budget. Consider factors such as scalability, integration with existing systems, and reporting capabilities.
Some software solutions can automate tasks like data entry and calculation, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving overall efficiency.
Calculating and Processing Payroll
Payroll processing is a critical aspect of any business, ensuring employees are paid accurately and on time. This crucial function demands meticulous attention to detail, adherence to legal regulations, and a robust system for error prevention. Effective payroll management not only avoids financial penalties but also fosters a positive work environment by maintaining trust and transparency with employees.Calculating employee wages and deductions accurately is the cornerstone of a smooth payroll process.
This involves a clear understanding of the various factors impacting an employee’s pay, including their hourly rate, overtime rules, and applicable taxes and deductions. Proper payroll processing requires meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of relevant regulations.
Calculating Employee Wages
Understanding the basis for calculating wages is essential. Wages are typically calculated by multiplying the employee’s hourly rate by the number of hours worked. However, various factors can influence the final calculation, such as overtime pay, special payments, and deductions.
- Regular Pay: Calculate regular pay by multiplying the employee’s hourly rate by the number of regular hours worked. For example, if an employee’s hourly rate is $15 and they worked 40 hours, their regular pay would be $600 (15
– 40). - Overtime Pay: Calculate overtime pay by multiplying the employee’s overtime rate (typically 1.5 times the regular hourly rate) by the number of overtime hours worked. For instance, if an employee works 45 hours and their regular rate is $15, their overtime pay for 5 hours of overtime would be $112.50 (7.5
– 15). - Special Payments: Special payments, such as bonuses or commissions, are calculated based on predetermined formulas or agreements. These payments are typically added to the employee’s regular pay. For example, a sales associate earning a 5% commission on sales of $2000 would receive a commission of $100 (2000
– 0.05).
Applying Tax Regulations
Accurate tax withholding is crucial. Failure to comply with tax regulations can lead to significant penalties and legal issues.
- Federal and State Taxes: Federal and state income tax withholdings are based on the employee’s tax bracket and allowances claimed on their W-4 form. Federal and state tax rates are determined by the governing tax authorities. These rates are often published annually. Payroll software usually handles the calculations automatically.
- Social Security and Medicare Taxes: Both federal social security and Medicare taxes are calculated as percentages of the employee’s earnings. These rates are set by the government and applied to gross pay, up to certain thresholds.
- Other Deductions: Deductions for health insurance, retirement contributions, and other benefits are handled similarly to tax calculations. The calculations depend on the terms and conditions of the benefit programs.
Verifying Payroll Calculations
Verifying calculations is a critical step to avoid errors.
- Reviewing Calculations: Carefully review each step in the payroll calculation, checking for mathematical errors, particularly in overtime calculations and special payments. Double-checking for any discrepancies is vital.
- Reconciliation: Reconcile payroll calculations with employee time records, payroll reports, and relevant tax forms to ensure accuracy. This helps to prevent costly errors.
- Internal Controls: Implement strong internal controls, such as segregation of duties and independent verification, to reduce the risk of errors and fraud. This ensures that one person is not solely responsible for the entire payroll process.
Adhering to Legal and Regulatory Standards
Compliance with payroll laws and regulations is paramount.
- Legal Requirements: Payroll processing must adhere to all federal, state, and local laws concerning wages, taxes, and deductions. These laws and regulations are frequently updated, so staying informed is vital. Failure to comply with these standards can lead to penalties.
- Regulations: Understanding and complying with regulations on overtime pay, minimum wage, and other employment laws is crucial. Regulations are available on government websites and through legal counsel.
Error Checking and Correction
Error checking and correction procedures are essential to maintain accuracy.
- Data Entry Checks: Implement data entry checks and validation rules to catch potential errors during the initial data entry process. This helps to prevent mistakes from propagating later in the process.
- Payroll Software Checks: Payroll software often includes error-checking features to flag potential issues. Use these features effectively. Payroll software is an invaluable tool for automating calculations and reducing manual errors.
- Review and Correction Procedures: Establish clear procedures for reviewing and correcting payroll errors. This ensures that mistakes are identified and corrected quickly and efficiently.
Payroll Reporting and Compliance
Payroll reporting and compliance are crucial aspects of running a smooth and legally sound business. Accurate and timely reporting ensures your business remains in good standing with tax authorities and protects you from potential penalties. This section delves into the various types of payroll reports, legal requirements, and procedures for filing essential tax forms, emphasizing the importance of regulatory compliance.
Payroll Report Types
Payroll reports provide a comprehensive overview of payroll activities, enabling businesses to track employee earnings, deductions, and taxes. Different reports cater to specific needs. Employee pay stubs are crucial for individual employee records, while summary reports offer a high-level view of the entire payroll process.
- Employee Pay Stubs: These detailed documents Artikel each employee’s earnings, deductions (taxes, insurance, etc.), and net pay for a specific pay period. They serve as an essential record for employees to verify their compensation and ensure accuracy.
- Summary Reports: These reports offer a concise overview of the entire payroll process. They encompass data such as total payroll expenses, deductions, and taxes for the period. These reports are invaluable for management in monitoring payroll costs and identifying potential discrepancies.
Legal Requirements for Payroll Records
Maintaining accurate and complete payroll records is a legal obligation. Regulations vary by jurisdiction, but generally, employers must retain records for a specified period, typically several years. These records are crucial for audits and ensuring compliance with tax laws.
- Record Retention: Payroll records must be kept for a legally mandated period, typically varying between three to seven years, depending on the jurisdiction and specific requirements. This period allows for audits and ensures compliance with tax laws.
- Accuracy and Completeness: Payroll records must be accurate and complete, reflecting all earnings, deductions, and taxes for each employee. Inaccuracies can lead to significant issues and potential penalties.
Filing and Submitting Tax Forms
Accurate and timely filing of tax forms is vital for compliance. Different forms, such as W-2 and 1099, are used for reporting employee compensation and payments to independent contractors.
- W-2 Forms: These forms are used to report wages paid to employees throughout the year. Failure to file these forms accurately and on time can result in significant penalties and legal ramifications.
- 1099 Forms: These forms are used to report payments made to independent contractors or freelancers. Proper completion and timely filing are essential for compliance.
Meeting Regulatory Deadlines and Compliance
Meeting regulatory deadlines is critical to avoid penalties and maintain compliance. Understanding the specific deadlines for your jurisdiction is crucial for timely submission of payroll taxes and other required forms.
Payroll Compliance Documents
The following table Artikels the essential documents required for payroll compliance. Remember to consult local regulations for specific requirements.
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| Employee W-4 Form | Employee’s withholding allowance information. |
| Employee Time Sheets | Accurate record of employee hours worked. |
| Payroll Records | Detailed record of all earnings, deductions, and net pay. |
| Tax Forms (W-2, 1099) | Forms used for reporting wages and payments. |
| Bank Account Information | Details for direct deposit of employee pay. |
Payroll Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Payroll-related risks can include errors, non-compliance, and fraud. Implementing best practices can help mitigate these risks.
- Accuracy Errors: Errors in calculations or data entry can lead to incorrect payments and tax filings. Employing payroll software and double-checking calculations can minimize these risks.
- Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with tax regulations can result in penalties and legal issues. Staying informed about and adhering to all relevant regulations is essential.
- Fraud: Payroll fraud can occur in various ways. Robust security measures and thorough verification processes can help prevent such risks. Implementing strict access controls and regular audits can reduce the likelihood of fraudulent activities.
Automation and Technology in Payroll
Payroll, once a cumbersome and time-consuming task, is now significantly streamlined by automation and technology. Modern payroll systems leverage software and APIs to handle calculations, data entry, and compliance, freeing up human resources for more strategic tasks. This shift towards digital solutions also allows for greater accuracy, reduced errors, and enhanced efficiency.Payroll automation tools not only speed up the process but also contribute to improved accuracy and compliance, reducing the risk of costly errors.
This technological advancement benefits businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large corporations.
The Role of Automation in Streamlining Payroll
Automation in payroll significantly reduces manual intervention, eliminating errors prone to human oversight. This is achieved through software-driven calculations, data validation, and automated report generation. Automating routine tasks such as data entry and calculation not only increases efficiency but also minimizes the potential for human error, leading to more accurate and timely payroll processing.
Figuring out payroll can be tricky, but understanding the essentials is key. Navigating those complexities often feels like walking a tightrope, especially when considering historical events like the Honan affair and the clouds dark lining that have shaped our understanding of financial accountability. The Honan affair and the clouds dark lining serve as a reminder of the importance of meticulous record-keeping and transparent processes.
Ultimately, mastering payroll management is crucial for any business to thrive.
Different Payroll Software Solutions and Their Features
Various payroll software solutions cater to different business needs and sizes. These solutions offer a range of features, from basic payroll processing to more advanced functionalities like benefits administration, tax calculations, and reporting. Essential features often include employee self-service portals, allowing employees to access pay stubs, make adjustments, and submit requests. Integrated time and attendance tracking is also a key feature, connecting seamlessly with payroll calculation for accuracy.
Comparison of Payroll Software Options for Various Business Sizes
Small businesses often benefit from user-friendly, affordable software with basic payroll features, while larger enterprises require more comprehensive systems capable of handling complex compensation structures and large employee populations. Mid-sized businesses need software that offers a balance between affordability and advanced functionalities. Some software providers offer tiered pricing plans to accommodate different business sizes and their varying payroll needs.
Payroll APIs and Their Use in Integration
Payroll APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) enable seamless data exchange between payroll software and other systems. This integration facilitates a smooth flow of information, such as employee data and time-tracking records, streamlining the entire process. Using APIs for integration with other HR systems eliminates redundant data entry and ensures data consistency across different platforms. For instance, an HR system can directly update employee records, which are then automatically reflected in the payroll system.
Benefits of Cloud-Based Payroll Systems
Cloud-based payroll systems offer numerous advantages, including accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. This feature allows for remote work and flexibility, enhancing employee satisfaction and improving business continuity. Cloud-based systems also typically offer automatic updates, ensuring compliance with changing regulations. These systems usually offer better data security and scalability than on-premise systems.
Steps for Integrating Payroll Systems with Other HR Systems
Integration of payroll systems with other HR systems often requires careful planning and execution. This involves identifying the necessary data points, ensuring compatibility between systems, and establishing clear data transfer protocols. This integration is essential for streamlined HR management, accurate data sharing, and improved efficiency. Companies should also carefully assess security protocols to protect sensitive employee data.
Testing and quality control are crucial to ensure the integrity and accuracy of data transfer.
Troubleshooting and Problem Solving: Navigating The Essentials Of Payroll Management

Payroll management, while crucial, is prone to errors. A well-structured troubleshooting process is essential for identifying, resolving, and preventing these issues. This section delves into the intricacies of identifying potential problems, resolving common issues, handling employee inquiries, and ultimately, preventing future problems.Payroll errors can stem from various sources, including data entry mistakes, calculation discrepancies, or compliance violations. These errors can lead to financial repercussions for both the employer and the employee.
A proactive approach to troubleshooting and problem-solving is paramount for minimizing the impact of such errors and maintaining a smooth payroll process.
Navigating the essentials of payroll management can feel overwhelming, especially when dealing with large numbers of employees. But as you delve into the intricacies, remember that with great amounts of data comes great responsibility, especially when it comes to payroll. Accuracy and meticulous attention to detail are paramount in ensuring fair and timely compensation for everyone.
Thorough record-keeping and adherence to regulations are key to smooth and successful payroll management.
Identifying Potential Payroll Errors
Payroll errors can arise from numerous sources, and recognizing the potential causes is crucial for effective problem-solving. Mistakes in data entry, such as incorrect hours worked or salary information, are a frequent cause. Misapplication of payroll rules or regulations, like overlooking overtime or statutory deductions, can also lead to inaccuracies. Software glitches or system malfunctions can also introduce errors.
In some cases, a lack of clear communication between the employee and the payroll department may contribute to problems.
Resolving Common Payroll Issues
A structured approach to resolving common payroll issues is essential. Firstly, carefully review the payroll records to identify the source of the error. If the error stems from data entry, double-check the data source and make the necessary corrections. If the error involves a misapplication of rules or regulations, consult the relevant policies and procedures to ensure accuracy.
Figuring out payroll can be a real headache, but understanding the essentials is key. It’s all about getting the calculations right and meeting deadlines, which can feel like a full-time job in itself. Thinking about how much time and effort goes into creating compelling online content, like in how much would you pay for that online news story , is a good way to realize the complexity behind the scenes of seemingly simple tasks.
Ultimately, mastering payroll management boils down to precision and organization.
If the error is related to a software glitch, contact the software provider for assistance or a work-around. Communication with the employee involved is vital throughout the process.
Handling Employee Inquiries About Their Pay
Prompt and professional handling of employee inquiries is critical. Establish clear communication channels for employees to report concerns. Provide detailed explanations regarding their pay stubs, including calculations, deductions, and any discrepancies. A well-defined process for addressing employee inquiries will prevent frustration and maintain a positive employer-employee relationship.
Common Payroll Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Net Pay | Incorrect hours entered, incorrect rate, missing deductions | Verify time and rate, review deduction codes, double-check all inputs |
| Missing Paychecks | System error, incomplete submission of required information, or late payment processing | Check the payroll system for errors, confirm submission of all necessary data, expedite payment processing |
| Incorrect Tax Deductions | Inaccurate tax information, misapplied tax rates, or incorrect tax year | Review employee tax forms, verify tax rates, and ensure correct tax year is used |
| Late Paychecks | Delayed submission of timesheets, system errors, or administrative issues | Establish a consistent timeline for submission and processing, check the payroll system for delays, and communicate with the affected employees. |
Preventing Payroll Errors
Implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce payroll errors. Establish clear procedures for data entry and validation. Regularly review and update payroll policies and procedures to align with any changes in legislation or company practices. Use payroll software with robust error-checking features. Provide comprehensive training to payroll staff on all aspects of payroll management, including compliance requirements.
Handling Payroll Disputes Effectively, Navigating the essentials of payroll management
Handling payroll disputes requires a fair and impartial approach. Actively listen to the employee’s concerns and gather all relevant information. Thoroughly investigate the dispute to determine the cause of the issue. Offer solutions that address the employee’s concerns while upholding company policies and regulations. Document all steps taken in resolving the dispute for future reference.
If necessary, seek advice from legal counsel to ensure compliance. Mediation or arbitration may be appropriate to reach a mutually agreeable resolution.
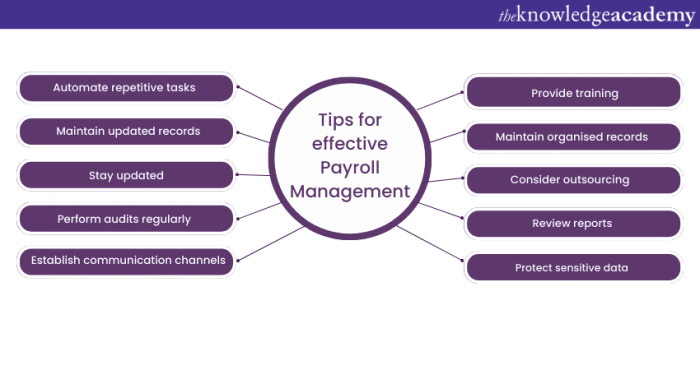
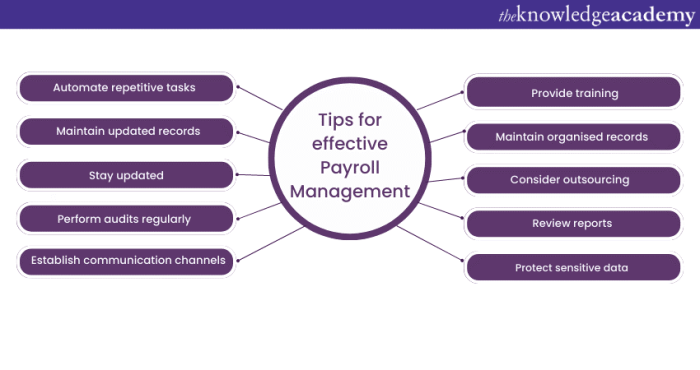
Best Practices for Payroll Management
Payroll management is a critical function for any organization. Effective practices ensure accurate and timely payments, maintain compliance, and foster a positive employee experience. Strong payroll procedures are essential for minimizing errors, reducing risk, and ultimately contributing to the smooth operation of the business.
Maintaining Data Security in Payroll Management
Robust security measures are paramount in payroll management. Protecting sensitive employee data, such as social security numbers and bank account information, is a top priority. This involves implementing strict access controls, regularly updating security protocols, and employing encryption techniques to safeguard data.
- Strong Access Controls: Restrict access to payroll data to authorized personnel only. Implement multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security. Regularly review and update access privileges to ensure only necessary individuals have access to sensitive information. Consider using role-based access control (RBAC) to tailor access to specific roles and responsibilities.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of existing security measures. These audits should cover all aspects of the payroll process, from data entry to transmission and storage.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive payroll data both in transit and at rest. Use strong encryption algorithms to protect data from unauthorized access, even if a system is compromised.
Optimizing the Payroll Process for Efficiency and Accuracy
Streamlining the payroll process is key to achieving efficiency and accuracy. Automation plays a significant role in reducing manual errors and saving time. Utilizing payroll software, for example, can significantly improve accuracy and speed up the entire process.
- Automation: Implement automated processes wherever possible, such as automated data entry, calculations, and reporting. This minimizes manual intervention, which reduces the chance of human error and speeds up processing time. This includes automating the verification of employee information and the deduction of taxes and other withholdings.
- Data Validation: Implement data validation checks at every stage of the payroll process. This ensures that data entered is accurate and consistent, preventing errors from propagating through the system. This includes verifying that employee hours are within acceptable ranges and that deductions are correctly applied.
- Regular Testing: Conduct regular testing of the payroll system and procedures to identify potential issues before they impact employees or the business. Testing should include simulating various scenarios, including unusual situations like large volume processing, to ensure that the system can handle such circumstances.
Improving Communication with Employees Regarding Their Pay
Transparent communication regarding employee pay is essential for building trust and maintaining a positive work environment. Providing clear and concise information about paychecks, deductions, and any changes is crucial.
- Clear Pay Stubs: Provide clear and understandable pay stubs that clearly Artikel all earnings, deductions, and net pay. Ensure all information is easily readable and accurately reflects the employee’s pay. Pay stubs should also include explanations of any unusual deductions or changes in withholding.
- Dedicated Communication Channels: Establish a dedicated communication channel, such as an email address or an online portal, for addressing employee questions and concerns regarding their pay. Make sure this channel is easily accessible and responsive.
- Regular Paycheck Distribution: Establish a consistent schedule for distributing paychecks, and adhere to it as much as possible. This helps employees plan their finances and reduces any anxiety associated with delayed payments.
Importance of Internal Controls in Payroll
Internal controls are critical in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and security of payroll data. They help prevent errors, fraud, and non-compliance. Effective internal controls should be implemented at all stages of the payroll process.
- Separation of Duties: Implement a system where different individuals are responsible for different aspects of the payroll process, such as data entry, calculations, and approval. This reduces the risk of errors and fraud by ensuring no single person has complete control over the entire process.
- Reconciliation Procedures: Implement procedures for reconciling payroll data with other related records, such as timekeeping and accounting records. This ensures accuracy and helps identify discrepancies early on.
- Independent Verification: Establish procedures for independent verification of payroll data and calculations to ensure accuracy and minimize errors. A second set of eyes can spot issues that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Policies and Procedures for Effective Payroll Management
Well-defined policies and procedures are essential for a smooth and efficient payroll process. These should be documented, communicated, and consistently followed.
- Documented Procedures: Develop detailed written procedures for each step of the payroll process, including data entry, calculations, reporting, and compliance. These procedures should be easily accessible to all relevant personnel.
- Employee Handbook Inclusion: Include payroll policies and procedures in the employee handbook to ensure employees are aware of their responsibilities and rights regarding payroll. Clearly Artikel the process for reporting errors or discrepancies.
- Compliance Standards: Ensure all payroll policies and procedures comply with all applicable local, state, and federal regulations. Staying updated on changes in legislation is critical to maintaining compliance.
Building a Strong Internal Payroll Team
A strong payroll team is crucial for a successful payroll process. Investing in skilled personnel and providing appropriate training are essential.
- Skilled Personnel: Recruit and hire individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage the payroll process effectively. Consider hiring individuals with experience in payroll software, accounting principles, and compliance regulations.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training to all payroll personnel on company policies, procedures, and relevant regulations. Regular training updates on changes in laws and software advancements are important.
- Teamwork and Communication: Foster a culture of teamwork and communication within the payroll team. Encourage open communication and collaboration to improve efficiency and problem-solving.
Epilogue
In conclusion, mastering payroll management involves a multi-faceted approach that encompasses data accuracy, compliance, and automation. By understanding the fundamentals and implementing best practices, businesses can streamline their payroll processes, reduce errors, and foster a positive employee experience. This guide offers a practical roadmap for successfully navigating the essentials of payroll management, empowering you to build a robust and reliable system that supports your business’s growth.

