Mental health at work is no longer a side issue; it’s a core component of a thriving workplace. This comprehensive guide delves into the crucial aspects of fostering a supportive environment where employees can thrive both professionally and personally. We’ll explore the definition of mental health in the workplace, the factors impacting it, strategies for recognizing and responding to issues, and actionable steps for promoting overall well-being.
From understanding the difference between mental health and illness to implementing effective support systems, we’ll cover a spectrum of critical elements. We’ll also examine successful case studies, discuss the importance of a supportive workplace culture, and address the crucial issue of reducing the stigma surrounding mental health. This is more than just a topic; it’s a necessary conversation for every organization.
Defining Mental Health at Work
Mental health in the workplace is more than just the absence of mental illness. It’s a crucial component of overall employee well-being, directly impacting productivity, engagement, and job satisfaction. A positive work environment fosters a sense of safety, belonging, and purpose, which in turn nurtures strong mental health. This article explores the multifaceted nature of mental health at work, differentiating it from mental illness and outlining key elements for a healthy work environment.A healthy work environment is not simply the lack of stress or negativity.
It encompasses a wide range of factors, including supportive leadership, fair policies, meaningful work, and opportunities for growth and development. Recognizing and addressing mental health concerns is a critical aspect of fostering a positive and productive work culture.
Defining Mental Health in the Workplace
Mental health in the workplace refers to the cognitive, emotional, and social well-being of employees. It encompasses their ability to cope with stress, adapt to change, and maintain healthy relationships with colleagues and supervisors. A strong sense of purpose and fulfillment in work is also a key component of positive mental health. It is not solely the absence of mental illness, but rather a state of flourishing and resilience in the professional context.
Talking about mental health at work is crucial, but sometimes it feels like a tiny whisper in a noisy world. Think about how much distraction we face daily, like the constant buzzing of notifications and the relentless demands of our jobs. Recent developments in tech, like Lightsquared fiddles with dial to cut GPS static here , highlight how even seemingly minor tech tweaks can significantly impact our environment.
Ultimately, fostering a supportive and less disruptive work environment is key to better mental well-being.
Key Elements of a Healthy Work Environment
A healthy work environment is built on several interconnected elements. These elements contribute significantly to the mental well-being of employees.
- Supportive Leadership: Leaders who prioritize employee well-being, foster open communication, and actively listen to concerns create a sense of trust and psychological safety. This allows employees to feel comfortable seeking help when needed without fear of judgment or reprisal.
- Fair Policies and Procedures: Clear, consistent, and fair policies regarding work expectations, compensation, and promotions reduce ambiguity and stress. This clarity fosters a sense of justice and fairness within the organization, reducing anxiety and promoting a positive work atmosphere.
- Meaningful Work: Work that is challenging yet achievable, provides a sense of purpose, and allows for autonomy and responsibility is more likely to contribute to positive mental health. Employees who feel their work matters are more likely to be engaged and satisfied.
- Opportunities for Growth and Development: Providing opportunities for professional development, training, and advancement demonstrates a commitment to employee growth and recognizes the value of their contributions. This fosters a sense of investment and encouragement, which is beneficial for mental well-being.
- Work-Life Balance: Organizations that prioritize work-life balance by offering flexible schedules, time off policies, and encouraging employees to disconnect after work hours contribute to overall well-being. This allows employees to recharge and manage stress more effectively.
Mental Health vs. Mental Illness
Distinguishing between mental health and mental illness is crucial in the workplace. Mental health encompasses a spectrum of emotional and psychological well-being, while mental illness represents diagnosable conditions that require professional intervention. Mental health challenges can be addressed through supportive strategies, while mental illnesses necessitate appropriate treatment and support.
Comparison of Mental Health in the Workplace and Personal Mental Health
While intertwined, mental health at work and personal mental health are distinct concepts. Workplace mental health focuses on the employee’s experience within the professional environment, considering factors like work-related stress, interpersonal relationships, and organizational culture. Personal mental health encompasses a broader range of factors impacting overall well-being, including relationships, personal interests, and physical health.
Framework for Understanding Mental Well-being at Work
A framework for understanding mental well-being at work should consider the interaction between individual factors, organizational factors, and environmental factors. This framework would enable a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing mental well-being in the workplace. A model could include individual resilience, coping mechanisms, and stress management strategies, as well as organizational support systems, policies, and culture.
Factors Impacting Mental Health
Navigating the modern workplace can be challenging, and understanding the factors that contribute to employee well-being is crucial for fostering a healthy and productive environment. Many elements, both internal and external to the organization, can significantly impact an employee’s mental health. This exploration delves into the key factors that often negatively affect mental well-being in the workplace.These factors, ranging from the pressures of the job itself to the social dynamics of the team, can have a profound impact on employee morale and overall mental health.
Addressing these factors head-on is a critical step toward creating a supportive and thriving work environment.
Work-Related Stress
Work-related stress stems from various sources, including heavy workloads, demanding deadlines, and difficult interpersonal interactions. This stress can manifest in a range of negative outcomes, including anxiety, burnout, and depression. Understanding the specific stressors faced by employees is vital to implementing effective interventions.
Workload
Excessive workloads, often coupled with unrealistic deadlines, can significantly impact mental health. Employees feeling overwhelmed by the demands of their job are more susceptible to stress and burnout. For instance, a software developer facing constant pressure to meet tight deadlines, coupled with a high volume of bugs and feature requests, can experience chronic stress. This can lead to reduced productivity, decreased job satisfaction, and ultimately, compromised mental health.
Unrealistic Deadlines, Mental health at work
Unrealistic deadlines are frequently cited as a key source of stress in the workplace. These deadlines, often imposed without consideration for the complexity of tasks or available resources, can lead to feelings of inadequacy and pressure. For example, a marketing team tasked with launching a new product campaign within a ridiculously short timeframe, with limited resources, may experience significant stress and anxiety, potentially compromising the quality of their work and their mental well-being.
Workplace Relationships and Team Dynamics
Positive relationships and effective team dynamics are crucial for a healthy work environment. Negative interactions, conflict, or lack of support can significantly impact employee well-being.
- Toxic Work Environments: A toxic work environment, characterized by bullying, harassment, or a lack of respect, can lead to severe mental health issues for employees. The constant negativity and pressure can negatively affect their mental and emotional state, and it can be difficult to overcome.
- Lack of Support: A lack of support from colleagues and supervisors can exacerbate stress and lead to feelings of isolation.
When employees feel unsupported or unheard, they may experience increased levels of anxiety and depression.
- Poor Communication: Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings, conflicts, and a lack of clarity, ultimately affecting the mental health of team members. This can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and ultimately reduced productivity.
Organizational Culture and Leadership Styles
Organizational culture and leadership styles play a significant role in shaping employee experiences and mental health.
- Supportive Cultures: A supportive culture fosters a sense of belonging and trust among employees, which can buffer against stress and promote mental well-being. This culture encourages open communication and recognizes the importance of employee well-being.
- Micromanagement: Micromanagement can create a sense of distrust and anxiety, undermining employee autonomy and potentially impacting mental health.
- Lack of Recognition: A lack of recognition for hard work can lead to feelings of de-motivation and dissatisfaction, affecting employees’ mental health.
- Leadership Styles: Leadership styles significantly impact the overall work environment and employee experiences. Transformational leadership, for instance, promotes employee growth and motivation, contributing to a positive impact on mental health. Conversely, autocratic leadership styles, lacking empathy and employee input, can lead to increased stress and dissatisfaction.
Work-Life Balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is essential for overall well-being. The inability to separate work from personal life can lead to burnout, stress, and decreased mental health.
- Burnout: Burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged or excessive stress. Employees who consistently work long hours without adequate time for rest and relaxation are more prone to burnout.
- Impact of Work-Life Imbalance: A poor work-life balance can manifest in a myriad of ways, including sleep disturbances, relationship problems, and decreased overall quality of life.
- Promoting Work-Life Balance: Organizations can implement strategies to promote work-life balance, such as flexible work arrangements, generous vacation time, and wellness programs. This proactive approach can significantly improve employee well-being.
Recognizing and Responding to Mental Health Issues
Navigating the complexities of mental health in the workplace requires a proactive and compassionate approach. Recognizing the signs of distress and implementing supportive strategies are crucial for fostering a healthy and productive work environment. Understanding the indicators of potential mental health concerns and how to respond effectively can significantly improve employee well-being and organizational success.Addressing mental health issues in the workplace is not just a ‘nice-to-have’ but a fundamental aspect of creating a supportive and thriving work culture.
By recognizing the warning signs and implementing a robust response plan, employers can create an environment where employees feel safe to seek help and support when needed. This, in turn, contributes to higher employee engagement, reduced absenteeism, and enhanced overall productivity.
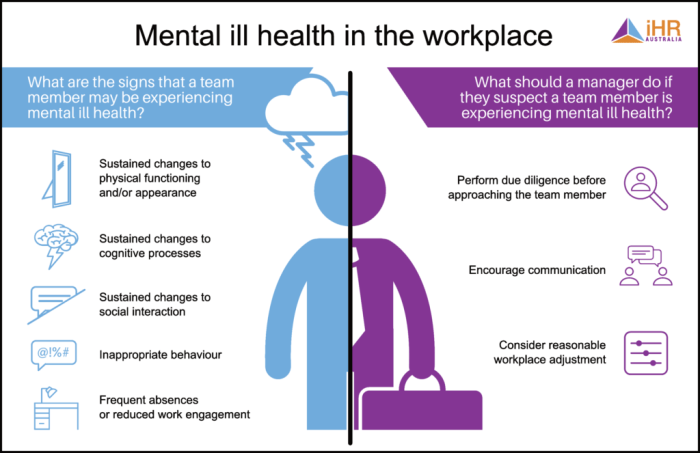
Signs and Symptoms of Potential Mental Health Concerns
Recognizing the subtle and sometimes overt signs of mental health concerns is essential for early intervention. These signs can manifest in various ways, impacting an individual’s behavior, mood, and overall well-being.
- Changes in mood, such as persistent sadness, irritability, or anxiety.
- Significant changes in sleep patterns, including insomnia or excessive sleeping.
- Decreased interest or enjoyment in previously enjoyed activities.
- Withdrawal from social interactions or isolation.
- Changes in appetite or eating habits.
- Difficulties concentrating or remembering things.
- Physical complaints such as headaches, stomach aches, or fatigue, that persist or worsen over time.
- Increased levels of stress, frustration, or anger.
- Displays of erratic or disruptive behavior.
- Substance abuse or misuse.
Importance of Early Intervention and Support Systems
Early intervention in cases of mental health concerns is critical. Prompt support can prevent escalating problems and facilitate a more effective recovery. Implementing robust support systems allows employees to access the resources they need to address their mental health challenges.
- Early intervention reduces the likelihood of worsening symptoms and promotes faster recovery.
- Support systems provide employees with a safe space to discuss their concerns and receive guidance.
- Addressing issues promptly can prevent the development of long-term mental health problems.
- Support systems foster a sense of community and belonging, promoting employee well-being.
Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication is key when addressing mental health concerns. Open and empathetic communication creates a supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable sharing their struggles.
- Active listening is crucial. Pay close attention to verbal and nonverbal cues, and acknowledge the employee’s feelings.
- Use empathetic language and avoid judgmental statements.
- Focus on understanding the situation from the employee’s perspective.
- Provide encouragement and support without offering unsolicited advice.
- If appropriate, offer suggestions for resources, such as employee assistance programs (EAPs) or mental health professionals.
Confidentiality and Reporting Process
Maintaining confidentiality is paramount when handling mental health concerns. A clear reporting process that prioritizes privacy and support is essential.
- Establish a confidential reporting mechanism, such as a designated employee assistance program (EAP) or a designated mental health professional.
- Ensure the confidentiality of any reported information, following all relevant legal and ethical guidelines.
- Develop a protocol for reporting and investigating concerns to ensure that employees feel safe and supported.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Understanding the legal and ethical considerations surrounding mental health support in the workplace is crucial. Navigating these aspects with sensitivity and compliance is vital.
Feeling stressed at work? Sometimes, a quick mental escape can help. Just like the exhilarating speed and electric power of Tesla’s Model X, teslas model x the fast and the electric provides a thrilling experience. But, we shouldn’t let the need for quick breaks overshadow the importance of a healthy work environment.
Finding a good balance between fast-paced work and mindful mental well-being is crucial.
- Compliance with relevant laws and regulations concerning employee privacy and confidentiality is essential.
- Ethical considerations include maintaining professional boundaries and avoiding judgment.
- Providing support in a non-discriminatory manner is paramount.
Promoting Mental Well-being in the Workplace

Cultivating a supportive and inclusive work environment is crucial for employee well-being. A healthy work culture acknowledges the importance of mental health and provides the necessary resources for employees to thrive. This goes beyond simply providing benefits; it involves creating a sense of belonging and fostering open communication about mental health challenges.Creating a psychologically safe space for employees to discuss their mental health is paramount to successful mental health promotion.
This involves a culture of empathy and understanding, where employees feel comfortable seeking help without fear of judgment or repercussions.
Practical Strategies for Fostering a Supportive Work Environment
A supportive work environment fosters a sense of belonging and trust, where employees feel comfortable expressing their needs and seeking help when necessary. Creating a supportive atmosphere is crucial to preventing mental health issues from escalating and encouraging open communication. Implementing these strategies can significantly impact employee well-being.
- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Open communication is vital. Implement regular check-ins, team meetings, and feedback mechanisms to foster dialogue about mental health concerns. Encourage peer-to-peer support and create opportunities for employees to connect with one another. Consider anonymous feedback mechanisms to address sensitive topics.
- Promote Work-Life Balance: Encourage employees to prioritize their well-being outside of work. Offer flexible work arrangements, generous vacation policies, and access to resources for stress management and relaxation techniques. Promoting healthy boundaries between work and personal life reduces stress and burnout.
- Cultivate a Culture of Empathy and Understanding: Encourage managers and supervisors to be mindful of the impact of their actions and communication on employees. Training programs on emotional intelligence and active listening skills can foster a more supportive and understanding environment. Actively address instances of bullying or harassment promptly and decisively.
- Recognize and Reward Employee Contributions: Acknowledging and appreciating employees’ efforts is crucial for boosting morale and reducing stress. Regular feedback, positive reinforcement, and opportunities for growth and advancement contribute to a sense of purpose and accomplishment. Recognizing achievements can also reduce the perception of being undervalued.
Incorporating Mental Health Resources and Support Programs
Integrating mental health resources into the company culture is crucial for creating a supportive environment. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to employee well-being and fosters a culture of openness.
- Integrate Mental Health Resources into Company Culture: Make mental health resources readily accessible and visible. Provide clear information about available support services, such as Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) and counseling options. Display brochures and posters in common areas, ensuring easy access to information.
- Offer Comprehensive Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): EAPs provide confidential counseling and support services for employees facing personal or work-related challenges. They offer access to mental health professionals, stress management workshops, and other resources. Highlighting the confidential nature of these programs is crucial for encouraging employees to utilize them.
- Offer a Variety of Support Programs: Provide a range of mental health support options to cater to diverse needs. This could include workshops on stress management, mindfulness, or time management, and access to online resources and self-help tools.
- Promote Open Communication and Transparency: Address the topic of mental health openly and transparently. Share success stories of employees who have utilized the support programs to demonstrate the value and efficacy of the resources.
Workshops and Training Sessions on Mental Well-being
Educational initiatives play a critical role in fostering a culture of mental well-being. Workshops and training sessions provide valuable tools and knowledge to employees for managing stress and improving their overall well-being.
- Offer Workshops and Training Sessions: Organize workshops and training sessions on stress management, mindfulness, time management, and other relevant topics. Incorporate interactive exercises and practical strategies that employees can immediately apply in their daily routines.
- Develop Mental Health Awareness Campaigns: Create initiatives to raise awareness about mental health and reduce the stigma surrounding it. Collaborate with external experts and mental health organizations to deliver informative sessions.
- Promote Self-Care Practices: Encourage employees to prioritize self-care activities such as exercise, healthy eating, and sufficient sleep. Provide resources on relaxation techniques, stress reduction methods, and creating healthy routines.
Flexible Work Arrangements and Their Impact on Mental Well-being
Flexible work arrangements can significantly improve employee well-being by reducing stress and promoting a healthier work-life balance. Implementing these arrangements thoughtfully can lead to increased productivity and job satisfaction.
- Implement Flexible Work Arrangements: Offer flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options, flexible hours, or compressed workweeks. These arrangements allow employees to better manage their personal responsibilities and reduce commuting time, contributing to overall well-being.
- Consider Individual Needs: Tailor flexible work arrangements to meet the specific needs of individual employees. For example, some employees may benefit from flexible start times, while others may prefer a completely remote work option. Ensure the arrangements align with the company’s operational needs.
Measuring and Monitoring Mental Health Initiatives
Tracking the effectiveness of mental health programs in the workplace is crucial for demonstrating their value and identifying areas for improvement. This involves more than just anecdotal evidence; quantifiable data provides a clear picture of the impact and allows for adjustments to enhance the programs’ effectiveness. A data-driven approach ensures the initiatives are aligned with employee needs and produce tangible results.
Metrics for Tracking Program Effectiveness
Understanding the impact of mental health programs requires establishing clear metrics. These metrics should align with the program’s goals and objectives, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation. Examples include measuring changes in employee stress levels, improvements in employee well-being, and a decrease in the number of reported mental health issues. Quantifying these improvements provides concrete evidence of the program’s effectiveness.
- Employee Stress Levels: Measuring stress levels through surveys, questionnaires, or physiological indicators (e.g., heart rate variability) can track changes before and after implementing mental health programs. Changes in these metrics demonstrate the program’s impact on stress reduction.
- Employee Well-being: Well-being can be assessed using validated questionnaires that measure factors like life satisfaction, happiness, and resilience. Increases in these scores indicate improved mental well-being as a result of the program.
- Mental Health Issue Reporting: Tracking the number of reported mental health issues before and after the program’s implementation provides a clear picture of the program’s effect on employee mental health concerns.
Collecting Data on Employee Perceptions and Experiences
Gathering feedback directly from employees is essential for understanding their experiences with mental health support. This data helps tailor programs to specific needs and concerns. Employee feedback is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring the program aligns with employee expectations.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Standardized surveys and questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative data on employee perceptions of mental health support resources. These tools can measure factors such as accessibility, helpfulness, and satisfaction with available resources.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups provide valuable qualitative data by allowing employees to express their opinions and concerns in a more open-ended format. Discussions in focus groups can reveal specific issues and preferences regarding mental health support that might not be evident in surveys.
- Employee Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing feedback mechanisms, such as suggestion boxes or anonymous online forms, enables employees to share their opinions and suggestions for improvement regarding mental health support. This constant stream of feedback ensures that programs remain relevant and meet the evolving needs of the workforce.
Evaluating the Impact of Interventions on Employee Mental Health
Evaluating the effectiveness of interventions requires a multifaceted approach. This encompasses tracking changes in employee behavior, productivity, and overall well-being. These indicators provide a more comprehensive understanding of the interventions’ impact on employee mental health.
- Changes in Employee Behavior: Observations of changes in employee behavior, such as increased participation in wellness activities or improved communication, provide insight into the impact of interventions. Increased engagement in wellness activities can be a positive indicator of the intervention’s effectiveness.
- Productivity Metrics: Monitoring productivity metrics, such as reduced absenteeism or increased efficiency, can provide insights into the correlation between mental health support and work performance. A reduction in absenteeism can demonstrate that mental health support is positively impacting employee productivity.
- Employee Well-being: Tracking employee well-being using validated questionnaires or assessments allows for a comprehensive understanding of the overall impact of interventions. Measuring improvements in well-being factors like stress levels and job satisfaction directly demonstrates the intervention’s success.
Using Feedback Mechanisms to Improve Mental Health Support Programs
Regular feedback mechanisms are essential for continuous improvement in mental health support programs. This involves actively seeking and incorporating employee feedback to enhance the program’s effectiveness. Continuous improvement ensures the program remains relevant and meets the evolving needs of the workforce.
- Regular Feedback Collection: Establishing a system for regularly collecting feedback ensures the program stays aligned with employee needs and preferences. Collecting feedback on a consistent basis, such as quarterly surveys or annual reviews, is crucial for maintaining a responsive program.
- Actionable Feedback Implementation: Translating feedback into concrete actions is essential for improvement. Developing specific plans based on employee feedback ensures the program addresses identified concerns and enhances its overall effectiveness.
Using Surveys and Questionnaires to Measure Employee Mental Health
Surveys and questionnaires can be valuable tools for assessing employee mental health. Careful selection and administration of these tools ensure accurate and meaningful results. Using validated tools guarantees reliable data for evaluating program effectiveness.
- Selecting Validated Tools: Using validated surveys and questionnaires ensures that the data collected is reliable and accurate. Selecting validated instruments increases the credibility of the findings and the ability to make data-driven decisions.
- Clear and Concise Questions: Formulating clear and concise questions ensures that employees understand the questions and provide accurate responses. This aspect is essential for avoiding misinterpretations and ensuring the survey’s reliability.
- Confidentiality and Anonymity: Guaranteeing confidentiality and anonymity fosters honest responses. This is crucial for collecting meaningful feedback from employees and ensures their comfort in sharing their experiences.
Case Studies of Successful Mental Health Programs
Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of employee mental well-being. Successful mental health programs go beyond simply offering resources; they integrate support into the fabric of the organization, fostering a culture of care and open communication. This approach not only improves employee well-being but also demonstrably boosts productivity and overall organizational performance.These programs aren’t one-size-fits-all solutions. They require careful planning, consideration of the specific needs of the workforce, and ongoing evaluation and adaptation to maintain their effectiveness.
A key aspect of success is tailoring programs to individual company cultures and employee demographics.
Google’s Employee Assistance Program
Google’s comprehensive approach to employee well-being, including mental health, has been widely lauded. Their employee assistance program (EAP) offers a range of resources, from confidential counseling services to workshops on stress management and mindfulness. They also provide access to mental health professionals and have created a supportive work environment.Google’s program has been credited with fostering a culture of open communication about mental health.
This approach reduces the stigma associated with seeking help and encourages employees to prioritize their well-being. The impact of this program on employee retention and productivity is substantial. Google’s approach has served as a model for other companies seeking to implement similar initiatives.
Taking care of your mental health at work is crucial, especially during periods of disruption. Think about how a well-planned maintenance window, like plan ahead to prevent maintenance window pain , can minimize stress and downtime. Effective preparation for these inevitable hiccups can translate directly into a calmer, more productive work environment, ultimately boosting overall well-being.
Microsoft’s Mental Health Initiatives
Microsoft has implemented several programs to support employee mental health. These programs include access to mental health professionals through the EAP, workshops on stress management, and flexible work arrangements. These initiatives recognize the diverse needs of the workforce and are designed to meet those needs.Microsoft has also promoted open conversations about mental health through internal communications and employee forums.
The company has consistently measured the effectiveness of these initiatives and adjusted them accordingly. The outcomes of these programs have been positive, reflecting the dedication of Microsoft to fostering a healthy work environment.
Salesforce’s Culture of Well-being
Salesforce has created a culture of well-being that extends beyond mental health. Their comprehensive approach integrates physical and emotional well-being into the company’s values. This approach is reflected in their flexible work arrangements, generous benefits, and employee resource groups.Salesforce recognizes the importance of creating a supportive and inclusive environment. This environment encourages employees to prioritize their well-being, which ultimately benefits the company’s overall success.
They have demonstrated the correlation between a supportive work environment and high employee satisfaction. Their model illustrates that holistic well-being initiatives can significantly contribute to a positive and productive work environment.
Key Factors Contributing to Program Success
Several key factors contribute to the success of these programs:
- Leadership Commitment: A strong commitment from leadership is crucial. This commitment sends a clear message that employee well-being is a priority.
- Confidentiality and Privacy: Protecting the confidentiality of employees’ mental health information is essential. This fosters trust and encourages employees to seek support when needed.
- Accessibility and Affordability: Ensuring that resources are accessible and affordable for all employees is critical. This ensures that programs are inclusive and benefit all members of the workforce.
- Ongoing Evaluation and Adaptation: Regular evaluation of program effectiveness and adjustments based on feedback are vital. This ensures programs remain relevant and impactful.
Lessons Learned and Application to Other Organizations
The case studies highlight the importance of a multi-faceted approach to mental health support. Companies should consider integrating mental health resources into their existing employee assistance programs and fostering a culture of openness and support.Furthermore, these examples demonstrate the value of ongoing evaluation and adaptation. Companies must monitor the effectiveness of their initiatives and make adjustments as needed.
Ultimately, the success of these programs depends on a commitment to creating a supportive and inclusive work environment.
Creating a Supportive Workplace Culture
Cultivating a supportive and inclusive workplace culture is paramount to employee well-being. A positive work environment fosters trust, reduces stress, and ultimately boosts productivity. When employees feel valued and understood, they’re more likely to thrive both personally and professionally. This culture isn’t just about feel-good initiatives; it’s about implementing tangible strategies that demonstrate a genuine commitment to employee mental health.A supportive workplace culture is built on more than just policies.
It’s about creating an environment where employees feel comfortable discussing their concerns, seeking help when needed, and knowing that their well-being is prioritized. This culture fosters a sense of belonging, encouraging open communication and reducing the stigma surrounding mental health challenges.
Fostering Open Communication and Empathy
Open communication is the cornerstone of a healthy work environment. Employees should feel comfortable expressing their needs, concerns, and even vulnerabilities without fear of judgment or reprisal. This requires creating a safe space for dialogue, where active listening and empathy are valued.Empathy is crucial for understanding and responding to the diverse needs of employees. Leaders and colleagues should actively try to understand different perspectives and experiences, demonstrating genuine care for the well-being of those around them.
This involves acknowledging that individuals experience stress and challenges in various ways, and adapting responses accordingly. Regular check-ins, feedback sessions, and opportunities for peer support can all contribute to this environment.
Building Trust and Psychological Safety
Trust is essential for fostering a psychologically safe environment. Employees need to feel confident that their concerns will be addressed fairly and respectfully. This requires transparency, consistency in communication, and demonstrable commitment from leadership to prioritize employee well-being.Psychological safety is characterized by the belief that one can take interpersonal risks without fear of negative consequences. Teams should encourage open dialogue, debate, and the sharing of ideas without judgment.
Encouraging collaborative problem-solving and creating opportunities for team members to get to know each other beyond work tasks can strengthen trust and psychological safety. Facilitating team-building activities and encouraging social interactions can significantly contribute to this atmosphere.
Implementing Policies and Procedures
Creating a mentally healthy workplace requires a comprehensive approach that integrates policies and procedures into daily operations. Policies should clearly Artikel expectations regarding employee well-being, including access to resources, leave options, and confidential support systems.A robust policy framework should encompass provisions for flexible work arrangements, mental health days, and access to professional support services. These policies should be communicated clearly and consistently to all employees, ensuring that they understand their rights and responsibilities in relation to their mental health.
Building a Mentally Healthy Workplace Culture: A Guide
This guide Artikels steps to create a mentally healthy workplace culture:
- Establish clear communication channels: Regular updates, feedback mechanisms, and transparent communication regarding mental health initiatives foster a culture of open dialogue.
- Promote empathy and understanding: Train employees on recognizing and responding to signs of stress and mental health concerns. This includes fostering an understanding of diverse perspectives and experiences.
- Encourage teamwork and collaboration: Facilitate team-building activities and encourage interactions beyond work tasks to strengthen trust and psychological safety.
- Implement flexible work arrangements: Allow employees to adjust their schedules to better manage work-life balance and reduce stress.
- Provide access to mental health resources: Offer resources such as counseling services, employee assistance programs (EAPs), and wellness programs to support employees’ well-being.
Implementing these strategies will foster a supportive and inclusive culture that values employee well-being, creating a more productive and engaged workforce.
Addressing Mental Health Stigma
Breaking down the walls of silence and prejudice surrounding mental health is crucial for fostering a supportive and productive workplace. Mental health challenges are common, and the stigma associated with them can prevent individuals from seeking help, impacting their well-being and overall performance. Creating a culture of openness and understanding is essential for creating a healthier and more inclusive environment.Addressing mental health stigma isn’t just about being polite; it’s about creating a genuine shift in attitudes and behaviors.
It requires proactive efforts from management and employees alike to challenge outdated beliefs and promote empathy and understanding. This is not a one-time event, but an ongoing process of education and engagement.
The Significance of Stigma Reduction
Reducing the stigma surrounding mental health in the workplace has a profound impact on employee well-being and organizational success. A culture free from stigma empowers individuals to seek help without fear of judgment or discrimination, leading to improved mental health outcomes. This, in turn, translates to increased productivity, reduced absenteeism, and a more engaged workforce. Open communication and acceptance can significantly reduce the risk of mental health conditions worsening, ultimately leading to healthier employees and a more positive work environment.
Fostering a Culture of Acceptance and Understanding
Creating a culture of acceptance and understanding requires a multifaceted approach. Management plays a critical role in setting the tone. Openly discussing mental health, modeling healthy coping mechanisms, and actively participating in mental health awareness programs can demonstrate a company’s commitment to employee well-being. Employee resource groups (ERGs) focused on mental health can provide valuable support and create a safe space for open dialogue.
Encouraging peer-to-peer support can be an effective strategy to combat the stigma.
- Leadership Commitment: Leaders must visibly demonstrate their commitment to mental health by actively participating in training, open discussions, and ensuring that mental health resources are readily available. This sets a positive example for other employees and reinforces the importance of mental well-being.
- Employee Resource Groups (ERGs): Dedicated ERGs can provide a safe and supportive space for employees to connect with others facing similar challenges. These groups can also serve as a platform for sharing information, raising awareness, and advocating for improved mental health support.
- Peer Support Programs: Implementing peer support programs allows trained colleagues to provide guidance and support to those struggling with mental health issues. This can reduce the burden on HR and create a more immediate and accessible support network.
Effective Communication Strategies
Clear and open communication about mental health is vital for reducing stigma. Avoid using stigmatizing language and replace it with accurate and empathetic terminology. Transparent communication about available resources and support systems can empower employees to seek help when needed. Promoting mental health literacy through workshops and training can also help dispel myths and misconceptions.
- Empathetic Language: Using inclusive language that avoids stereotypes and focuses on the person rather than the diagnosis is crucial. Phrases like “experiencing mental health challenges” or “managing a mental health condition” are preferable to stigmatizing terms.
- Open Dialogue: Encourage open conversations about mental health by creating safe spaces for sharing experiences and concerns. Initiate discussions at company meetings, team events, or through internal communication channels.
- Resource Availability: Clearly communicate the availability of mental health resources, including employee assistance programs (EAPs), counseling services, and helplines. Make sure the information is easily accessible and prominently displayed.
Resources for Employees
Providing accessible and varied resources is critical for supporting employees’ mental well-being. This can include links to reputable mental health organizations, guides on stress management, and access to mental health professionals. Encourage employees to share these resources with others, fostering a sense of community and support.
- Internal Resource Hub: Create a dedicated internal website or intranet page that houses various resources on mental health, including articles, videos, and contact information for support services.
- Mental Health Professionals: List mental health professionals or organizations that offer services and provide contact information. Make sure these resources are easily accessible, ideally in multiple formats like brochures, links, and in-person posters.
- Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): Promote the availability of EAPs and ensure that employees understand how to access these confidential support services.
Developing a Mental Health Awareness Campaign
Developing a successful mental health awareness campaign requires a strategic approach. It’s crucial to align the campaign with the company’s values and culture, ensuring that it resonates with employees. Involve employees in the design and execution of the campaign to maximize buy-in and participation. Track and evaluate the campaign’s effectiveness to continuously improve and refine future initiatives.
- Campaign Objectives: Clearly define the campaign’s goals, such as raising awareness, reducing stigma, or encouraging help-seeking behaviors. Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
- Target Audience: Identify the specific demographics and needs of the employees who would benefit most from the campaign. Tailor messaging to resonate with different groups and address their unique concerns.
- Interactive Activities: Integrate interactive activities and events to engage employees and encourage participation. This could include workshops, webinars, or online forums where employees can share experiences and ask questions.
Last Recap: Mental Health At Work
In conclusion, creating a mentally healthy workplace isn’t just about implementing programs; it’s about fostering a culture of understanding, empathy, and support. By acknowledging the importance of mental well-being, organizations can cultivate a more productive, engaged, and fulfilling environment for all employees. This holistic approach will lead to a more positive and sustainable work environment for everyone.

