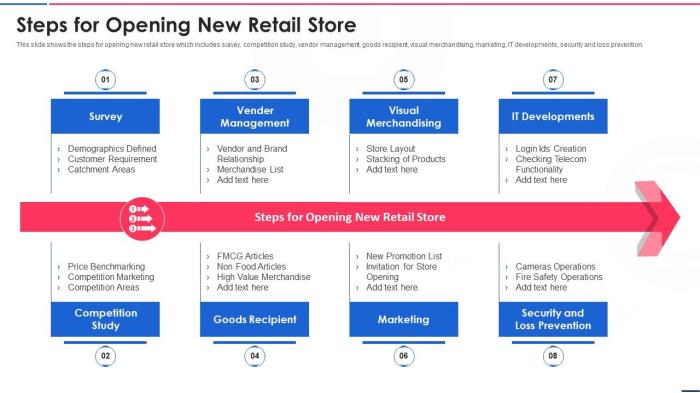
How to open a retail store? This guide dives deep into the essential steps for launching your own retail venture. From meticulous planning and research to navigating legal requirements and managing finances, we’ll cover it all. We’ll explore crafting a robust business plan, understanding your target market, and selecting the perfect location. This isn’t just about opening a shop; it’s about building a successful business from the ground up.
The process involves several key areas: thorough market research to identify your ideal customer and understand your competition; legal compliance, ensuring you have the necessary licenses and permits; designing a functional and attractive store layout; developing a compelling marketing strategy; and mastering financial management to maintain profitability. We’ll break down each stage, providing practical advice and actionable strategies to help you succeed.
Planning and Research
Opening a retail store requires meticulous planning and research to ensure success. A well-defined business plan, thorough market analysis, and strategic location selection are crucial for navigating the competitive landscape and achieving profitability. Understanding your target customer, developing effective pricing strategies, and forecasting financial performance are equally important elements in establishing a solid foundation for your retail venture.Thorough planning and research are essential to building a sustainable retail business.
Opening a retail store requires meticulous planning, from sourcing the perfect location to crafting a compelling product line. While the FCC’s plan to boost inflight wifi, as detailed in this article fcc plan to boost inflight wifi takes off with turbulence , might seem unrelated, the underlying principle of careful planning holds true. Ultimately, successful retail ventures hinge on understanding the market and anticipating potential challenges.
A robust plan lays the groundwork for success, while detailed market research allows you to tailor your offerings to customer needs and compete effectively. Understanding the financial projections is crucial for making informed decisions and securing necessary funding.
Opening a retail store requires careful planning, from securing funding to choosing the right location. One crucial aspect often overlooked is understanding digital strategies, like how “what’s yours is Google’s mine” impacts your business. whats yours is googles mine highlights the importance of online presence. Ultimately, successful retail requires a blend of traditional and modern approaches.
Creating a Retail Store Business Plan
A comprehensive business plan is a roadmap for your retail store. It Artikels the vision, strategy, and financial projections. It should include an executive summary, company description, market analysis, products and services, marketing and sales strategy, management team, financial projections, and appendix. The business plan serves as a tool for attracting investors, securing loans, and guiding daily operations.
A well-crafted business plan clearly defines the store’s purpose, target audience, and competitive advantage.
Market Research Methods
Effective market research is vital for identifying potential customers and competitors. Qualitative methods, such as focus groups and surveys, can uncover customer preferences and pain points. Quantitative methods, such as market size estimations and competitor analysis, provide measurable data. Combining these approaches yields a holistic understanding of the market landscape. Analyzing sales data from similar stores, reviewing industry reports, and conducting online surveys are examples of quantitative and qualitative methods, respectively.
Choosing a Suitable Location
The location of your retail store significantly impacts its success. Consider factors like foot traffic, visibility, accessibility, and proximity to competitors. Analyzing demographics, competition, and local regulations is crucial for selecting a suitable location. High foot traffic areas, such as malls or busy streets, can boost sales. Analyzing competitor locations, parking availability, and local zoning regulations can help ensure your chosen location is feasible.
Defining the Target Customer Base
Identifying your target customer is essential for tailoring your products and marketing efforts. Consider factors like age, income, lifestyle, and interests. Demographics, psychographics, and buying behavior can be used to segment your target customer base. Detailed market research will reveal the characteristics and needs of your ideal customer, guiding your marketing strategies.
Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies significantly impact profitability. Consider factors like cost of goods, market competition, and desired profit margins. Competitive pricing, value-based pricing, and premium pricing are common strategies. Competitive pricing is based on the prices of similar products, value-based pricing reflects the perceived value of the product, and premium pricing targets customers willing to pay more for a perceived superior product.
Pricing strategy is crucial for optimizing revenue and achieving profitability.
Financial Projections
Accurate financial projections are essential for managing cash flow and securing funding. Projecting revenue, expenses, and profit over a specific period is necessary. These projections allow for planning and adapting to changes in the market. Realistic projections should account for startup costs, operating expenses, and potential sales fluctuations.
| Year | Revenue | Expenses | Profit/Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $100,000 | $80,000 | $20,000 |
| Year 2 | $150,000 | $100,000 | $50,000 |
| Year 3 | $200,000 | $120,000 | $80,000 |
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Opening a retail store involves navigating a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements. Thorough understanding and compliance are crucial for smooth operations and avoiding costly mistakes. This section dives deep into the essential legal aspects, from licensing and permits to business structures and insurance.
Business Structures
Different business structures have distinct legal and financial implications. Sole proprietorships are straightforward to set up but offer limited liability protection. Partnerships require a formal agreement outlining responsibilities and profit sharing. Corporations provide more comprehensive liability protection but involve more complex administrative procedures. Limited liability companies (LLCs) combine the benefits of both partnerships and corporations, offering limited liability with a more flexible structure.
Choosing the right structure is critical for protecting your personal assets and managing tax obligations.
Licenses and Permits
Obtaining the necessary licenses and permits is a critical step. These vary significantly depending on the type of retail store, location, and products sold. Examples include business licenses, zoning permits, health permits (especially for food or prepared goods), and alcohol licenses (if applicable). Failure to obtain the required permits can result in fines, legal action, and even business closure.
Research local regulations thoroughly. Local government websites and business licensing agencies are excellent resources.
Insurance and Liability Protection
Insurance is essential for protecting your retail store from unforeseen events. General liability insurance covers claims of bodily injury or property damage arising from your business operations. Product liability insurance protects against claims related to defective products. Professional liability insurance, also known as errors and omissions insurance, covers claims related to professional advice or services. Understanding the different types of insurance and their coverage is vital for mitigating potential risks.
Product Sourcing and Sales
Legal considerations related to product sourcing and sales are extensive. Contracts with suppliers should clearly define responsibilities, payment terms, and product specifications. Compliance with labeling laws and regulations is crucial, including providing accurate information about ingredients, materials, and country of origin. Know your local regulations concerning pricing, sales promotions, and consumer protection laws.
Opening a retail store takes meticulous planning. You need a solid business plan, secure funding, and a killer location strategy. Think about the latest tech trends, like the innovative Microsoft and Huawei partnership in the ” microsoft huawei mount african smartphone expedition “. This could offer some interesting insights into consumer preferences. Ultimately, thorough market research and a flexible approach are key to a successful retail launch.
Licensing and Permit Procedures
Obtaining licenses and permits typically involves submitting an application, providing required documents (proof of business structure, location, etc.), and paying associated fees. Each jurisdiction has its specific procedure. Consult with your local government agencies or a legal professional for detailed information. The process can take time, so start early.
Legal Regulations by Location
| Location | License Types | Required Documents | Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | Business license, Seller’s permit, Health permit | Business plan, proof of address, business structure documents | Variable, based on specific license type |
| New York | Business license, sales tax permit, zoning permit | Business registration documents, lease agreement, business plan | Variable, based on specific license type |
| Florida | Business license, alcohol license (if applicable), zoning permit | Business registration, proof of address, site plan | Variable, based on specific license type |
| Texas | Business license, sales tax permit, health permit | Business registration documents, proof of address, business structure documents | Variable, based on specific license type |
This table provides a general overview. Always verify the most up-to-date regulations for your specific location and type of business.
Store Design and Operations
Transforming a great business plan into a thriving retail store requires meticulous attention to design and operations. This stage is where the customer experience is crafted, and ultimately, where sales are made or lost. Careful consideration of store layout, equipment, inventory management, and customer service strategies are crucial for success.
Store Layouts and Customer Experience
Store layout significantly impacts the customer journey. A well-designed layout encourages exploration, minimizes frustration, and maximizes sales. Different layouts cater to varying needs and products. For example, a clothing store might benefit from a linear layout showcasing different categories, while a grocery store may use a grid-like layout for easier navigation.
Importance of Store Design Elements
The aesthetic and functional elements of a store directly affect customer perception and purchasing decisions. Color schemes, lighting, and signage create the atmosphere. For example, warm lighting might create a welcoming environment for a boutique, while cool lighting might be appropriate for a tech store. Proper signage ensures easy navigation and product discovery. Visual merchandising techniques, such as strategically placed displays and product groupings, can boost impulse buys and enhance the overall shopping experience.
Essential Retail Store Equipment
Appropriate equipment is critical for smooth operations and efficient service. Cash registers, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and inventory management software streamline transactions and track stock. Shelving, display units, and fitting rooms are essential for showcasing products and facilitating customer interaction. Security systems, such as surveillance cameras and alarms, protect both the store and its inventory.
Inventory Management Systems
Efficient inventory management is vital for profitability and customer satisfaction. Real-time inventory tracking systems, such as barcode scanners and software programs, ensure accurate stock levels and minimize stockouts. Proper storage solutions maintain product quality and reduce waste. By accurately forecasting demand and managing supply chains, businesses can optimize inventory levels, preventing overstocking or shortages.
Customer Service Strategies
Excellent customer service is the cornerstone of a successful retail store. Providing knowledgeable and helpful staff can significantly improve customer satisfaction. Offering personalized service, addressing concerns promptly, and providing helpful product information contribute to positive customer experiences. Loyalty programs, rewards systems, and exceptional customer service build brand loyalty and encourage repeat business.
Retail Store Layout Comparison
| Layout Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Customer Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid Layout | Easy navigation, efficient use of space, high visibility of products. | Can feel impersonal, may not encourage exploration, less emphasis on visual merchandising. | Straightforward and predictable, customers easily find desired items. |
| Free-Flow Layout | Encourages exploration, allows for a more personalized shopping experience, can showcase a wide variety of products. | Difficult to manage inventory, less efficient use of space, may confuse customers if not carefully planned. | Customers have more freedom to wander, potentially leading to discovery of unexpected items. |
| Linear Layout | Easy to navigate, maximizes space utilization, allows for clear product categorization. | May not encourage browsing, less flexibility in product placement. | Customers move sequentially through the store, focusing on specific product categories. |
| Boutique Layout | Creates a unique atmosphere, fosters a sense of community, can highlight specific brands or styles. | Can be expensive to maintain, requires specialized products. | Customers may feel immersed in the store’s theme. |
Marketing and Promotion

Opening a retail store is more than just stocking shelves; it’s about connecting with your target audience. Effective marketing and promotion are crucial for attracting customers, driving sales, and ultimately, building a thriving business. This involves understanding your customer base, crafting a compelling brand identity, and utilizing various marketing channels to reach potential buyers. A well-defined marketing strategy is essential for success in the competitive retail landscape.A robust marketing plan anticipates different stages of store operation, from pre-opening buzz to long-term customer engagement.
Adapting strategies to changing market trends and customer preferences is key to maintaining relevance and profitability.
Effective Marketing Strategies for Attracting Customers
A comprehensive marketing strategy should encompass various channels to reach the target audience. This involves a blend of online and offline tactics, tailored to resonate with specific customer segments. Understanding the unique needs and preferences of each segment is vital for effective communication.
- Targeted Advertising: Utilizing platforms like social media and search engines, businesses can precisely target customers based on demographics, interests, and online behavior. This ensures marketing efforts reach the most receptive audience, optimizing return on investment (ROI).
- Public Relations: Building relationships with local media outlets can generate positive press coverage, enhancing brand awareness and credibility. Collaborating with influencers and bloggers relevant to the target market can also extend reach and build trust.
- Community Engagement: Participating in local events and initiatives builds brand recognition and fosters a sense of community. This creates a positive brand image and attracts customers interested in supporting local businesses.
Promotional Strategies for Driving Sales
Promotional strategies are essential for driving sales and attracting new customers. A well-structured promotional plan can incentivize purchases, create excitement, and encourage repeat business.
- Limited-Time Offers: Offering discounts, promotions, or exclusive bundles for a specific period creates a sense of urgency and encourages immediate purchases. Examples include “buy one, get one free” deals, seasonal discounts, or introductory offers for new customers.
- Loyalty Programs: Implementing loyalty programs rewards repeat customers with exclusive discounts, early access to sales, or personalized offers. This incentivizes repeat purchases and fosters long-term relationships with valued customers.
- Contests and Giveaways: Engaging contests and giveaways generate excitement and attract new customers. This can include contests on social media or in-store promotions. A well-executed giveaway strategy can amplify brand visibility and encourage participation.
Branding and its Impact on Customer Loyalty
Branding is the cornerstone of customer loyalty. A strong brand identity creates a unique perception of the store, sets it apart from competitors, and fosters customer recognition and trust.
A compelling brand story resonates with customers, connecting them emotionally to the store’s values and mission.
A consistent brand image across all marketing channels strengthens brand recognition and fosters customer trust. This involves using a consistent color palette, logo, and messaging across all marketing materials.
Social Media Marketing Strategies for Retail Stores
Social media is a powerful tool for reaching a vast audience. Effective social media marketing strategies leverage the platform’s potential to engage with customers, showcase products, and drive sales.
- Creating Engaging Content: High-quality images and videos of products are essential. Content should be relevant to the target audience, highlighting product benefits and features in a visually appealing way.
- Interactive Content: Engage customers with polls, quizzes, Q&A sessions, or contests. This creates a sense of community and encourages interaction with the brand.
- Utilizing Influencer Marketing: Partnering with relevant influencers can amplify brand reach and credibility. Influencers can provide valuable endorsements and showcase products to their followers.
Methods for Building Customer Relationships
Building strong customer relationships is essential for long-term success. Positive interactions and personalized experiences cultivate loyalty and encourage repeat business.
- Personalized Service: Providing exceptional customer service and tailoring interactions to individual needs builds strong relationships. This involves actively listening to customer feedback and addressing their concerns promptly.
- Collecting Customer Feedback: Gathering customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media interactions allows for a deeper understanding of customer needs and preferences. This provides valuable insights for improving products and services.
- Customer Retention Strategies: Implementing customer retention strategies such as loyalty programs and personalized communication fosters customer loyalty and encourages repeat business. This is vital for maintaining a strong customer base and ensuring sustained profitability.
Marketing Plan for Different Phases of Store Operation
A well-defined marketing plan adapts strategies to different stages of store operation. This includes pre-opening promotions, launch campaigns, and long-term strategies for building brand loyalty.
| Phase | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Pre-Opening | Generating excitement and anticipation through social media campaigns, pre-launch promotions, and media outreach. |
| Launch | Implementing grand opening events, exclusive offers for early adopters, and showcasing new products. |
| Growth | Monitoring customer feedback, analyzing sales data, and adapting marketing strategies to meet evolving needs. |
Financial Management
Opening a retail store requires careful financial planning. Ignoring financial aspects can quickly lead to problems, from cash flow issues to insolvency. This section dives into the crucial financial elements of running a successful retail business.
Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management is vital for a retail store’s survival. It ensures the business has enough liquid funds to meet its short-term obligations, like paying suppliers and employees. A healthy cash flow cycle allows for the smooth operation of day-to-day activities. A significant problem arises when cash outflows exceed inflows, leading to a cash crunch and potentially impacting operations.
Forecasting future cash needs is essential, particularly during seasonal fluctuations.
Managing Accounts Payable and Receivable
Managing accounts payable and receivable is critical for maintaining financial stability. Accounts payable represent the money owed to suppliers for goods or services received, while accounts receivable represent the money owed to the store by its customers.
- Accounts Payable Management: Establish clear payment terms with suppliers. This may involve negotiating extended payment periods, potentially securing discounts for early payments, or utilizing credit lines. Prompt payment reduces interest charges and maintains a positive relationship with suppliers. Tracking invoices and due dates is crucial to avoid late payments and potential penalties.
- Accounts Receivable Management: Implement a system for tracking customer payments. Offering incentives like discounts for early payments or payment plans can encourage timely payments. A clear and effective credit policy is essential. This policy should specify acceptable credit limits, payment terms, and procedures for handling delinquent accounts. Collecting overdue payments in a timely manner is essential.
Controlling Expenses and Maximizing Profits
Controlling expenses and maximizing profits are essential for long-term sustainability. Strategies for expense control should include careful monitoring of inventory levels, efficient staffing management, and careful vendor selection to secure the best prices.
- Inventory Management: Effective inventory management can reduce storage costs and minimize the risk of obsolete stock. Proper forecasting and tracking of inventory levels are crucial for minimizing waste and maximizing profitability.
- Pricing Strategies: Analyze market pricing trends and competitor strategies to set competitive and profitable prices. Consider cost-plus pricing models, value-based pricing, or dynamic pricing strategies to optimize profitability.
- Cost Optimization: Identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses. Negotiate favorable contracts with vendors and explore opportunities to streamline operations. Implement cost-saving measures without compromising product quality or customer service.
Financial Tools for Tracking Performance
Various financial tools are essential for monitoring performance and making informed decisions.
- Profit and Loss (P&L) Statements: These statements track revenue and expenses over a specific period, highlighting profitability trends. Analyzing these statements is critical for understanding revenue sources and expenditure patterns.
- Balance Sheets: These statements reflect the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. This helps in assessing the company’s financial position.
- Cash Flow Statements: These statements detail the movement of cash into and out of the business over a period, highlighting cash inflows and outflows. They show the ability of the company to generate cash from its operations.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): KPIs provide specific metrics for evaluating the store’s performance. Examples include sales per square foot, conversion rates, customer lifetime value, and inventory turnover.
Financial Reporting Requirements, How to open a retail store
Retail stores need to comply with various financial reporting requirements. These requirements vary based on the legal structure of the business and local regulations. Consult with a financial advisor or accountant to ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are valuable tools for assessing the financial health of a retail store.
| Ratio | Formula | Calculation Example | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Profit Margin | (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue | ($100,000 – $40,000) / $100,000 = 60% | Indicates the profitability of the core business operations. A higher ratio generally suggests better profitability. |
| Inventory Turnover | Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory | $40,000 / (($10,000 + $12,000) / 2) = 4 | Indicates how efficiently the company manages its inventory. A higher ratio suggests faster inventory turnover. |
| Current Ratio | Current Assets / Current Liabilities | ($20,000 / $10,000) = 2 | Measures the ability of the company to pay its short-term obligations. A higher ratio suggests a greater ability to meet short-term obligations. |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Total Debt / Total Equity | ($30,000 / $20,000) = 1.5 | Indicates the proportion of financing that comes from debt. A higher ratio suggests a greater reliance on debt financing. |
Conclusion: How To Open A Retail Store
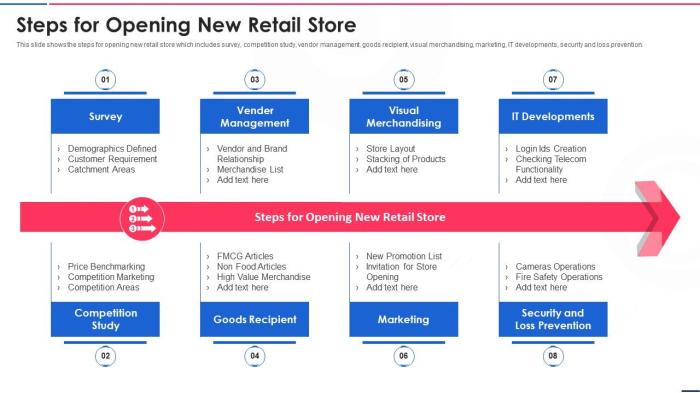
Launching a retail store is a significant undertaking, but with careful planning and execution, it can be a rewarding experience. This comprehensive guide provides a roadmap to help you navigate each stage of the process, from initial planning to ongoing financial management. Remember, success in retail is a journey, not a destination, and continuous learning and adaptation are key to long-term profitability.
By understanding the key aspects of each step, you’ll be well-equipped to confidently open your retail store and build a thriving business.

