
Graduate jobs in science and pharmaceuticals offer exciting opportunities for recent graduates with a passion for scientific advancement. This guide explores the diverse career paths available, from research and development to clinical trials and regulatory affairs, providing insights into the skills and qualifications employers seek. We’ll delve into specific science disciplines, the pharmaceutical industry landscape, and effective job search strategies to help you navigate this dynamic field.
The current job market for science and pharmaceutical graduates is competitive but rewarding. Understanding the specific requirements of different roles, the importance of both technical and soft skills, and the various career paths within the industry will be key to landing your dream job. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to succeed in your job search.
Pharmaceutical Industry Focus
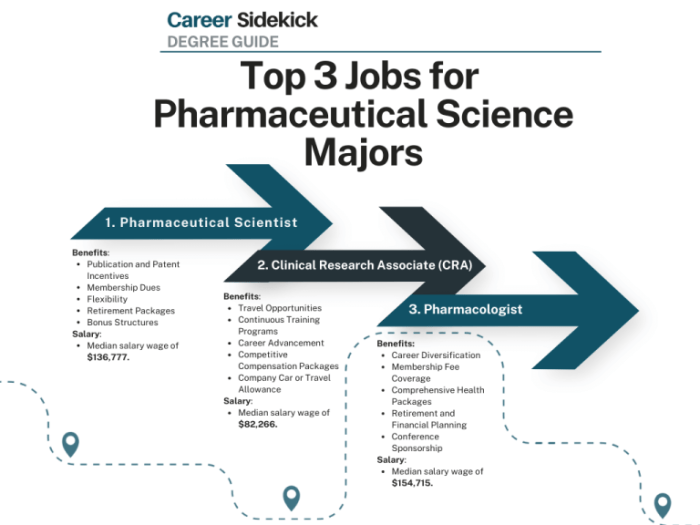
The pharmaceutical industry is a dynamic and multifaceted sector, encompassing a wide range of companies and organizations dedicated to drug discovery, development, manufacturing, and marketing. From small biotech startups to large multinational corporations, the industry plays a crucial role in human health and well-being. Understanding the diverse types of organizations and the various career paths available is key to navigating this exciting field.The pharmaceutical industry is characterized by a complex interplay of research, regulation, and commercialization.
This intricate system shapes the career paths available, demanding diverse skills and knowledge. Navigating this landscape requires a comprehensive understanding of the different roles and responsibilities within each segment.
Types of Pharmaceutical Companies and Research Organizations
Pharmaceutical companies vary significantly in size, focus, and research areas. Large, multinational corporations like Pfizer and Johnson & Johnson often have extensive research and development departments, encompassing various therapeutic areas. Smaller biotech companies, on the other hand, might focus on specific diseases or therapies, often partnering with larger firms for later-stage development. Academic research institutions, like universities and research hospitals, also play a vital role in pharmaceutical innovation, often conducting fundamental research and fostering collaborations with industry partners.
Career Paths in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Graduates entering the pharmaceutical industry can pursue diverse career paths, each requiring specific skill sets and knowledge. These paths encompass roles in research and development, clinical trials, regulatory affairs, marketing, and manufacturing. A clear understanding of these diverse paths can help individuals tailor their skills and education to specific career goals.
Roles for Graduates in Research and Development, Graduate jobs in science and pharmaceuticals
Graduates entering research and development (R&D) often begin with roles focused on basic research, compound screening, or preclinical studies. They may contribute to drug discovery, optimization of existing drugs, or development of novel drug delivery systems. Their responsibilities often involve conducting experiments, analyzing data, and reporting findings. Examples include laboratory technicians, research associates, and research scientists.
Roles for Graduates in Clinical Trials
Graduates in clinical trials may assist in the design, execution, and monitoring of clinical trials. These trials are critical for evaluating the safety and efficacy of new drugs in human subjects. Graduates may work as clinical research coordinators, data managers, or monitors. They will play a vital role in ensuring the ethical conduct and integrity of clinical trials.
Roles for Graduates in Regulatory Affairs
Regulatory affairs professionals ensure that pharmaceutical products meet regulatory requirements in different countries. Graduates in this field may contribute to the submission of regulatory documents, manage regulatory interactions with agencies, or conduct compliance assessments. Regulatory affairs specialists are crucial for navigating the complex regulatory landscape of the pharmaceutical industry.
Roles for Graduates in Marketing
Marketing professionals in the pharmaceutical industry focus on promoting and selling products to healthcare professionals and patients. Graduates may work in market research, product launch, or sales. Effective communication, understanding of the healthcare landscape, and knowledge of regulatory compliance are crucial for success.
Roles for Graduates in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Manufacturing roles involve ensuring the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products throughout the production process. Graduates may work in quality control, process development, or operations. Maintaining high standards of manufacturing is critical for ensuring patient safety and product efficacy.
Comparison of Roles in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, Research, and Sales
| Category | Manufacturing | Research | Sales |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Ensuring quality and safety of production | Discovering and developing new drugs/treatments | Promoting and selling products |
| Typical Tasks | Quality control, process optimization, GMP compliance | Laboratory work, data analysis, scientific research | Market research, sales presentations, building relationships |
| Required Skills | Technical expertise, attention to detail, strong analytical skills | Scientific knowledge, critical thinking, problem-solving skills | Communication skills, relationship building, sales acumen |
| Typical Career Progression | Quality Assurance Manager, Production Supervisor, Manufacturing Director | Research Scientist, Principal Investigator, Head of Research | Sales Representative, Account Manager, Sales Director |
Skills & Qualifications for Success: Graduate Jobs In Science And Pharmaceuticals
Landing a graduate role in the science and pharmaceuticals sector requires more than just technical expertise. A strong foundation in soft skills, coupled with demonstrable technical proficiencies, is crucial for success. Graduates need to adapt to the dynamic environment, collaborate effectively, and communicate their knowledge clearly to thrive in this competitive field.Beyond theoretical knowledge, the pharmaceutical industry values practical application and problem-solving skills.
The ability to analyze data, interpret results, and translate findings into actionable strategies is highly sought after. Furthermore, strong communication and teamwork skills are essential for navigating complex projects and fostering productive collaborations within teams.
Soft Skills for Graduate Success
Soft skills are increasingly valued in the pharmaceutical industry, as they are critical for effective communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. These skills, often overlooked, are vital for navigating the complexities of research, development, and commercialization. Graduates who demonstrate strong soft skills are better equipped to collaborate with colleagues, manage projects effectively, and contribute to a positive work environment.
- Communication: Clear and concise communication is paramount. This includes both written and verbal communication, encompassing the ability to explain complex scientific concepts to both technical and non-technical audiences. Active listening is equally important for understanding diverse perspectives and contributing meaningfully to discussions. Examples of showcasing communication in a resume or interview include highlighting previous presentations, participation in group discussions, and experience in conveying complex ideas through written reports.
- Teamwork: Pharmaceutical research and development are often collaborative efforts. The ability to work effectively within a team, respecting diverse perspectives, and contributing constructively to shared goals is highly valued. Demonstrating teamwork involves highlighting previous group projects, leadership roles within teams, and contributions to collaborative research endeavors.
- Problem-solving: The pharmaceutical industry faces complex challenges. The ability to identify problems, analyze situations, and develop creative solutions is crucial for progress. Highlighting instances where you identified and resolved issues, and how your analytical skills were applied, showcases this valuable skill.
Technical Skills for Graduate Roles
Technical skills are foundational for graduates entering the science and pharmaceutical sector. These skills directly impact research, development, and commercialization efforts. Strong proficiency in specific techniques and tools is essential for success.
- Data Analysis: The ability to analyze and interpret complex data is crucial. Modern pharmaceutical research heavily relies on statistical analysis, data visualization, and interpretation. Examples of demonstrating data analysis skills include quantifying data from experiments, drawing conclusions, and presenting findings using graphs or tables in reports.
- Laboratory Techniques: Proficiency in laboratory techniques is fundamental. This includes a range of skills from basic laboratory safety to advanced techniques such as chromatography, spectroscopy, and cell culture. Highlighting experience with these techniques, and demonstrating your proficiency through practical laboratory work, is vital for showcasing your technical skills.
Communication and Teamwork in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Effective communication and teamwork are essential for navigating the complexities of the pharmaceutical industry. Collaborative efforts are crucial for research, development, and the successful launch of new products. A strong understanding of how to effectively collaborate within teams, understanding and appreciating different perspectives, and communicating complex ideas clearly is essential.
| Skill Type | Description | Examples of showcasing in resume/interview |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Articulating ideas clearly, both verbally and in writing | Highlighting presentations, reports, or discussions where complex ideas were communicated effectively. |
| Teamwork | Collaborating effectively with colleagues, respecting diverse perspectives, and contributing constructively | Emphasizing group projects, leadership roles in teams, and demonstrating active participation in collaborative settings. |
| Problem-solving | Identifying problems, analyzing situations, and developing creative solutions | Illustrating instances where issues were identified and resolved, showcasing analytical skills and problem-solving strategies. |
| Data Analysis | Analyzing and interpreting complex data | Presenting data analysis using charts, graphs, and tables in reports or presentations. Highlighting the interpretation of data and the drawing of conclusions. |
| Laboratory Techniques | Proficiency in various laboratory procedures | Listing specific laboratory techniques mastered, such as chromatography, spectroscopy, and cell culture. Demonstrating practical laboratory experience through project descriptions. |
Job Search Strategies
Landing a graduate-level position in science or pharmaceuticals requires a strategic approach. Simply submitting a generic resume won’t cut it in today’s competitive job market. A well-defined job search strategy, incorporating targeted networking, tailored applications, and proactive research, significantly increases your chances of success. This section delves into the various methods for finding these coveted positions, empowering you with the tools to excel in your job hunt.
Job Search Engines and Portals
Finding graduate-level jobs in science and pharmaceuticals often begins with online searches. Dedicated job boards and portals are crucial resources. They typically feature a wide range of roles across various companies and specializations, providing a comprehensive overview of available opportunities. These platforms usually offer advanced search filters to refine your results based on location, industry, job title, and other criteria.
Networking and Industry Connections
Networking is an indispensable component of a successful job search. Building connections within the pharmaceutical industry can provide valuable insights, lead to hidden opportunities, and open doors to potential employers. Attend industry events, conferences, and workshops to meet professionals in your field. Engage with alumni networks and connect with mentors who can offer guidance and advice. Remember, networking is not just about collecting contacts; it’s about building genuine relationships.
Tailoring Your Application Materials
Crafting a resume and cover letter that effectively highlight your skills and experiences is paramount. Avoid generic templates. Instead, tailor your application materials to each specific role, showcasing how your qualifications directly align with the requirements Artikeld in the job description. Demonstrate your understanding of the company and its mission, and articulate how your skills and experience will contribute to their success.
This personalized approach makes your application stand out and resonates with potential employers.
Job Search Method Strategies
A well-structured job search incorporates a variety of strategies. A systematic approach allows you to maximize your efforts and improve your chances of success. This table Artikels different methods, descriptions, and tips for success.
| Job Search Method | Description | Tips for Success |
|---|---|---|
| Online Job Portals | Specialized websites dedicated to posting job openings in various industries, including science and pharmaceuticals. | Use s relevant to your skills and experience. Filter your search based on location, job type, and company size. Regularly check these portals for new openings. |
| Networking Events | Attending industry conferences, workshops, and seminars to connect with professionals and potential employers. | Prepare thoughtful questions to ask potential employers. Exchange contact information with people you meet. Follow up with connections after the event. |
| Company Websites | Directly exploring the careers pages of companies you are interested in. | Identify specific roles that align with your interests and qualifications. Research the company’s values and culture to demonstrate your understanding. Highlight specific projects or experiences that relate to their work. |
| Professional Organizations | Joining relevant professional associations and groups to stay updated on industry trends and job opportunities. | Attend meetings, workshops, and webinars to network with peers and experts. Check their job boards for potential openings. Actively participate in discussions and events. |
Career Development & Advancement
Climbing the ladder in the pharmaceutical industry requires strategic planning and a commitment to continuous learning. Graduates enter with a strong foundation, but navigating the nuances of career progression and leveraging opportunities for advancement are key to long-term success. This journey often involves mastering specialized skills, taking on increased responsibilities, and seeking out professional development opportunities.Career advancement in pharmaceuticals, like many industries, is not solely dependent on formal education.
Experience, demonstrable skills, and a proactive approach to learning and networking play a crucial role. Understanding the typical career paths and the skills needed for each stage allows graduates to strategize their development and capitalize on opportunities. Success often hinges on a blend of technical expertise, interpersonal skills, and a commitment to staying current with industry trends.
Typical Career Progression for Science Graduates
The path for science graduates in pharmaceuticals often starts with entry-level roles like research assistant, technician, or quality control analyst. These roles provide a valuable foundation in practical application of scientific knowledge and exposure to the industry’s day-to-day operations. Graduates typically gain experience in laboratory techniques, data analysis, and project management. With increasing experience and demonstrated performance, opportunities for advancement arise.
Factors Influencing Career Advancement
Several factors contribute to career advancement in the pharmaceutical industry. Strong communication skills are essential for collaborating effectively with colleagues and stakeholders. Demonstrated problem-solving abilities, especially in complex scientific situations, are highly valued. Proactive engagement in professional development activities, such as attending conferences and workshops, and actively seeking mentorship are also important. Finally, a commitment to continuous learning and adapting to evolving industry standards is critical.
Professional Development Opportunities and Training Programs
The pharmaceutical industry offers a wide range of professional development opportunities. Companies often provide internal training programs focused on specific skills or emerging technologies. Attending industry conferences and workshops can expose graduates to cutting-edge research and best practices. Furthermore, seeking mentorship from experienced professionals can provide invaluable guidance and insights. Taking advantage of these opportunities is crucial for career progression.
Graduate jobs in science and pharmaceuticals are incredibly diverse, offering everything from lab research to marketing roles. Imagine a future where robots like the “machine speak robot baby learns words” ( machine speak robot baby learns words ) could assist in drug discovery or manufacturing processes, streamlining the entire pipeline. This technological advancement, though, doesn’t diminish the need for skilled graduates to ensure these innovations are ethically and efficiently implemented in the industry.
Networking within and outside the company is equally vital, as it fosters connections and knowledge sharing.
Career Paths, Milestones, and Required Skills
| Career Path | Typical Milestones | Required Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Research Scientist | Entry-level research assistant, publication author, grant application experience, leading research projects | Strong scientific knowledge, analytical skills, data interpretation, problem-solving, communication, teamwork |
| Quality Control Specialist | Quality control technician, auditing, quality improvement initiatives, technical writing | Attention to detail, analytical skills, knowledge of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), technical proficiency, documentation skills |
| Regulatory Affairs Specialist | Compliance review, regulatory filing, regulatory submissions, drafting and reviewing documents | Knowledge of regulatory guidelines (e.g., FDA), excellent writing and communication skills, meticulousness, attention to detail |
| Clinical Research Associate | Clinical trial participant interaction, data management, report generation, trial monitoring | Strong scientific background, interpersonal skills, data analysis, project management, communication |
Note: This table provides a general overview. Specific milestones and required skills may vary based on the company and specific role.
Industry Trends & Future Outlook
The pharmaceutical industry is in a constant state of evolution, driven by technological advancements and shifting patient needs. Graduates entering this field need to be adaptable and understand the forces reshaping the landscape. This section explores current trends and potential future directions, highlighting emerging technologies and growth areas.The future of graduate jobs in science and pharmaceuticals is characterized by a dynamic interplay of established practices and revolutionary innovations.
Staying informed about these developments is crucial for navigating the competitive job market and maximizing career potential.
Current Industry Trends
The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing significant transformations, driven by factors such as increasing research intensity, regulatory changes, and evolving patient expectations. These trends are creating opportunities and challenges for graduates, demanding a keen understanding of the evolving landscape. The focus on personalized medicine, driven by advances in genomics and bioinformatics, is creating new career paths. Simultaneously, the demand for cost-effective and sustainable solutions is prompting innovation in drug delivery systems and manufacturing processes.
Emerging Technologies
Several groundbreaking technologies are rapidly transforming the pharmaceutical industry. Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used for drug discovery, accelerating the identification of potential drug candidates. Machine learning algorithms are being deployed to analyze massive datasets of biological and chemical information, leading to the development of more precise and targeted therapies. Big data analytics is also becoming increasingly crucial for understanding patient populations and tailoring treatments to individual needs.
Growth Areas for Graduates
Several sectors within the pharmaceutical industry are experiencing significant growth, presenting promising career prospects for graduates. Personalized medicine, combining genomics with targeted therapies, is a key area. This field necessitates graduates with strong analytical skills and a deep understanding of biological systems. Another area of growth is the development of biosimilars, which offer cost-effective alternatives to existing patented drugs.
Landing a graduate job in science or pharmaceuticals can be tough, but the competitive landscape is definitely mirrored in the online gaming world. Think about the real-world marauders that infest online games, like real world marauders infest online games. It’s a constant battle for resources and position, much like the cutthroat pursuit of a coveted science or pharmaceutical internship.
Ultimately, a strong academic record and demonstrable skills are key to succeeding in either realm.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on digital health solutions presents opportunities for graduates with expertise in software development, data analysis, and healthcare informatics.
Emerging Research Areas & Job Opportunities
The advancement of science is generating exciting new research areas with corresponding graduate job opportunities. One notable area is the development of novel drug delivery systems, aiming for improved efficacy and reduced side effects. This requires expertise in materials science, engineering, and pharmaceutical sciences. Another emerging research area involves the exploration of novel therapeutic targets in complex diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s.
Graduates with strong backgrounds in molecular biology, genetics, and pharmacology can contribute significantly in this area. The convergence of biotechnology and information technology is also leading to new research avenues in areas like bioinformatics and computational biology.
Graduate jobs in science and pharmaceuticals are often highly sought after, offering exciting opportunities for young professionals. However, the world of technology, as highlighted by the recent case of a hacking software guru facing the music in US court here , reminds us that ethical considerations are crucial in the tech sector. Ultimately, a strong foundation in scientific principles, combined with ethical practices, will be key for success in these fields.
Examples of Emerging Research Areas and Job Opportunities
- Cancer Immunotherapy: This research area focuses on harnessing the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Graduates with expertise in immunology, oncology, and bioengineering are highly sought after.
- Precision Medicine: This field utilizes genetic information to tailor treatments to individual patients. Graduates with strong backgrounds in genomics, bioinformatics, and pharmacology are well-positioned for success in this area.
- Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology: Nanotechnology is being used to develop more targeted and effective drug delivery systems. Graduates with expertise in materials science, chemical engineering, and pharmaceutical sciences can excel in this field.
Illustrative Examples of Graduate Roles

Stepping into the pharmaceutical industry as a graduate opens doors to diverse and impactful roles. These positions often require a blend of theoretical knowledge gained during your studies and practical skills honed through internships or extracurricular activities. This section dives deep into specific graduate-level roles in research and development, and regulatory affairs, highlighting their responsibilities, required skills, and potential career paths.
Graduate Research and Development Roles
Research and development (R&D) is a cornerstone of the pharmaceutical industry, driving innovation and new drug development. Graduate-level roles in R&D offer exciting opportunities for scientific exploration and problem-solving.
A specific example is a Graduate Scientist in drug discovery. These individuals are typically involved in various stages of the drug development pipeline, from target identification to preclinical testing.
- Responsibilities: Conducting laboratory experiments, analyzing data, contributing to research reports, and collaborating with a team of scientists.
- Required Skills: Strong scientific knowledge, laboratory skills (e.g., cell culture, molecular biology techniques), data analysis skills, communication skills (written and verbal), and teamwork skills.
- Career Progression: A graduate scientist can progress to more senior roles such as a research associate, senior research scientist, and eventually a principal investigator, leading their own research projects.
Graduate Regulatory Affairs Roles
Regulatory affairs professionals play a critical role in ensuring that pharmaceutical products meet the required safety and efficacy standards set by regulatory bodies. This function is essential for bringing new medications to market.
A specific example is a Regulatory Affairs Associate. This role is typically focused on gathering, organizing, and reviewing documentation related to regulatory submissions.
- Responsibilities: Preparing regulatory documents (e.g., clinical trial reports, new drug applications), ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines, interacting with regulatory agencies, and supporting the overall regulatory strategy.
- Required Skills: Strong understanding of pharmaceutical regulations (e.g., FDA guidelines), attention to detail, strong organizational skills, effective communication skills, and proficiency in using regulatory software.
- Career Progression: An associate can progress to more senior roles like regulatory affairs specialist, regulatory affairs manager, and potentially regulatory affairs director, managing larger regulatory projects or portfolios.
Comparison of Different Career Paths
Choosing a career path in the science and pharmaceutical industry requires careful consideration of personal interests, skills, and potential career growth. This section will explore the diverse options available to graduates, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of different paths, and the skills and qualifications needed for success in each. From research to regulatory affairs, the pharmaceutical landscape offers numerous avenues for passionate individuals.
Research and Development
Research and development (R&D) roles are at the forefront of innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. These roles involve conducting experiments, analyzing data, and developing new drugs or therapies. Success in this area depends on a strong scientific foundation and a dedication to meticulous work.
- Strengths: R&D careers offer the potential for significant impact on human health, driving innovation and contributing to breakthroughs in treatment. These roles often provide opportunities for intellectual stimulation and creative problem-solving. Strong academic background and lab skills are valued. Research positions frequently lead to further studies, academic collaborations, and patents.
- Weaknesses: The R&D field can be highly competitive, with long hours and demanding workloads. There’s no guarantee of success in every project or a swift path to leadership. Funding constraints, regulatory hurdles, and lengthy timelines can also be significant challenges.
- Skills and Qualifications: Strong scientific background, meticulous attention to detail, problem-solving skills, critical thinking, analytical skills, and data interpretation are crucial. Hands-on experience in laboratories, familiarity with scientific software, and knowledge of relevant regulations are also highly desirable.
Regulatory Affairs
Regulatory affairs professionals ensure that new drugs and medical devices meet safety and efficacy standards set by regulatory bodies. Their work is critical in bringing innovative treatments to market, while upholding public safety and ethical considerations. This role involves navigating complex regulatory frameworks and procedures.
- Strengths: Regulatory affairs roles offer stability and a well-defined career path. They often involve working with diverse teams and collaborating with scientists, clinicians, and legal professionals. The work directly impacts public health and contributes to the responsible development of life-saving therapies. Good communication and interpersonal skills are vital.
- Weaknesses: Regulatory affairs can be highly bureaucratic and involve navigating intricate regulatory requirements. This field often requires a significant understanding of legal frameworks and procedures. The nature of the work might not involve hands-on scientific research or product development.
- Skills and Qualifications: Strong communication skills, both written and verbal, are essential. Detail-oriented individuals with strong analytical skills and a good understanding of legal frameworks and pharmaceutical regulations are in high demand. Experience in the pharmaceutical industry or related fields can be a significant advantage.
Clinical Research
Clinical research involves conducting studies to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new therapies in human subjects. This field bridges the gap between laboratory research and patient care, requiring a deep understanding of both medical and scientific principles.
- Strengths: Clinical research roles offer a balance between scientific rigor and patient interaction. These roles often involve direct contributions to improving human health. Good problem-solving skills and an understanding of medical ethics are valued.
- Weaknesses: Clinical research can be challenging and demanding, involving complex ethical considerations and adherence to strict protocols. Project timelines and funding can impact career trajectory. Navigating ethical and regulatory guidelines is paramount.
- Skills and Qualifications: Clinical research requires a strong scientific background, understanding of clinical trials methodology, and an ability to work with diverse teams and patients. Good communication and interpersonal skills are crucial for interacting with patients and collaborators. A strong understanding of medical ethics and regulations is essential.
Comparison Table
| Role | Required Skills | Salary Expectations (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| Research Scientist | Scientific expertise, analytical skills, laboratory experience, attention to detail | £30,000 – £50,000+ (depending on experience and location) |
| Regulatory Affairs Specialist | Strong communication skills, knowledge of regulations, analytical skills, attention to detail | £35,000 – £60,000+ (depending on experience and location) |
| Clinical Research Associate | Scientific knowledge, clinical trial experience, communication skills, attention to detail | £28,000 – £45,000+ (depending on experience and location) |
Salary expectations are approximate and can vary based on factors like experience, location, and specific role responsibilities.
Last Word
In conclusion, graduate jobs in science and pharmaceuticals offer a wide range of possibilities for ambitious individuals. By understanding the industry landscape, honing essential skills, and employing effective job search strategies, graduates can successfully launch rewarding careers. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, from the introductory concepts to the future outlook, and practical advice on job searching and career development.
Remember to tailor your approach to specific roles and leverage networking opportunities to increase your chances of success.

