Employee engagement getting leaders to care – Employee engagement: getting leaders to care is crucial for organizational success. It’s not just about happy employees; it’s about fostering a work environment where individuals feel valued, motivated, and committed to the company’s goals. This exploration delves into the critical role leadership plays in driving engagement, examining effective strategies, common obstacles, and long-term solutions for creating a truly engaged workforce.
The article will define employee engagement, detailing the characteristics of engaged, not engaged, and actively disengaged employees. It will also discuss leadership styles that foster engagement, transparent communication, and the creation of a culture of trust and respect. Furthermore, various methods for measuring employee engagement, including surveys and feedback mechanisms, will be explored. The importance of demonstrating ROI, integrating engagement into leadership development, and promoting engagement across departments will be highlighted.
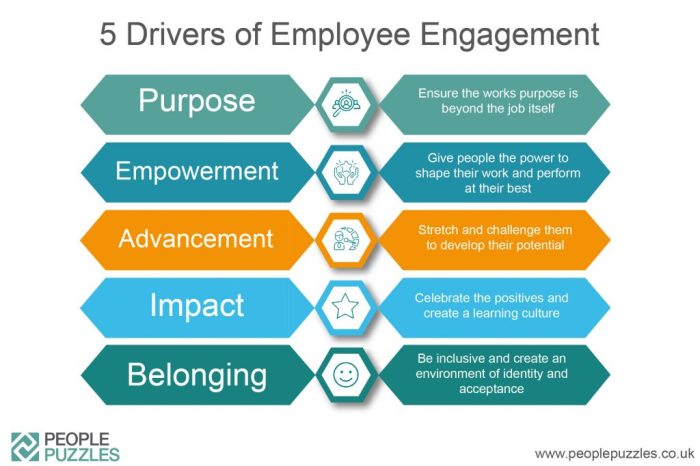
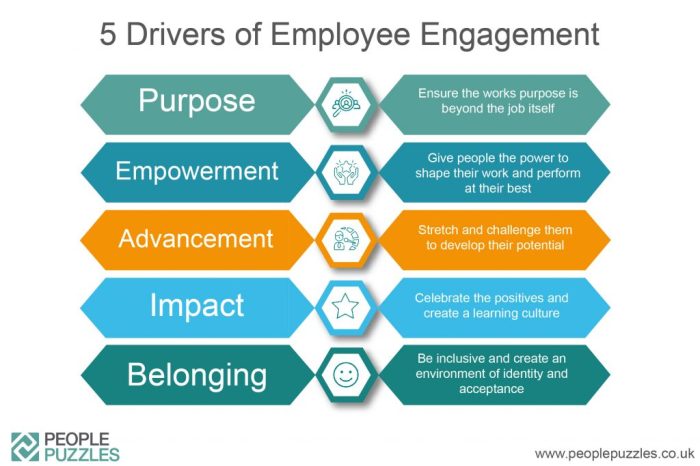
Defining Employee Engagement

Employee engagement is a critical aspect of a thriving workplace. It goes beyond simply having employees show up for work; it encompasses a deep emotional connection to the organization and its goals. Understanding the different levels of engagement is crucial for leaders seeking to cultivate a positive and productive work environment.Engaged employees are more than just happy; they are actively involved and invested in their work and the success of the company.
Their commitment is evident in their daily actions and their desire to contribute meaningfully. This active participation translates into higher productivity, better quality work, and a stronger sense of purpose within the organization.
Defining Engagement Levels
Understanding the spectrum of employee engagement—from fully invested to completely disengaged—is vital for effective leadership. Differentiating between these levels allows managers to tailor their strategies and address specific needs within their teams. This proactive approach enables a more targeted and effective approach to employee well-being and organizational success.
Characteristics of Engaged Employees
Engaged employees are characterized by several key attributes. They are enthusiastic about their work, consistently demonstrate initiative, and actively seek opportunities for growth and development. These employees often go the extra mile, fostering a positive work environment for their colleagues.
- Passion and enthusiasm for their work, evident in their daily interactions and contributions.
- Proactive problem-solving and a willingness to take initiative.
- Strong commitment to the organization’s goals and values.
- A desire to learn and develop their skills, often seeking opportunities for advancement.
- A willingness to collaborate effectively with colleagues and contribute to a positive team environment.
Classifying Employee Engagement States
Employees can be categorized into three distinct engagement states: engaged, not engaged, and actively disengaged. Recognizing these differences is essential for developing targeted strategies to improve overall employee well-being and organizational performance.
| Engagement State | Description | Impact on the Workplace |
|---|---|---|
| Engaged | Highly involved in their work and committed to the organization. They are passionate about their roles and actively contribute to the team’s success. | Increased productivity, higher quality work, stronger team cohesion, and a positive work environment. |
| Not Engaged | Employees who are essentially present but not fully invested in their work or the organization. Their engagement is characterized by a lack of enthusiasm and initiative. | Minimal impact on the workplace. Productivity and quality of work may be average or slightly below average. Team cohesion may be impacted due to a lack of contribution. |
| Actively Disengaged | Employees who are not only uninvolved but actively opposed to the organization’s goals. They are often negative and critical, potentially undermining the morale of their colleagues. | Decreased productivity, lower quality work, negative impact on team morale, and potential damage to the overall work environment. |
The Role of Leadership in Engagement
Leadership isn’t just about delegating tasks; it’s about fostering a culture where employees feel valued, respected, and empowered. Effective leaders recognize that engaged employees are the key to a thriving organization. Their actions ripple through the entire company, impacting everything from individual performance to overall productivity. This section will explore the crucial role leadership plays in creating a truly engaged workforce.Strong leadership sets the tone for the entire organization.
Leaders who prioritize employee well-being and actively cultivate a positive work environment are more likely to see high levels of engagement. Their actions, decisions, and communication all contribute to the overall atmosphere, directly affecting employee morale and motivation.
Leadership Styles that Foster Engagement
Different leadership styles can have vastly different impacts on employee engagement. Transformational leaders, for example, inspire and motivate their teams by setting a compelling vision and empowering individuals to contribute to achieving shared goals. Servant leadership, on the other hand, focuses on understanding and meeting the needs of employees, fostering a supportive and collaborative environment. Effective leaders adapt their style to suit the specific needs of their team and the context of the situation.
Impact of Leadership Actions on Employee Morale
Leadership actions directly influence employee morale. Positive actions, like recognizing and rewarding good performance, build confidence and encourage continued effort. Conversely, negative actions, such as micromanagement or a lack of communication, can quickly erode morale and decrease engagement. The way leaders react to challenges and address conflicts also significantly impacts employee perceptions and attitudes.
Importance of Transparent Communication from Leaders
Open and honest communication is fundamental to building trust and fostering engagement. Leaders who openly share information, actively listen to employee concerns, and provide clear direction create a sense of transparency and shared purpose. This fosters a sense of belonging and reduces ambiguity, allowing employees to understand their role in the organization’s success.
Examples of Leaders Who Successfully Foster Engagement
Many successful leaders have demonstrated the power of fostering employee engagement. Jack Welch, former CEO of General Electric, is often cited for his transformational leadership style, which emphasized employee empowerment and development. His focus on clear communication and challenging teams contributed to a highly engaged workforce. Similarly, leaders like Sheryl Sandberg, known for her leadership roles at Facebook and LeanIn.org, have focused on building inclusive cultures and fostering a sense of community within their organizations.
These examples highlight the importance of visionary leadership and its impact on engagement.
Creating a Culture of Trust and Respect, Employee engagement getting leaders to care
A culture of trust and respect is built on consistent positive interactions and mutual understanding. Leaders who demonstrate respect for their team members, actively listen to their concerns, and create opportunities for open dialogue pave the way for trust to flourish. This trust extends to decisions made, with employees feeling their voices matter and that their opinions are considered.
Employee engagement hinges on leaders who genuinely care. A recent example of a company failing to show that care is Microsoft’s decision to pull support from its Kin program, a program that helped employees with their well-being, as detailed in microsoft turns its back on kin. This highlights the critical need for leadership to prioritize employee well-being, which directly impacts engagement and overall company success.
Such a culture enables employees to feel safe to express ideas and contribute their best work.
Empowering Employees Through Effective Delegation
Effective delegation is a key aspect of empowering employees. Leaders who delegate tasks appropriately, trust their team members’ abilities, and provide necessary support create an environment where employees feel valued and capable. This trust fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, leading to increased motivation and engagement. Delegation should be accompanied by clear expectations, regular feedback, and opportunities for growth.
Measuring Employee Engagement: Employee Engagement Getting Leaders To Care
Understanding employee engagement is crucial for any organization striving to thrive. It’s not just about happy employees; it’s about identifying factors driving motivation, productivity, and overall organizational success. Measuring engagement provides actionable insights into employee experiences, allowing for targeted interventions and improvements.Accurate measurement enables leaders to identify areas needing attention and implement strategies for boosting engagement. This process is continuous and iterative, requiring ongoing assessment and adaptation to maintain a high level of employee well-being and performance.
Different Methods for Measuring Employee Engagement
Various methods exist for measuring employee engagement, each with its strengths and weaknesses. These methods range from formal surveys to informal feedback mechanisms. Careful selection of the appropriate method is critical for obtaining accurate and useful results.
- Surveys: Surveys are a common and structured approach to gathering employee feedback. They offer a comprehensive view of employee attitudes and opinions, allowing for data-driven analysis and comparison across different groups or departments.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups allow for in-depth discussions and exploration of specific engagement topics. This method facilitates deeper understanding of the underlying reasons behind engagement levels and identifies areas needing improvement.
- One-on-One Interviews: In-depth interviews provide personalized insights into employee experiences. These conversations allow for exploring individual perspectives and tailoring strategies to address specific concerns or challenges.
- Pulse Surveys: Short, frequent surveys, known as pulse surveys, enable leaders to track changes in employee engagement over time. These quick checks offer a more dynamic view of engagement and help identify emerging trends or issues.
Employee Feedback Mechanisms
Effective feedback mechanisms are crucial for building trust and fostering open communication. They empower employees to share their experiences, concerns, and suggestions, contributing to a more positive and productive work environment.
- Suggestion Boxes: Suggestion boxes provide a simple and anonymous platform for employees to voice their opinions and offer suggestions. This approach is particularly helpful for gathering diverse perspectives and encouraging input from all levels.
- Employee Resource Groups (ERGs): ERGs provide structured channels for employees to connect with others who share similar backgrounds or interests. These groups offer opportunities for open communication and feedback.
- Feedback Forms: Standardized feedback forms can be used for specific projects or events. They enable collecting organized feedback, allowing for focused analysis and improvements.
- Open Door Policies: Open door policies encourage employees to approach managers directly with concerns or suggestions. This approach facilitates direct communication and promotes a culture of transparency.
Importance of Anonymous Feedback
Anonymity is paramount in fostering honest feedback. Employees are more likely to share honest opinions and concerns without fear of reprisal when feedback mechanisms are anonymous. This is especially true for issues that could potentially impact their careers or relationships with coworkers.
- Encourages Honest Feedback: Anonymity is key to ensuring that employees feel comfortable sharing their true thoughts and feelings. Honest feedback is essential for effective improvements in engagement.
- Reduces Bias: Anonymous feedback reduces the potential for bias or pressure from superiors or peers, allowing for a more accurate representation of employee experiences.
- Increased Participation: Knowing that their feedback will remain confidential encourages more employees to participate in feedback mechanisms.
Metrics Quantifying Engagement Levels
Quantifiable metrics are essential for assessing the effectiveness of engagement initiatives. These metrics provide a clear picture of engagement levels and allow for comparisons across different time periods or groups.
- Employee Turnover Rate: Low turnover rates often indicate high engagement levels, as employees are more likely to stay with a company they value and where they feel engaged.
- Employee Satisfaction Scores: High satisfaction scores demonstrate a positive employee experience, often indicating a high level of engagement.
- Productivity Levels: Higher productivity levels frequently correlate with higher engagement levels, as motivated employees are more likely to be productive.
- Employee Absenteeism: Low absenteeism rates indicate a healthy work environment, potentially correlating with greater employee engagement.
Engagement Survey Design
A well-designed employee survey is critical for collecting accurate and useful data. Carefully crafting questions is paramount to obtaining relevant information that can drive meaningful changes.
Employee engagement hinges on leadership, and getting them to care is key. A recent Senate bill, like the one giving DHS a cybersecurity whip, demonstrates the importance of prioritizing security. Ultimately, leadership commitment to employee well-being and growth directly impacts engagement levels. Strong leadership fosters a positive work environment, which is essential for keeping employees motivated and productive.
| Survey Type | Description | Example Questions |
|---|---|---|
| 360-Degree Feedback | Involves collecting feedback from various stakeholders, including supervisors, peers, and subordinates. | “How effectively does this employee communicate with their team members?” |
| Employee Satisfaction Survey | Focuses on assessing employees’ overall satisfaction with their jobs, work environment, and company culture. | “How satisfied are you with your current job responsibilities?” |
| Engagement Survey | Aims to measure the level of engagement and commitment of employees to the company. | “How likely are you to recommend this company to a friend or colleague?” |
Creating an Employee Survey
A well-structured survey requires careful consideration of question design and survey administration. The goal is to create a survey that is both engaging and yields useful data.
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the goals of the survey and the specific insights you seek to obtain.
- Choose the Right Questions: Select questions that accurately reflect the objectives and target the desired insights.
- Pilot Test: Conduct a pilot test with a small group of employees to identify any issues with the survey’s design and administration.
- Survey Distribution and Administration: Use a secure platform to distribute and administer the survey to all employees.
Strategies for Getting Leaders to Care
Prioritizing employee engagement is no longer a “nice-to-have” but a critical component of organizational success. Leaders who understand and champion engagement create a positive work environment, boost productivity, and foster a strong company culture. This requires a conscious effort to shift mindsets and integrate engagement into the fabric of leadership.Leaders often prioritize tasks that seem more immediately impactful, sometimes overlooking the long-term benefits of a highly engaged workforce.
This requires a strategic approach that demonstrates the direct link between engaged employees and tangible organizational results.
Motivating Leaders to Prioritize Employee Engagement
Leaders need to be convinced that employee engagement isn’t just a feel-good initiative but a powerful driver of business outcomes. Data consistently shows a correlation between high engagement levels and increased profitability, reduced turnover, and improved customer satisfaction. Sharing these statistics with leaders can help them see the value proposition. Creating compelling case studies illustrating how other organizations have benefited from engaged workforces can also be highly effective.
Integrating Engagement into Leadership Development Programs
Integrating employee engagement into leadership development programs is crucial. These programs should explicitly address the skills and knowledge leaders need to foster engagement within their teams. This includes training on active listening, providing constructive feedback, recognizing contributions, and creating a culture of psychological safety. Leaders need to understand that their behaviors directly impact employee engagement levels.
Benefits of Leader Engagement for the Organization
A leader’s commitment to employee engagement has significant positive impacts on the entire organization. A culture of engagement often leads to increased productivity, innovation, and employee retention. This translates to reduced recruitment costs, lower training expenses, and higher quality work output. Furthermore, engaged employees are more likely to be ambassadors for the company, enhancing its reputation and attracting top talent.
Demonstrating the ROI of Engaged Employees
Quantifying the return on investment (ROI) of engaged employees is essential. Metrics such as employee retention rates, productivity levels, customer satisfaction scores, and even reduced absenteeism can be used to illustrate the financial benefits of a highly engaged workforce. Consider creating dashboards that track these key performance indicators (KPIs) over time. Presenting this data in a clear and concise format makes the case for engagement compelling.
Promoting Engagement Across Different Departments
Employee engagement isn’t limited to a single department; it’s a company-wide effort. Leaders across all departments need to be involved and contribute to creating an engaging work environment. This can be achieved through consistent communication, shared goals, and cross-departmental collaboration opportunities. It is important to understand the unique needs and challenges of each department and tailor engagement strategies accordingly.
Importance of Consistent Messaging from Leadership
Leaders must consistently communicate the importance of employee engagement. This messaging should be integrated into all forms of communication, from town halls and emails to one-on-one conversations. A consistent message fosters a clear understanding of the organization’s values and commitment to employee well-being. This consistency reinforces the importance of engagement and builds trust.
Actionable Steps for Leaders to Improve Employee Engagement
- Actively listen to employee feedback and concerns.
- Regularly provide opportunities for recognition and appreciation.
- Establish clear communication channels and foster open dialogue.
- Promote a culture of trust and psychological safety.
- Encourage collaboration and teamwork.
- Create opportunities for professional development and growth.
- Demonstrate fairness and transparency in decision-making.
Effective leadership is key to a highly engaged workforce. These actionable steps, when consistently implemented, can create a positive and productive work environment.
Framework for a Leader Engagement Initiative
A successful leader engagement initiative requires a structured approach. This includes:
- Assessment: Conducting a thorough assessment of the current state of employee engagement and leadership practices.
- Goal Setting: Defining clear and measurable goals for improving engagement levels.
- Action Planning: Developing a detailed action plan with specific strategies and timelines for achieving those goals.
- Implementation: Implementing the chosen strategies and tracking progress toward goals.
- Evaluation: Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of the initiative and making adjustments as needed.
This framework provides a solid foundation for a sustained and successful effort in improving employee engagement from the top down.
Challenges and Obstacles
Cultivating a truly engaged workforce isn’t always straightforward. Obstacles to employee engagement can stem from various sources within an organization, impacting not just individual performance but the overall success of the business. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward developing effective strategies to overcome them. Successfully navigating these obstacles requires a proactive approach and a willingness to adapt to the evolving needs of the workforce.Organizational structure, workplace culture, and leadership support all play critical roles in fostering or hindering employee engagement.
A poorly designed structure can stifle initiative, while a toxic culture can breed resentment and disengagement. Leaders who aren’t committed to employee well-being can create an environment where engagement efforts are doomed to fail. Addressing these factors head-on is essential for building a truly engaged workforce.
Common Obstacles to Employee Engagement
Various factors can impede employee engagement. Lack of clarity on organizational goals, poor communication, and a lack of opportunities for growth and development often contribute to employee disengagement. A lack of recognition for hard work, insufficient resources, and a perceived lack of fairness in treatment can also negatively impact engagement levels.
Employee engagement hinges on leaders who genuinely care. It’s easy to get lost in the demands of the modern workplace, especially when you’re working in what feels like a constant state of surveillance. This is especially relevant in the tech industry, where the “invisible panopticon” of constant monitoring and performance tracking can stifle genuine connection. It’s crucial to remember that engagement isn’t just about perks and policies; it’s about fostering a culture where employees feel valued and heard.
Read more about this phenomenon in the fascinating article “life in technologys invisible panopticon” here to better understand how it affects employee engagement and ultimately, how to encourage leaders to truly care.
- Lack of Clarity on Organizational Goals: Employees need to understand how their work contributes to the overall objectives of the company. Ambiguous or poorly communicated goals lead to a sense of aimlessness and a lack of purpose, hindering engagement.
- Poor Communication: Effective communication is crucial for keeping employees informed, fostering trust, and promoting collaboration. Poor communication creates confusion, misunderstandings, and a lack of transparency, all of which can stifle engagement.
- Limited Growth and Development Opportunities: Employees who feel stagnant in their roles are less likely to be engaged. Opportunities for professional development, skill enhancement, and advancement are vital for maintaining enthusiasm and motivation.
- Insufficient Recognition: Employees want to feel valued for their contributions. A lack of recognition for hard work can lead to feelings of de-motivation and decreased engagement.
- Insufficient Resources: Adequate resources are critical for employees to perform their tasks effectively. A lack of resources, such as tools, training, or support, can lead to frustration and hinder engagement.
- Perceived Lack of Fairness: Employees are more engaged when they perceive fairness and equity in their treatment. Perceived bias, favoritism, or unfair policies can create resentment and lead to disengagement.
Impact of Organizational Structure on Engagement
Organizational structure significantly influences employee engagement. A rigid, hierarchical structure can stifle innovation and autonomy, while a flat, decentralized structure can promote collaboration and empowerment. Understanding the relationship between structure and engagement is crucial for tailoring strategies to improve engagement.
- Hierarchical Structures: These structures can create a sense of distance between employees and leadership, potentially hindering communication and collaboration. This can lead to a feeling of being undervalued and unheard.
- Decentralized Structures: These structures often foster greater autonomy and responsibility, leading to increased ownership and motivation. This can translate to a more engaged workforce.
Impact of Workplace Culture on Engagement
Workplace culture is a powerful determinant of employee engagement. A positive and supportive culture fosters trust, collaboration, and open communication, leading to a more engaged workforce. Conversely, a negative or toxic culture can erode morale and motivation. This is where leadership plays a crucial role.
- Positive Cultures: These cultures foster a sense of belonging, support, and respect. Employees feel valued and empowered, leading to increased engagement.
- Negative Cultures: These cultures often involve negativity, fear, and lack of trust. Employees feel discouraged and demotivated, which can lead to low engagement.
Barriers to Leadership Support of Engagement Initiatives
Leaders play a pivotal role in fostering employee engagement, but certain barriers can impede their support of engagement initiatives. These barriers can stem from a lack of understanding, misaligned priorities, or a perceived lack of value. Addressing these barriers is crucial for success.
- Lack of Understanding: Leaders who don’t fully grasp the importance of employee engagement may not prioritize initiatives designed to improve it.
- Misaligned Priorities: If a leader’s priorities are not aligned with employee engagement, initiatives may be sidelined or overlooked.
- Perceived Lack of Value: Leaders may not see the direct impact of engagement initiatives on the bottom line, leading to skepticism and reduced support.
Solutions for Overcoming Challenges
Implementing solutions to overcome these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach. Clear communication, effective training, and a focus on creating a positive and supportive work environment are crucial elements.
- Implementing clear communication strategies: Establishing clear channels of communication and ensuring that employees are kept informed about organizational goals and progress can greatly improve engagement.
- Providing opportunities for growth and development: Offering training programs, mentorship opportunities, and other avenues for skill enhancement and career advancement can boost employee engagement.
- Creating a positive and supportive work environment: Focusing on fostering a positive and supportive work environment that promotes collaboration, trust, and recognition can significantly increase employee engagement.
Creating a Supportive Work Environment
A positive and supportive work environment is the bedrock of employee engagement. When employees feel valued, respected, and supported, they’re more likely to be invested in their work and contribute to the overall success of the organization. This chapter delves into strategies for building such a supportive environment, recognizing the vital role of recognition and rewards, and understanding the interconnectedness of employee well-being and engagement.A supportive work environment fosters trust, collaboration, and open communication.
This, in turn, leads to increased job satisfaction, reduced stress, and ultimately, higher productivity and retention rates. Creating such an environment is not a one-time event but an ongoing process of building and nurturing positive relationships and systems within the organization.
Building a Positive Work Environment
Creating a positive work environment requires a multifaceted approach that considers various aspects of employee experience. This includes fostering a culture of trust, respect, and open communication where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns. Leaders play a crucial role in setting the tone and demonstrating these values through their actions and interactions. Furthermore, the physical workspace design and organization can contribute significantly to a positive and productive atmosphere.
Elements such as natural light, comfortable seating, and well-organized spaces can improve employee well-being and productivity.
Recognizing and Rewarding Employees
Employee recognition and reward programs are crucial for reinforcing desired behaviors and motivating employees. Recognition can take many forms, from simple verbal praise to formal awards and bonuses. A well-designed program fosters a sense of appreciation and acknowledges the contributions of individual employees, thus boosting morale and engagement. It’s essential that recognition is timely, specific, and sincere.
Examples of Employee Recognition Programs
A variety of programs can effectively recognize employee contributions. These include peer-to-peer recognition platforms where colleagues can commend each other for outstanding work; employee of the month awards; and bonus programs tied to specific performance goals. Formal recognition ceremonies, quarterly or annual awards, and public acknowledgments in company newsletters or announcements can further strengthen the impact of recognition.
Employee Well-being and Engagement
Employee well-being is intrinsically linked to engagement. When employees feel supported in their physical, mental, and emotional well-being, they’re more likely to be engaged and productive. This includes providing resources for stress management, promoting work-life balance, and offering access to wellness programs. A focus on employee well-being is not simply a “nice-to-have” but a crucial component of a thriving and engaged workforce.
Promoting Work-Life Balance
Promoting work-life balance is essential for employee well-being and engagement. Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options or flexible hours, can significantly impact employee satisfaction. Offering opportunities for employees to disconnect from work outside of regular working hours, and providing resources for childcare or eldercare, are additional strategies that support work-life balance.
Components of a Supportive Work Environment
| Category | Description ||—|—|| Culture | Fostering trust, respect, and open communication. || Leadership | Leaders demonstrating values through actions and interactions. || Workspace | Design that considers natural light, comfort, and organization. || Recognition | Timely, specific, and sincere acknowledgment of employee contributions. || Well-being | Resources for stress management, work-life balance, and access to wellness programs.
|| Opportunities | Offering professional development and growth opportunities. |
Workplace Perks
Workplace perks can contribute to a supportive work environment. These perks can range from providing subsidized meals or gym memberships to offering flexible work arrangements, on-site childcare, or employee assistance programs. The specific perks that are most effective will vary depending on the company’s culture and the needs of its employees. For example, a company with a younger, more tech-savvy workforce might find that providing access to high-speed internet and flexible work schedules are more effective than a company targeting a more senior, traditional demographic.
Long-Term Strategies for Engagement
Sustaining employee engagement isn’t a one-time project; it’s an ongoing commitment. A strong engagement strategy requires a long-term vision and consistent effort to build a culture of appreciation, growth, and opportunity. This necessitates a proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential issues before they impact morale and productivity.A successful long-term engagement strategy acknowledges that employee needs and expectations evolve over time.
Organizations must adapt their strategies to meet these evolving needs, ensuring that the initial engagement efforts remain relevant and impactful years down the line. This proactive approach is crucial for maintaining high levels of employee satisfaction and loyalty.
Continuous Feedback and Improvement
Regular feedback mechanisms are essential for identifying areas needing improvement in engagement initiatives. This feedback loop, encompassing both formal and informal channels, allows for a dynamic adjustment of strategies. Continuous feedback enables a data-driven approach to employee engagement, helping organizations to identify and address issues promptly. Regular surveys, focus groups, and one-on-one discussions can provide valuable insights into employee experiences and perceptions.
Analyzing this feedback allows for iterative improvements to policies, programs, and leadership styles, ensuring that the engagement strategy remains relevant and effective over time.
Ongoing Leadership Training
Investing in ongoing leadership training is crucial for sustaining engagement. Leadership development programs equip leaders with the skills to foster a positive work environment and effectively manage their teams. These programs often include training on communication, conflict resolution, emotional intelligence, and effective delegation. This ensures that leaders are equipped to create a culture of trust, respect, and collaboration, which are essential elements of employee engagement.
Examples include coaching and mentoring sessions, workshops on emotional intelligence, and specialized training on communication styles. A strong leader understands the importance of creating an environment where employees feel valued, supported, and empowered.
Employee Development Programs
Employee development is vital for maintaining engagement. Organizations that offer opportunities for skill development and career advancement demonstrate their commitment to employee growth and well-being. Providing employees with access to training programs, mentorship opportunities, and challenging assignments fosters a sense of growth and recognition. This creates a positive feedback loop where employees feel valued, motivated, and invested in their future with the organization.
This could include internal promotions, cross-training initiatives, tuition reimbursement, or specialized training courses. Employees are more engaged when they see a clear path for professional growth within the company.
Roadmap for Maintaining Engagement
A roadmap for maintaining engagement over several years should include clearly defined goals, measurable metrics, and a timeline for achieving them. The roadmap should Artikel the specific steps to be taken to enhance employee experiences, including training, feedback mechanisms, and development opportunities. This structured approach helps to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and ensure the initiative remains focused on the long-term goals.
Key elements of this roadmap include:
- Establish baseline metrics: Understanding current engagement levels allows for accurate measurement of progress over time.
- Set clear goals: Define specific and measurable targets for engagement improvements, ensuring alignment with organizational objectives.
- Develop a phased implementation plan: Breaking down the initiative into smaller, manageable steps allows for better tracking and adjustment.
- Regular reviews and adjustments: Ongoing monitoring and analysis allow for the adaptation of strategies to meet evolving employee needs.
Building an Engaged Organization
Building an engaged organization requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing leadership development, employee growth opportunities, and a culture of recognition and appreciation. These factors work in synergy to foster a positive work environment that drives high levels of engagement and performance.
- Cultivate a culture of trust and transparency: Open communication and clear expectations foster a sense of belonging and shared purpose.
- Promote recognition and appreciation: Regularly acknowledging and rewarding employees’ contributions builds morale and reinforces positive behaviors.
- Foster a sense of community: Encouraging social interaction and team-building activities strengthens relationships and creates a sense of camaraderie.
Engagement Initiative Timeline
A sample timeline for an employee engagement initiative might include:
| Phase | Activities | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Assessment | Conducting surveys, focus groups, and interviews to understand current engagement levels. | Months 1-2 |
| Phase 2: Strategy Development | Developing action plans based on assessment results, outlining specific strategies and goals. | Months 3-4 |
| Phase 3: Implementation | Implementing identified strategies, providing training, and launching initiatives. | Months 5-12 |
| Phase 4: Monitoring and Evaluation | Tracking progress, collecting feedback, and making adjustments to strategies. | Ongoing |
This structured approach ensures that the engagement initiative is well-planned, implemented, and evaluated over a period of time.
Final Conclusion
Ultimately, fostering employee engagement requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses both individual and organizational factors. By understanding the role of leadership, implementing effective strategies, and creating a supportive work environment, organizations can cultivate a culture of engagement that drives success. This article provides a framework for creating a sustained and engaged workforce.






