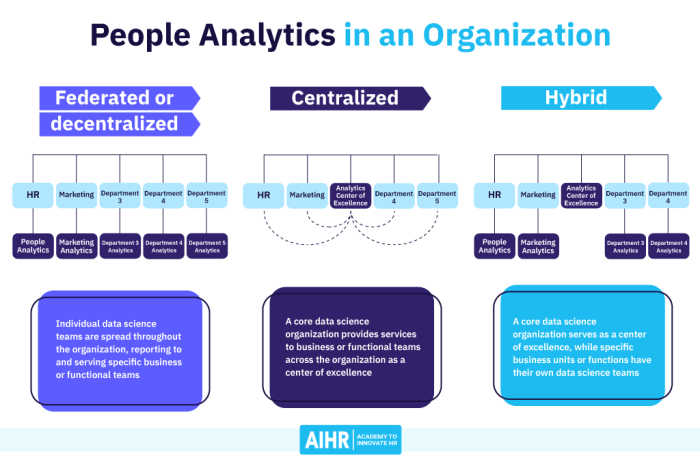
Buying building people analytics – Buying and building people analytics is about understanding your workforce to drive business success. This deep dive explores defining people analytics, crafting a strategy, collecting and prepping data, analyzing insights, and finally, putting those insights into action. We’ll cover the entire process, from initial setup to achieving tangible results. From identifying employee turnover to improving hiring processes, we’ll look at the metrics, data sources, and tools needed to create a robust people analytics program.
Defining Building People Analytics: Buying Building People Analytics

Building people analytics is more than just crunching numbers; it’s about using data-driven insights to improve the employee experience and organizational performance. It’s a strategic approach that leverages data from various sources to understand employee behavior, identify trends, and make informed decisions regarding talent management, recruitment, and overall organizational success. This involves not only gathering data but also analyzing it effectively and implementing actionable strategies based on the findings.Building people analytics differs significantly from other forms of analytics, such as financial or marketing analytics.
While those focus on external factors and market trends, people analytics delves into the internal dynamics of the organization, focusing on employee engagement, productivity, and retention. It’s about understanding what motivates employees, what challenges they face, and how to optimize their performance for the benefit of the entire organization.
Buying and building people analytics is crucial for any company, but the data collection practices of mobile apps raise serious concerns. Recent calls for the FTC to investigate mobile app snooping practices, like the one from Sen. sen wants ftc to take a hard look at mobile apps snooping practices , highlight the ethical dilemmas in the data collection process.
Ultimately, responsible data handling is key for building accurate and reliable people analytics strategies.
Key Differences from Other Analytics
People analytics distinguishes itself by focusing on human capital. It analyzes factors such as employee satisfaction, performance, and retention, in contrast to financial analytics which focuses on profitability and market share, or marketing analytics which examines customer behavior. The data collected and the questions asked are fundamentally different.
Stages in Building a People Analytics Function, Buying building people analytics
Establishing a people analytics function within an organization involves several key stages. The initial phase often focuses on defining clear goals and objectives, aligning the analytics function with the overall organizational strategy. This is crucial to ensure that the insights generated are relevant and impactful. The next stage typically involves data collection and preparation, including identifying appropriate data sources and ensuring data quality.
The final stage emphasizes analysis, interpretation, and implementation of recommendations based on the insights. Effective communication of findings to relevant stakeholders is also essential to drive action and ensure buy-in.
Data Sources in People Analytics
People analytics relies on a variety of data sources to paint a comprehensive picture of the workforce. These include Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) for employee records, performance management systems for tracking individual and team performance, payroll data to identify trends, and survey data to gauge employee satisfaction. Social media listening tools can also provide valuable insights into employee sentiment and culture.
Combining multiple data sources provides a more complete and nuanced understanding of employee behavior and organizational dynamics.
Common People Analytics Metrics
Understanding and tracking key metrics is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of people-related initiatives. The following table Artikels some commonly used metrics in people analytics.
| Metric | Description | Data Source | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Turnover Rate | Percentage of employees leaving the company within a given period. | HRIS, Payroll | Identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement |
| Employee Engagement | Measure of employee satisfaction, commitment, and involvement. | Employee surveys, feedback systems | Assess morale, identify potential issues |
| Employee Performance | Measure of individual or team output. | Performance management systems, project tracking | Identify top performers, areas needing support |
| Time-to-Hire | Average time taken to fill a vacant position. | Recruitment systems, HRIS | Optimize recruitment processes, improve efficiency |
| Diversity and Inclusion Metrics | Measure representation and equity in the workforce. | HRIS, Employee demographics | Identify disparities, foster inclusive environments |
Building a People Analytics Strategy
Crafting a robust people analytics strategy is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage data-driven insights to improve workforce performance and achieve business objectives. This involves a deep understanding of the organization’s unique needs, a clear definition of goals, and a structured approach to data collection, analysis, and implementation. A well-defined strategy will translate into actionable insights that drive tangible results, from optimizing recruitment to enhancing employee engagement.A successful people analytics strategy is not just about collecting data; it’s about using that data to inform decisions and create a positive impact on the workforce and the bottom line.
It requires a meticulous process of defining goals, selecting the right data, analyzing the information effectively, and translating findings into concrete actions.
Developing a Comprehensive People Analytics Strategy
A comprehensive people analytics strategy involves several key steps. Firstly, understanding the organization’s current state of affairs regarding human capital data is paramount. This includes identifying existing data sources, evaluating their quality and completeness, and understanding the limitations. Next, defining specific business objectives and aligning them with people analytics goals is essential. This requires a deep understanding of the business context and a clear articulation of the desired outcomes.
The strategic use of data analysis tools and techniques is also critical, ensuring that the chosen methods are appropriate for the type of data being analyzed.
Aligning People Analytics with Business Objectives
Effective alignment between people analytics and business objectives is crucial for maximizing the impact of initiatives. This involves clearly identifying key business metrics and linking them to specific people analytics goals. For instance, if a company aims to reduce employee turnover, people analytics can be used to identify factors contributing to attrition and develop targeted interventions. This could involve analyzing employee demographics, performance reviews, and feedback data to identify trends and patterns.
Establishing Clear Goals and KPIs for People Analytics Initiatives
Setting clear goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is vital for measuring the success of people analytics initiatives. This involves translating business objectives into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for people analytics. For example, a goal might be to reduce employee turnover by 10% within the next year. This goal can be broken down into smaller, measurable KPIs, such as the number of employees leaving the company each month, or the percentage of employees who rate their work experience as positive.
Data Governance and Security in People Analytics
Data governance and security are paramount in people analytics. Robust data governance policies ensure that data is collected, stored, and used ethically and responsibly. This includes defining clear roles and responsibilities for data management, establishing data quality standards, and implementing data security protocols to protect sensitive employee information. Security measures are critical to maintain confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, is also essential.
Roadmap for Building a People Analytics Function
A roadmap for building a people analytics function from scratch should consider a phased approach. Phase one, focusing on establishing the foundational elements of the function, might include data acquisition, establishing data governance, and building initial analytical capabilities. This phase can take 3-6 months. Phase two, lasting another 6-9 months, would focus on developing specific analytical projects to address business objectives.
The third phase, focusing on scaling and embedding people analytics, could take another 6-12 months. Essential resources include data scientists, analysts, and business leaders who can guide the process and ensure alignment with business objectives.
Relationship Between People Analytics and Business Outcomes
| People Analytics Initiative | Business Outcome | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Improved hiring process | Reduced time-to-hire | Increased efficiency, cost savings |
| Enhanced employee engagement | Increased productivity, reduced absenteeism | Higher profitability, improved employee morale |
| Targeted training and development | Improved employee skills, increased employee retention | Enhanced employee performance, reduced training costs |
| Effective performance management | Increased employee performance, higher quality output | Improved business outcomes, greater efficiency |
Data Collection and Preparation
Building a robust people analytics program hinges on the quality of the data it uses. This phase, data collection and preparation, is critical for ensuring accurate insights and actionable recommendations. Thorough planning and meticulous execution are essential to avoid pitfalls and maximize the value derived from your data.
Best Practices for Data Collection
Effective data collection for people analytics requires a strategic approach. This involves identifying the specific metrics needed to address your organizational goals, choosing appropriate data sources, and ensuring data quality from the outset. Crucially, data should be collected consistently and transparently, minimizing bias and ensuring reliable results. Define clear data collection procedures, including who collects the data, when, and how.
Methods of Data Validation and Cleansing
Data validation and cleansing are vital steps in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your people analytics data. Validation checks the data against predefined rules and standards, identifying inconsistencies or errors. Cleansing, on the other hand, addresses these errors and inconsistencies to improve data quality. Common validation techniques include comparing data across different sources, checking for logical inconsistencies, and confirming that data falls within expected ranges.
Cleansing methods include handling missing values, removing duplicates, and correcting errors.
Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Data privacy and ethical considerations are paramount in any people analytics initiative. Organizations must adhere to relevant data privacy regulations (like GDPR or CCPA) and obtain explicit consent from employees for data collection. Maintaining confidentiality and protecting sensitive employee information are crucial aspects of ethical data handling. Transparency about data usage is also critical to build trust and maintain a positive work environment.
Data Transformation and Preparation for Analysis
Data transformation and preparation are essential steps for making data usable for analysis. Raw data from various sources often needs restructuring, standardization, and formatting before it can be analyzed. This involves converting data formats, unifying inconsistent data structures, and handling missing or erroneous values. Transforming data into a structured format suitable for analysis is critical for ensuring that the data can be used effectively in analytical tools.
Thinking about buying building people analytics? It’s a smart move, but consider this: your new second car could be an e-bike! Check out this article on the environmental and financial benefits. Ultimately, a solid people analytics strategy is still crucial for a thriving company, and those insights can inform your decisions.
Comparison of Data Collection Methods
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surveys | Collecting data through questionnaires. | Gather detailed information; relatively cost-effective for large-scale data collection; can be tailored to specific needs | Potential for bias (response bias, social desirability bias); may have low response rates; difficulty in reaching certain employee groups |
| HRIS Data | Data extracted from the Human Resources Information System. | Comprehensive, readily available, usually consistent; provides historical context | May not contain all the desired information; data may not be fully integrated; requires technical expertise for extraction and manipulation |
| Employee Performance Reviews | Data from performance evaluations and feedback sessions. | Insight into individual employee performance; identifies trends in team performance; can offer specific actionable items for improvement | Potential for subjectivity; may be subject to bias or lack of clarity; not always readily available or structured for analysis |
| Exit Interviews | Gathering data from employees leaving the organization. | Identify key factors contributing to employee turnover; pinpoint pain points in the employee experience; allows for proactive change | Data may be limited to departing employees’ perspective; can be difficult to maintain confidentiality; response rates may be low |
Analyzing People Data
Unleashing the power of people data requires more than just collection; it demands insightful analysis. This phase transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, revealing patterns, trends, and insights that drive informed decisions about your workforce. Effective analysis is crucial for optimizing employee engagement, performance, and retention strategies.Effective people analytics involves understanding the nuances of employee behavior, performance, and experience, and using that knowledge to create a more effective and efficient organization.
The insights gleaned from this analysis can be used to improve hiring practices, enhance employee development, and boost overall organizational productivity.
Different Analytical Techniques
Various analytical techniques are employed in people analytics, each serving a specific purpose. Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing and understanding past employee data. Diagnostic analytics delves deeper, exploring the reasons behind trends and patterns. Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future outcomes, such as employee attrition or performance. Prescriptive analytics goes a step further, recommending actions to improve future outcomes.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
Identifying trends and patterns in people data involves careful examination of key metrics and indicators. Techniques such as data visualization, including charts and graphs, help identify anomalies and patterns. Statistical methods like correlation analysis reveal relationships between variables, such as employee tenure and performance. These methods can reveal trends like increased employee turnover in specific departments or correlations between training programs and performance improvements.
Statistical Models and Machine Learning
Statistical models and machine learning play a vital role in people analytics. Regression models can analyze the relationship between different variables, helping predict employee performance or identify factors contributing to turnover. Clustering techniques group employees with similar characteristics, which can help in targeted interventions and personalized development plans. Machine learning algorithms, like decision trees and support vector machines, can identify complex patterns in data that might be missed by traditional methods.
For example, a machine learning model could identify characteristics of employees who are most likely to leave the company, allowing proactive measures to be implemented.
Interpreting Results
Interpreting results from people analytics projects requires careful consideration of context and limitations. Results should be presented in a clear and concise manner, using visualizations to communicate key findings effectively. Interpretations should always consider external factors and potential biases in the data. For example, a significant increase in employee turnover in one department might be due to a change in management rather than a problem within the department itself.
Buying and building people analytics is a crucial part of any successful business, especially when trying to understand employee engagement and performance. Interestingly, the recent HTC updates, like the ones featured in their new Desire phones, with a revamped Sense UI htc gives sense ui a facelift in new desire phones , highlight the importance of user interface design.
Ultimately, a strong people analytics strategy is key to a positive company culture, mirroring the user-centric approach evident in these phone updates.
Therefore, it’s crucial to consider the broader context when interpreting results.
Tools for Analyzing People Data
Various tools facilitate people data analysis, offering different functionalities and features. Software like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense provide visualization capabilities for exploring data and identifying trends. Statistical software packages like R and Python offer advanced analytical techniques and model building. Specialized HR analytics platforms provide pre-built dashboards and reports, simplifying the process of analyzing employee data.
- Tableau: A popular data visualization tool that allows for creating interactive dashboards and reports, providing insights into employee data through various charts and graphs.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s business intelligence tool, offering a user-friendly interface for data exploration and analysis, useful for creating reports and visualizing trends in employee data.
- Qlik Sense: A data visualization and analytics platform that allows users to explore data in various ways, providing a comprehensive view of employee data and trends.
- R: A programming language and environment for statistical computing and graphics, widely used in people analytics for building complex models and conducting statistical analyses.
- Python: A versatile programming language with extensive libraries like Pandas and Scikit-learn, suitable for data manipulation, statistical modeling, and machine learning tasks in people analytics.
- HR Analytics Platforms: Specialized software platforms designed for HR data analysis, often providing pre-built dashboards and reports for common HR metrics, offering a streamlined approach to analyzing employee data.
Implementing and Using Insights
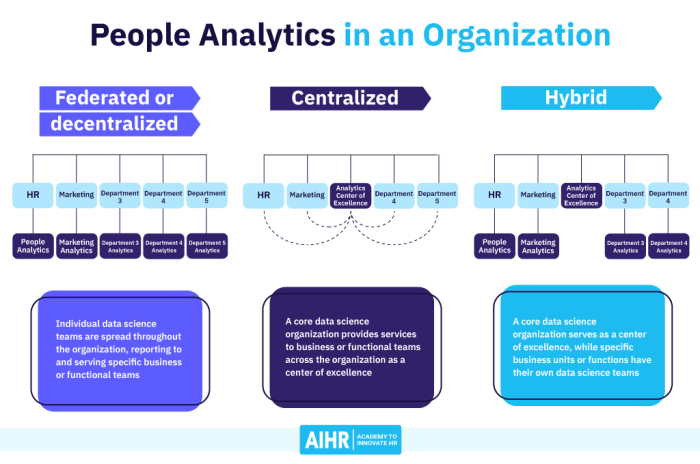
Turning people analytics data into tangible results requires careful implementation. It’s not enough to gather and analyze data; the insights gleaned must be translated into actionable strategies that drive positive change within the organization. This involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on communication, collaboration, and a clear understanding of how to effectively present the findings to key stakeholders.
Steps in Implementing People Analytics Insights
Implementing people analytics insights is a multi-stage process. First, identify specific areas where the insights can create value. Then, develop clear and measurable goals that directly link the insights to desired outcomes. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Subsequently, create a detailed action plan outlining the steps needed to achieve the goals.
Finally, monitor the progress towards these goals and adapt the plan as needed. This iterative process ensures the insights are effectively applied and provide continuous improvement.
Importance of Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are critical for successful implementation. People analytics insights are often complex and require clear explanations to diverse audiences. Open dialogue with stakeholders is essential for understanding their perspectives and concerns, and for tailoring the communication strategy to their specific needs. A collaborative approach involving HR, managers, and other relevant departments ensures buy-in and shared ownership of the implementation process.
This shared understanding of the insights and their potential impact creates a supportive environment for change.
Presenting People Analytics Findings to Stakeholders
Presenting findings to stakeholders should be tailored to their specific needs and technical understanding. Use visual aids such as charts, graphs, and dashboards to present complex data in an easily digestible format. Focus on clear, concise communication, highlighting the key takeaways and their implications for the organization. Clearly articulate the problem the insights address, the proposed solution, and the expected benefits.
This clear and concise approach ensures that stakeholders understand the value proposition of the insights and can effectively support the implementation process.
Translating Insights into Actionable Strategies
People analytics insights provide a wealth of information about employee behavior, performance, and engagement. This data can be used to develop tailored strategies that address specific issues and enhance overall organizational performance. For example, if the analysis reveals high employee turnover in the sales department, a potential strategy could involve implementing a new training program for sales representatives.
The training program could focus on improving sales techniques, product knowledge, and customer service skills. Other potential actionable strategies include adjusting compensation and benefits, providing opportunities for career advancement, and improving the work environment.
Correlation Between People Analytics Insights and Organizational Performance
| Insight | Actionable Strategy | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| High employee turnover in the sales department | Implement a new training program for sales representatives and offer incentives for high performers | Reduced turnover, improved sales performance, and increased customer satisfaction |
| Low employee engagement in the marketing team | Implement team-building activities and offer opportunities for skill development | Increased engagement, improved team collaboration, and higher productivity |
| High absenteeism rate among customer service representatives | Analyze factors contributing to absenteeism (e.g., workload, work-life balance) and implement flexible work arrangements, and offer wellness programs | Reduced absenteeism, improved service quality, and enhanced employee well-being |
| Skills gap in the IT department | Implement a comprehensive training program to upskill employees and explore options for external talent acquisition | Bridged skills gap, improved project completion rates, and enhanced efficiency |
Final Review
In conclusion, building a people analytics function is a powerful way to gain a competitive edge. By understanding your workforce data, you can make strategic decisions, improve employee engagement, and boost overall business performance. This comprehensive guide provides a framework for building a successful people analytics program, from defining your goals to implementing actionable strategies. Remember that data is only valuable when it’s used to create positive change.
Let’s unlock the potential within your organization!

