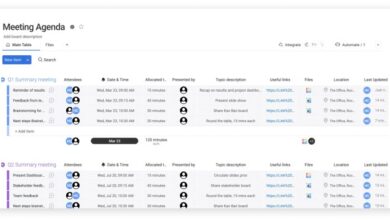
Project management meeting agenda: This guide dives deep into crafting effective project management meetings. From defining the purpose of the meeting to managing discussions and post-meeting follow-up, we’ll cover everything you need to run successful, productive sessions. This isn’t just about creating a list of items; it’s about optimizing your entire project process.
We’ll explore different agenda structures, from bullet points to numbered lists, examining their strengths and weaknesses. We’ll also delve into preparing for the meeting, outlining the crucial steps in gathering materials and ensuring attendees are prepared. Effective meeting management techniques, including strategies for time management and handling unexpected issues, will also be addressed. Finally, the post-meeting process, including creating and distributing minutes and tracking action items, will be Artikeld to maximize the impact of each meeting.
Defining the Meeting Agenda
A project management meeting agenda is a structured Artikel of the topics and activities to be discussed during a meeting. It serves as a roadmap, ensuring the meeting stays focused and productive. It’s crucial for maintaining efficiency and achieving project goals. A well-defined agenda helps to allocate time effectively and prevent unnecessary tangents.A well-organized agenda is essential for successful project management.
It enables project teams to discuss key issues, make critical decisions, and move the project forward in a coordinated and efficient manner. Without a clear agenda, meetings can easily become disorganized and unproductive, wasting valuable time and resources.
Key Components of a Well-Structured Agenda
A well-structured project management meeting agenda comprises several essential components. These elements collectively contribute to a productive and efficient meeting. These components ensure the meeting stays on track, facilitating discussion of critical issues and decisions, thereby moving the project forward.
- Date and Time: Specifies the exact date and time of the meeting, facilitating accurate scheduling and preparation.
- Attendees: Lists all individuals invited to the meeting, ensuring everyone relevant is present and informed.
- Meeting Objective: Clearly states the purpose of the meeting, guiding the discussion and ensuring focused efforts.
- Action Items: Artikels specific tasks assigned to individuals, ensuring accountability and timely completion.
- Discussion Points: Provides a list of topics to be discussed, focusing the meeting on essential matters.
- Materials: Specifies any documents or presentations required for the meeting, ensuring all necessary information is available.
- Estimated Time Allocation: Allotting specific time slots for each agenda item, maintaining a reasonable timeframe for completion.
Importance of an Agenda for Project Success
A project management agenda plays a pivotal role in achieving project success. A well-defined agenda keeps the team focused on the project’s objectives, ensuring that everyone is on the same page. It minimizes the potential for misunderstandings and disagreements, promoting efficient decision-making and task allocation. It streamlines the entire project process, making it more manageable and productive.
Types of Project Management Meetings and Their Agendas
Different types of project management meetings have specific agenda structures, catering to the unique needs of each meeting.
- Status Meetings: Focus on project progress, highlighting achievements and challenges. The agenda typically includes a brief overview of recent activities, discussion of roadblocks, and updates on key tasks. This is often a concise agenda focusing on immediate progress.
- Planning Meetings: Designed for strategic planning and decision-making. The agenda might include detailed discussions of project scope, schedule, budget, and resource allocation. This necessitates more in-depth analysis and detailed discussions.
- Problem-Solving Meetings: Aim to identify and address issues impacting project progress. The agenda typically focuses on the problem at hand, proposing potential solutions, and determining the best course of action. The objective is to efficiently resolve the problem and get the project back on track.
Examples of Project Management Meeting Agendas
The structure of a project management meeting agenda varies across different project phases.
- Initiation Phase: The agenda for the initiation phase focuses on defining the project’s scope, objectives, and key stakeholders. This phase establishes the foundation for the project’s success. The agenda should include discussions of project goals, initial estimations, and potential risks.
- Planning Phase: During the planning phase, the agenda centers on developing detailed project plans, including schedules, budgets, and resource allocation. The agenda should incorporate detailed task breakdowns, dependencies, and risk assessments.
- Execution Phase: In the execution phase, the agenda should cover progress updates, issue resolution, and task assignments. It should address potential delays and deviations from the project plan, allowing for proactive adjustments.
- Monitoring and Controlling Phase: The agenda for this phase involves tracking project progress, identifying deviations, and taking corrective actions. The agenda should be focused on progress reports, performance analysis, and risk management.
- Closure Phase: The agenda for the closure phase centers on finalizing deliverables, conducting post-project reviews, and documenting lessons learned. It should include the review of project outcomes and performance, and the finalizing of documentation.
Essential Elements of a Project Management Meeting Agenda
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Date/Time | Specific date and time of the meeting. |
| Attendees | List of individuals invited to the meeting. |
| Meeting Objective | Clear statement of the meeting’s purpose. |
| Action Items | Specific tasks assigned to attendees. |
| Discussion Points | List of topics to be discussed. |
| Materials | Documents or presentations required for the meeting. |
| Estimated Time Allocation | Time allotted for each agenda item. |
Agenda Structure and Content

Crafting a project management meeting agenda is crucial for effective communication and decision-making. A well-structured agenda ensures that all critical items are addressed, fostering a productive and focused meeting. This section delves into the intricacies of agenda design, from its structure to essential components.
Agenda Structure for Project Management Meetings
A well-organized agenda streamlines the project management meeting, facilitating efficient discussions and decisions. The structure should mirror the project’s lifecycle, encompassing planning, execution, monitoring, and closure stages. A typical project management meeting agenda will follow a logical flow, addressing key issues in a structured and methodical manner.
Typical Project Management Meeting Agenda Template
This template offers a structured framework for project management meetings. It is adaptable to various project phases and specific needs.
- Meeting Overview: Introductions, brief project update, and any necessary housekeeping items.
- Review of Action Items from Previous Meeting: Addressing outstanding tasks and responsibilities from the prior meeting, confirming completion or rescheduling.
- Project Status Update: Presenting a comprehensive overview of the project’s current status, including progress against milestones, key achievements, and challenges encountered. This should incorporate visual aids like charts and graphs, if applicable.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Identifying potential risks impacting the project and discussing mitigation strategies. Highlighting any emerging risks and their potential impact on the project schedule or budget.
- Issue Resolution: Addressing any project-related issues, outlining solutions, and assigning responsibilities. This section should focus on finding solutions and actionable steps.
- Decision Making: Presenting key decisions made since the last meeting and any decisions needing to be made in the current meeting. This should include the rationale behind the decisions.
- Planning for Next Steps: Outlining the tasks for the upcoming period, including assigning responsibilities and setting deadlines. This should detail the planned actions, deadlines, and responsible parties.
- Wrap-up and Action Items: Summarizing key decisions and assigning action items for the next meeting. This section ensures clarity and accountability.
Importance of Clear and Concise Language
Precise language in agenda items is paramount for effective communication. Ambiguous or overly complex wording can lead to misunderstandings and hinder productive discussions. Using clear, concise language ensures that everyone understands the purpose and scope of each agenda item. This is crucial for successful decision-making.
So, prepping for that project management meeting agenda? Don’t forget the crucial security element. Modern gadgets, like smartphones and tablets, are increasingly used in the workplace, but this also opens up potential security risks, like inadvertently exposing sensitive information during a project meeting. For example, did you know that how mobile gadgets can tear a hole in breach disclosures can be a serious issue?
Ultimately, your meeting agenda needs to consider the security protocols for mobile devices to prevent any breaches. This is a vital aspect to keep in mind when scheduling your next project management meeting.
Logical Flow of the Agenda
A well-structured agenda follows a logical sequence, moving from introductory items to more detailed discussions. Items are presented in a way that facilitates efficient progress through the agenda.
Agenda Formats
Different formats can be used to present the agenda. Choosing the appropriate format depends on the meeting’s complexity and the specific needs of the project.
| Format | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Bullet points | Concise and easy to read; visually appealing. | Can lack structure and organization, potentially leading to missed items or disjointed discussions. |
| Numbered list | Provides a clear order and structure, allowing for easy tracking of items. | Can feel rigid and less flexible for adjustments during the meeting. |
| Paragraph format | Allows for detailed explanations and context. | Can be less visually appealing and more difficult to scan quickly. |
Preparing for the Project Management Meeting
Effective project management meetings hinge on meticulous preparation. A well-prepared team ensures efficient use of meeting time, focused discussions, and clear action items. This section delves into the critical steps for ensuring your project meetings are productive and successful.Preparing for a project management meeting is more than just showing up; it’s about actively engaging with the agenda and anticipating potential roadblocks.
By proactively gathering necessary materials and anticipating participant needs, you pave the way for a smooth and productive session.
Preparing Meeting Materials
Thorough preparation of materials is crucial for a productive meeting. This includes gathering relevant documents, data, and any supporting information Artikeld in the agenda. The key is to anticipate the information needed for discussion and ensure it’s readily available.
- Gather Documents: Collect all pertinent documents, reports, presentations, and any other materials referenced in the agenda. This might include project plans, risk assessments, financial reports, or meeting minutes from previous sessions. Ensure all participants have access to the required documents in advance, ideally through a shared online platform.
- Compile Data: If the meeting involves data analysis, collect and organize relevant data sets. Present data in a clear and concise format, such as charts or graphs, to facilitate understanding and discussion.
- Prepare Visual Aids: If presentations are required, prepare slides or other visual aids in advance. Use visuals to clarify complex information and maintain engagement.
Anticipating Potential Issues
Anticipating potential issues and formulating contingency plans is a proactive approach to successful project management meetings. By anticipating potential problems and developing solutions beforehand, you can maintain composure and keep the meeting on track.
- Identify Potential Roadblocks: Review the agenda and identify potential roadblocks or challenges that could arise during the meeting. This may include disagreements, delays, or unexpected information. Examples could be a critical resource unavailable or a new piece of legislation impacting project timelines.
- Develop Contingency Plans: For each potential issue, develop a contingency plan outlining alternative solutions. This allows the team to remain flexible and adapt to unforeseen circumstances. For instance, if a critical stakeholder is absent, a backup plan for addressing their concerns must be prepared.
Preparing Participants for Effective Participation
Preparing participants beforehand significantly impacts the meeting’s effectiveness. This involves ensuring participants understand the agenda, relevant materials, and their roles in the discussion.
- Communicate the Agenda: Clearly communicate the agenda to all participants in advance. This allows them to prepare relevant information and contribute effectively to the discussion.
- Assign Roles: Assign roles or responsibilities to participants to ensure a clear understanding of their contribution to the meeting. This helps to keep discussions focused and on track. Examples of roles include note-taker, facilitator, or content contributor.
- Encourage Pre-Meeting Preparation: Encourage participants to review relevant documents and prepare questions in advance. This fosters active participation and facilitates more in-depth discussions.
Reviewing Previous Meeting Minutes and Action Items
Reviewing previous meeting minutes and action items is essential for maintaining project momentum and ensuring accountability. This step helps to identify any outstanding issues and ensure that previously agreed-upon actions have been completed.
- Review Minutes: Carefully review the minutes from the previous meeting. Identify any outstanding action items and ensure they are tracked and completed.
- Follow Up on Action Items: Follow up with individuals responsible for action items to confirm completion and gather any relevant updates.
Organizing Relevant Documents
Organizing relevant documents ensures easy access and efficient use of meeting time. This includes creating a clear filing system and providing copies to participants as needed.
- Develop a Filing System: Establish a clear filing system for all project documents. This will make it easy to locate information quickly and efficiently. Use a system that ensures clarity and ease of access.
- Prepare Meeting Materials: Prepare copies of relevant documents and materials for each participant. Ensure all participants have the necessary information in advance, ideally through a shared online platform or a physical binder.
Managing the Meeting
Project management meetings are crucial for staying on track. Effective meeting management ensures alignment, efficient problem-solving, and successful project execution. A well-managed meeting keeps everyone engaged and focused on the agenda, maximizing the value of the time spent.
Adhering to the Agenda
Meeting agendas are essential roadmaps for project progress. A well-structured agenda provides a framework for productive discussion. Following the agenda ensures that all key topics are addressed and prevents digressions. Strict adherence helps to stay on schedule and within the allotted time. This clarity prevents wasted time and ensures that everyone’s contributions are valuable and pertinent to the agenda’s objectives.
Facilitating Discussions and Decision-Making
Effective facilitation is crucial for productive meetings. A skilled facilitator guides discussions, encourages participation from all attendees, and keeps the conversation focused on the agenda items. This involves actively listening to different perspectives, ensuring all voices are heard, and managing disagreements constructively. The facilitator should create a safe environment for open dialogue, leading to well-informed decisions.
Strategies for Facilitating Discussions
A facilitator’s role involves guiding discussions, not dominating them. Active listening is key to understanding diverse perspectives. Encouraging participation from quiet members is equally important. Summarizing key points and rephrasing questions in simpler terms helps clarify misunderstandings. The facilitator should be adept at maintaining a respectful atmosphere.
This prevents conflict and fosters a collaborative environment.
Common Pitfalls in Managing Project Management Meetings and Solutions
Meetings can falter due to various factors. Lack of preparation by attendees often leads to unproductive discussions. Off-topic tangents can easily derail a meeting. Poor time management can also contribute to ineffective meetings. Addressing these pitfalls requires proactive strategies.
Facilitators should clearly communicate the meeting’s purpose and agenda beforehand. Timeboxing each discussion point prevents tangents and keeps the meeting on schedule.
Managing Time Effectively During the Meeting
Time management is critical for efficient meetings. Each agenda item should have a designated time frame. Sticking to the schedule prevents delays and ensures that all important topics receive adequate attention. Using timers or visual aids can help keep the meeting on track. If a discussion extends beyond its allocated time, consider postponing the discussion to a future meeting or prioritizing to move on.
Handling Unexpected Issues
Unexpected issues can arise during project management meetings. A prepared facilitator can address these effectively. If a significant issue arises, the facilitator should acknowledge it, document the issue, and propose a course of action. This might involve postponing the meeting, scheduling a follow-up session, or assigning a team to investigate the matter. Flexibility and adaptability are essential.
Role of the Meeting Facilitator in Ensuring Agenda Adherence
The facilitator plays a critical role in keeping the meeting on track. The facilitator must actively monitor the discussion and redirect conversations if they stray from the agenda. By reminding participants of the meeting’s purpose and agenda, the facilitator keeps the discussion focused. This keeps the meeting productive and achieves its objectives.
Managing Different Types of Meeting Participants
Different participants have varying communication styles. A facilitator must adapt their approach to accommodate different personalities. Enthusiastic participants may need to be gently guided to maintain focus. Quiet participants should be encouraged to share their insights. Understanding these nuances allows for more inclusive and effective meetings.
Post-Meeting Actions
Following a productive project management meeting, the crucial next step is to ensure that all agreed-upon actions are implemented effectively. This section Artikels the essential post-meeting procedures to ensure the project stays on track and achieves its objectives. A well-defined follow-up process translates to a smoother project execution, minimizing delays and maximizing efficiency.A strong post-meeting action plan ensures that decisions made in the meeting are not forgotten and that everyone involved understands their responsibilities.
Planning a project management meeting agenda can be tricky, but it’s crucial for efficiency. Staying ahead of the curve, like Verizon’s recent decision to phase out some 4G handsets, verizon tips its 4G handset hand requires careful consideration of the impact on our team’s current projects. Ultimately, a well-structured agenda will ensure productive discussions and keep everyone on track.
This proactive approach strengthens team collaboration and accountability, fostering a culture of shared responsibility for project success.
Documenting Meeting Outcomes and Decisions
Effective documentation of meeting outcomes and decisions is paramount. This ensures that everyone is on the same page and that future reference points are available. It prevents misunderstandings and ensures that the project stays aligned with the agreed-upon goals. Thorough documentation also serves as a valuable historical record, allowing for analysis of past performance and improvements for future projects.
Creating Meeting Minutes
Meeting minutes are a comprehensive record of the discussion, decisions, and action items arising from the meeting. They serve as a reference point for all attendees and stakeholders. A well-structured template facilitates a clear and concise summary of the meeting.
- Date and Time: The specific date and time the meeting was held.
- Attendees: A list of all participants who attended the meeting.
- Meeting Subject: A brief description of the meeting’s purpose.
- Discussion Points: A summary of the key topics discussed, including relevant context and background information.
- Decisions: A clear articulation of all decisions made, including who is responsible for implementing them.
- Action Items: A list of specific tasks that need to be completed, along with assigned owners, due dates, and brief descriptions.
- Next Steps: A summary of the planned follow-up actions and the next scheduled meeting.
Distributing Meeting Minutes and Action Items
Prompt distribution of meeting minutes and action items is critical. This ensures that all stakeholders are informed of the decisions and their associated responsibilities. The method of distribution should be chosen based on the project’s needs and communication preferences.
Just wrapped up a productive project management meeting, focusing on streamlining workflows. The discussion naturally shifted to the interesting dilemma of Sony’s PS3 strategy, particularly regarding their decision to end support. It’s a fascinating case study, similar to the challenges faced by businesses when making difficult choices regarding discontinued product support, like is Sony playing a dangerous game with PS3 customers.
Overall, the meeting reinforced the importance of careful planning and proactive communication in managing any project, especially when dealing with potential pitfalls like those seen in the console market.
- Email: A reliable and widely used method for disseminating information.
- Project Management Software: Utilizing project management tools to centralize and track action items, making them easily accessible to all team members.
- Shared Document Platforms: Facilitates collaborative editing and provides a single source of truth for the project’s documentation.
Tracking Action Item Completion and Deadlines
Tracking action item completion and deadlines is essential to monitor project progress. A dedicated system, whether it’s a spreadsheet or a project management tool, is vital for this task. This allows for timely identification of potential roadblocks and ensures proactive intervention to prevent delays.
- Status Updates: Regular updates from assigned owners regarding the status of their action items.
- Progress Reports: Scheduled reports outlining the progress of each action item, allowing for timely intervention.
- Reminders: Automated reminders for upcoming deadlines.
Importance of Follow-up Actions for Project Success
Follow-up actions are essential for successful project completion. They ensure that decisions are implemented, tasks are completed, and the project stays on track. This proactive approach mitigates risks and fosters a culture of accountability within the project team. The proactive management of action items ensures that the project remains on schedule and that resources are effectively allocated.
Agenda Examples and Illustrations
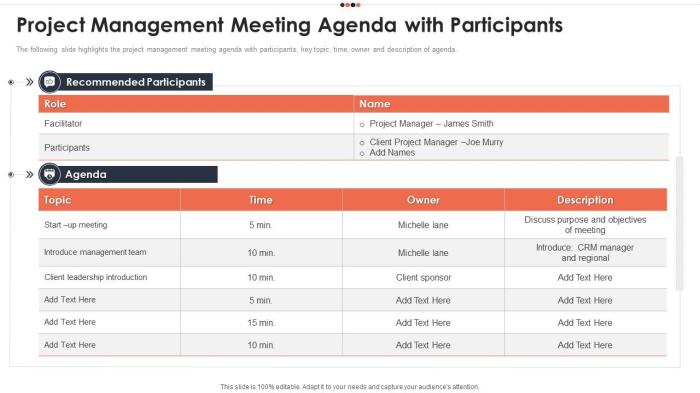
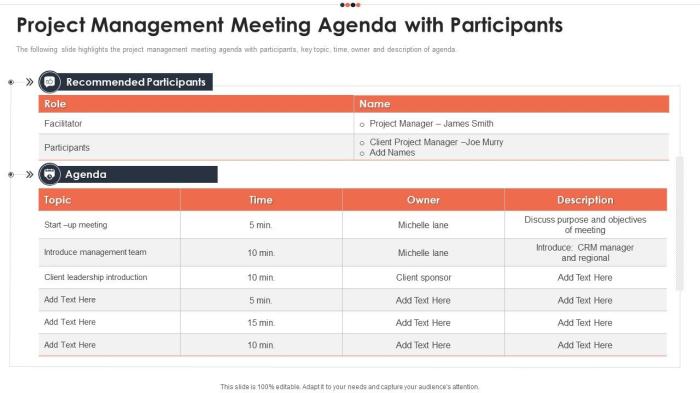
Crafting effective project meeting agendas is crucial for successful project management. A well-structured agenda ensures clarity, focus, and efficient use of everyone’s time. It sets the stage for productive discussions and facilitates decision-making. This section provides concrete examples of project meeting agendas for various stages, highlighting key elements and visual presentation strategies.This section dives into practical examples of project meeting agendas, demonstrating how to structure them for different project phases.
These examples serve as templates, adaptable to specific project needs and contexts.
Project Initiation Meeting Agenda
A project initiation meeting sets the foundation for the entire project. This meeting establishes project goals, scope, and key stakeholders.
- Introduction and Welcome (5 minutes): Review project overview, welcome participants, and introduce meeting objectives.
- Project Overview (10 minutes): Present the project background, goals, and anticipated outcomes. Include high-level project timelines and key milestones.
- Stakeholder Identification and Roles (15 minutes): Identify key stakeholders, their roles, and responsibilities. Clarify communication channels and expectations.
- Project Scope Definition (20 minutes): Define project boundaries, deliverables, and acceptance criteria. Use a visual aid like a project scope statement or flowchart.
- Risk Assessment (10 minutes): Identify potential risks and mitigation strategies. A simple risk register table is helpful here.
- Next Steps and Action Items (10 minutes): Artikel immediate actions, responsibilities, and deadlines. Create an action items list.
- Q&A and Closing (5 minutes): Address any questions or concerns. Confirm meeting follow-up actions and next steps.
Project Planning Meeting Agenda
Project planning meetings focus on detailed project plans, resource allocation, and task breakdowns.
- Review of Project Initiation Meeting Outcomes (10 minutes): Recap decisions made during the initiation phase to ensure alignment and consistency.
- Detailed Project Schedule Development (20 minutes): Develop a detailed project schedule with tasks, dependencies, and deadlines. Use a Gantt chart or project management software.
- Resource Allocation (15 minutes): Assign resources (personnel, budget, materials) to project tasks. Visualize resource allocation using a table.
- Risk Management Plan (15 minutes): Elaborate on the risk assessment from the initiation meeting. Detail contingency plans and risk response strategies.
- Communication Plan (10 minutes): Artikel the communication plan for the project, including frequency, channels, and responsible parties.
- Action Items and Next Steps (10 minutes): Confirm action items, responsibilities, and deadlines for tasks assigned to specific team members.
- Q&A and Closing (5 minutes): Address any questions or concerns and finalize meeting actions.
Project Execution Meeting Agenda
Project execution meetings monitor progress, address issues, and ensure adherence to the project plan.
- Progress Review (15 minutes): Review the project’s progress against the planned schedule. Use project dashboards and charts.
- Issue Resolution (20 minutes): Address any roadblocks or challenges encountered during project execution. Record and prioritize issues.
- Resource Management (15 minutes): Review resource utilization and allocation. Ensure resources are available and efficiently used.
- Communication Updates (10 minutes): Review and discuss recent communication updates and feedback.
- Action Items and Next Steps (10 minutes): Clarify action items, responsibilities, and deadlines.
- Q&A and Closing (5 minutes): Address any questions and concerns.
Project Monitoring Meeting Agenda
Project monitoring meetings track project performance and identify deviations from the plan.
- Performance Reporting (20 minutes): Review project performance metrics and KPIs against the planned targets. Use visual aids like charts and graphs.
- Variance Analysis (15 minutes): Analyze any deviations from the project plan and determine the cause. Use variance analysis tools.
- Risk Review (10 minutes): Assess any new or emerging risks and update the risk register.
- Schedule Update (10 minutes): Review and update the project schedule based on the current progress and any changes.
- Action Items and Next Steps (10 minutes): Assign action items and set deadlines for addressing any identified issues.
- Q&A and Closing (5 minutes): Address any questions and finalize meeting actions.
Project Closure Meeting Agenda
Project closure meetings formally end the project and document lessons learned.
- Project Completion Review (15 minutes): Verify all deliverables have been completed and accepted.
- Lessons Learned (15 minutes): Identify lessons learned throughout the project lifecycle and document them for future projects.
- Project Closure Documentation (15 minutes): Review and finalize project documentation, including the final report, project archive, and any other required materials.
- Team Recognition (5 minutes): Acknowledge and appreciate the team’s efforts and contributions.
- Q&A and Closing (5 minutes): Address any questions and finalize meeting actions.
Visual Elements of an Agenda
Visuals are essential for an effective agenda. Use a clear, concise title for each section. Include the date, time, and location of the meeting. Organize agenda items logically, grouping related topics. Use bullet points or numbered lists for clarity.
Include a timeline of activities, clearly defining start and end times for each item. A table for action items is helpful for tracking responsibilities and deadlines.
Presenting the Agenda Visually, Project management meeting agenda
Present the agenda in a professional, easy-to-read format. Use a consistent font and color scheme. Avoid clutter; keep the design clean and uncluttered. Consider using a slide deck or a document format. Ensure the agenda is easily accessible to all participants.
Final Conclusion: Project Management Meeting Agenda
In conclusion, a well-structured project management meeting agenda is essential for project success. This guide has provided a roadmap for crafting, preparing for, and managing meetings effectively. By understanding the different stages and incorporating the tips provided, you’ll be equipped to lead productive meetings that drive your projects forward. Remember, a well-managed meeting translates to clear communication, timely decisions, and ultimately, a successful project outcome.