Work experience key to tackling skills shortages is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving job market. Industries face significant gaps in crucial skills, impacting businesses and the economy. From technology to healthcare, the demand for specific expertise often outpaces the supply, highlighting the urgent need for practical, hands-on learning. This article explores how work experience can bridge this skills gap, complementing traditional education and training, and preparing individuals for future career success.
This article delves into the multifaceted relationship between work experience and the current skills shortages. We will examine the specific skills developed through practical experience and how they translate into in-demand expertise. Moreover, the discussion will encompass a range of solutions for bridging the gap between education and the workplace, from apprenticeships and internships to innovative training programs.
Defining Skills Shortages
Skills shortages represent a significant challenge across numerous industries, impacting businesses and economies worldwide. They occur when the demand for skilled workers exceeds the available supply, leading to difficulties in filling critical roles. This gap in talent can hinder productivity, innovation, and overall economic growth. Understanding the factors contributing to these shortages is crucial for developing effective solutions.
Defining the Scope of Skills Shortages
Skills shortages are not a new phenomenon; however, their complexity and scale are increasing. They manifest in various ways, affecting different industries and roles in unique ways. These shortages are not simply about a lack of workers; they encompass a gap between the skills needed and the skills possessed by the available workforce. This gap can be attributed to a multitude of factors.
Factors Contributing to Skills Shortages
Several interconnected factors contribute to the growing problem of skills shortages. Technological advancements, such as automation and artificial intelligence, are rapidly transforming job markets, rendering some existing skills obsolete while creating new demands. Demographic shifts, including changing age distributions and varying educational levels, also play a significant role. The evolving needs of industries, driven by innovations and shifting market trends, create further skill gaps.
This combination of factors often results in a significant mismatch between the skills employers require and the skills possessed by the available workforce.
Impact of Skills Shortages on Businesses and the Economy
Skills shortages negatively impact businesses and the wider economy in numerous ways. Businesses face challenges in maintaining productivity and efficiency, hindering their ability to compete effectively. The search for qualified personnel can lead to increased recruitment costs and extended hiring cycles. This can ultimately result in decreased profitability and innovation. On a larger scale, skills shortages can slow economic growth and limit opportunities for individuals and communities.
Comparing Skills Shortages Across Sectors
The nature and severity of skills shortages vary across different sectors. A comparison across key sectors highlights the diverse challenges involved.
| Sector | Specific Skills Shortages | Contributing Factors | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Software development, cybersecurity, data science, artificial intelligence | Rapid technological advancements, high demand, limited training opportunities | Increased costs, delays in projects, decreased innovation |
| Healthcare | Nurses, doctors, medical technicians, pharmacists | Aging population, increasing demand for healthcare services, insufficient training programs | Longer wait times for appointments, reduced access to care, potential strain on healthcare systems |
| Manufacturing | Machinists, welders, skilled tradespeople | Automation, declining interest in vocational training, aging workforce | Reduced production capacity, increased costs, disruptions in supply chains |
The Role of Work Experience
Work experience is a cornerstone of addressing the pervasive skills gap plaguing many industries today. It bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, equipping individuals with the hands-on expertise employers actively seek. This crucial link directly impacts the availability of qualified candidates and strengthens the workforce’s overall competency.Practical experience in a specific field often reveals and refines skills that theoretical learning alone cannot.
The nuanced application of knowledge, the ability to adapt to real-world scenarios, and the development of problem-solving skills within a professional setting are all essential elements fostered by work experience. This hands-on learning significantly contributes to the crucial skills shortage issues.
Direct Addressing of Skills Shortages
Work experience directly tackles skills shortages by providing individuals with the practical application of theoretical knowledge. It offers a platform for honing skills needed in the modern workplace, bridging the gap between academic learning and professional requirements. The emphasis on practical implementation is crucial in a market demanding demonstrable expertise rather than just theoretical understanding.
Specific Skills Gained Through Practical Experience
Practical experience cultivates a diverse array of crucial skills. Problem-solving abilities, critical thinking, and adaptability are honed through navigating real-world challenges. Teamwork and communication skills are strengthened in collaborative environments. Time management and prioritization become essential assets when juggling multiple tasks and responsibilities. Furthermore, experience allows for the development of essential soft skills like leadership, initiative, and resilience.
Translation of Work Experience into In-Demand Skills
Work experience directly translates into in-demand skills. A marketing internship, for instance, allows an individual to develop practical knowledge in social media marketing, content creation, and campaign management – all crucial skills sought after by marketing departments. Similarly, a software development co-op provides practical experience in coding languages, project management, and debugging, skills highly valued in the tech industry.
This practical application is precisely what many companies look for in their employees.
Correlation Between Work Experiences and Industry-Needed Skills
The table below illustrates the correlation between specific work experiences and the industry-needed skills they cultivate.
| Work Experience | Industry-Needed Skills |
|---|---|
| Retail Sales Associate | Customer service, communication, problem-solving, time management |
| Marketing Internship | Social media marketing, content creation, campaign management, data analysis |
| Software Development Co-op | Coding languages, project management, debugging, teamwork, problem-solving |
| Customer Support Representative | Communication, empathy, problem-solving, conflict resolution, technical skills |
| Research Assistant | Data analysis, research methodology, critical thinking, writing, time management |
Bridging the Gap
Closing the skills gap requires a multifaceted approach, recognizing that traditional education models alone are often insufficient to meet the evolving demands of the modern workplace. Bridging this gap necessitates a comprehensive strategy that encompasses both formal education and practical experience, fostering a symbiotic relationship between learning and application. This involves adapting educational methods to better prepare individuals for the complexities of the job market and empowering them with the transferable skills employers seek.Traditional education models often focus on theoretical knowledge, while modern approaches emphasize practical application and adaptability.
This disconnect can lead to graduates lacking the crucial hands-on experience and industry-specific skills required for immediate employment. Apprenticeships and internships play a pivotal role in bridging this gap by providing real-world learning environments that directly link theoretical knowledge with practical application.
Traditional vs. Modern Approaches to Skill Development
Traditional education systems often rely heavily on lectures and textbooks, with limited opportunities for hands-on learning and industry interaction. Modern approaches, in contrast, emphasize experiential learning, project-based learning, and collaboration. This shift towards practical application is crucial for developing the critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills highly valued by employers. The incorporation of technology and digital tools in modern learning environments also facilitates personalized learning experiences and continuous skill development.
The Role of Apprenticeships and Internships, Work experience key to tackling skills shortages
Apprenticeships and internships provide invaluable opportunities for students to gain practical experience in a specific field. These programs often involve structured training, mentorship, and ongoing evaluation, providing a clear pathway to career advancement. Employers benefit from the ready availability of skilled workers and the potential for talent development, while apprentices and interns gain valuable experience, build networks, and develop their professional profiles.
Work experience is undeniably crucial in bridging the skills gap plaguing many industries. Recent developments like the EU’s cybersecurity plan, requiring members to report attacks, highlight the importance of practical application. For example, this new initiative from the EU ( eus cybersecurity plan requires members to report attacks ) underscores the need for a workforce equipped to handle emerging challenges.
Ultimately, real-world experience remains the key to effectively tackling these skills shortages.
Internships, in particular, often serve as a crucial stepping stone to full-time employment, providing a valuable platform for both students and employers to assess suitability and commitment.
Innovative Training Programs Integrating Work Experience
Many innovative training programs now integrate work experience into their curriculum. These programs often involve collaborative projects, simulations, and industry partnerships. For example, some coding bootcamps offer internships with tech companies, providing students with practical experience alongside structured classroom learning. Similarly, some culinary schools incorporate restaurant internships, enabling students to apply their skills in a real-world kitchen environment.
These integrated programs demonstrate the growing recognition of the importance of practical experience in the learning process.
Examples of Innovative Training Programs
- Coding Bootcamps with Internships: Many coding bootcamps now partner with tech companies, offering internships during or after the program. This allows students to gain practical experience in coding and software development while also building their network within the industry.
- Design Schools with Collaborative Projects: Design schools often incorporate collaborative projects with design firms or clients, providing students with real-world design challenges and the opportunity to apply their skills in a practical setting.
- Healthcare Programs with Clinical Rotations: Healthcare programs frequently integrate clinical rotations in hospitals or clinics, allowing students to apply their theoretical knowledge and gain practical experience in a real-world medical setting.
How Work Experience Complements Formal Education
Work experience provides a valuable complement to formal education by allowing individuals to apply their knowledge in real-world situations. This practical application solidifies learning, identifies gaps in knowledge, and develops essential soft skills like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. It also enhances employability by demonstrating a willingness to learn and adapt to the specific demands of the job market.
This combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience makes graduates more competitive and prepared for the challenges of the professional world.
Comparison of Training Programs and Their Connection to Work Experience
| Training Program | Connection to Work Experience |
|---|---|
| Coding Bootcamps | Internships with tech companies, real-world projects |
| Design Schools | Collaborative projects with design firms, client interaction |
| Healthcare Programs | Clinical rotations in hospitals, patient interaction |
| Engineering Apprenticeships | Structured training with mentorship, on-the-job learning |
Practical Application in the Workplace
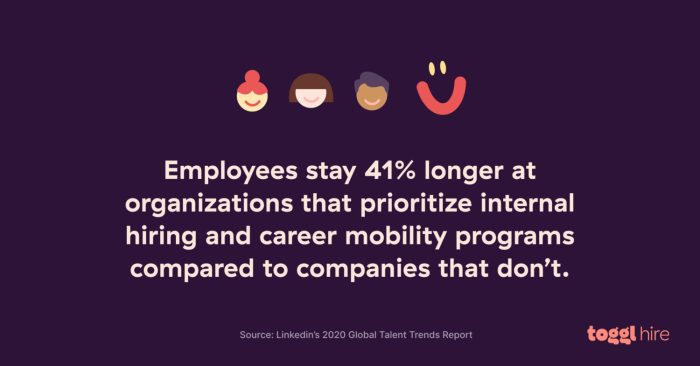
Bridging the skills gap requires a multifaceted approach, and businesses play a crucial role in fostering talent development. Implementing work experience programs effectively is key to attracting and training future employees, thereby addressing the skills shortage proactively. A comprehensive strategy should include not only recruitment but also structured on-the-job training and mentorship programs.Integrating work experience into the recruitment pipeline is a powerful strategy.
It allows companies to identify and select candidates with the potential to excel, rather than relying solely on theoretical knowledge. This practical experience, coupled with structured training, can significantly boost the success rate of new hires.
Incorporating Work Experience into Recruitment Strategies
Businesses can proactively incorporate work experience into their recruitment strategies by actively seeking out candidates with relevant practical experience, even if it’s through internships or volunteer work. This approach helps identify candidates who possess practical skills and a demonstrated ability to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. Tailoring job descriptions to explicitly value and highlight practical experience can encourage qualified candidates to apply.
While work experience is undeniably key to tackling skills shortages, it’s fascinating to consider how innovation might also play a part. Take, for example, the recent development of new mighty microlattice material weighs next to nothing , a truly remarkable advancement. Ultimately, both practical experience and groundbreaking discoveries like this are vital for a future workforce ready to meet the challenges ahead.
By including relevant work experience as a crucial factor in the hiring process, businesses can confidently select candidates better equipped to handle the demands of the role. Companies should also consider offering apprenticeships or entry-level positions that include on-the-job training components.
Mentorship Programs for Skill Development
Mentorship programs provide invaluable support and guidance for individuals navigating their careers. Experienced professionals can share their knowledge, insights, and practical advice, helping to accelerate skill development and foster professional growth. Structured mentorship programs often provide a clear framework for knowledge transfer, offering a tangible and measurable pathway for skill improvement. A successful mentorship program creates a supportive environment where mentees feel empowered to ask questions and seek guidance, ultimately enhancing their overall professional development.
Strategies for Effective On-the-Job Training
Effective on-the-job training programs are critical for skill development and retention. These programs should be tailored to the specific needs of the company and the roles being filled. A comprehensive approach involves structured learning paths, incorporating both theoretical and practical elements. Regular feedback and performance evaluations are vital to identify areas for improvement and provide opportunities for skill enhancement.
Clear communication and defined expectations for each role, coupled with regular coaching and feedback, can greatly enhance on-the-job learning effectiveness.
Work experience is undeniably crucial for bridging the skills gap. Companies are constantly facing challenges in finding qualified candidates, and it’s clear that hands-on experience is a major factor. This is further complicated by the fact that platforms like YouTube are struggling to moderate the negativity of anonymous comment sections, as highlighted in this article on youtube paws feebly at foul mouthed anonymous commenters.
Ultimately, fostering a strong emphasis on practical skills development through internships and apprenticeships is essential for creating a workforce ready to meet the demands of the modern job market.
Leveraging Work Experience for Continuous Professional Development
Work experience provides an invaluable platform for continuous professional development. Employees gain firsthand experience in applying new knowledge and skills, often exceeding what’s covered in traditional training programs. Regular opportunities for upskilling and reskilling, integrated into the work experience, will enhance the employees’ abilities. Providing employees with the resources and encouragement to pursue professional certifications and development courses reinforces a culture of continuous learning.
This proactive approach fosters skilled employees who are adaptable and capable of contributing effectively to a company’s evolving needs.
Workplace Scenarios Requiring Work Experience
| Workplace Scenario | Importance of Work Experience |
|---|---|
| Software Development | Practical experience in coding, debugging, and project management is crucial for successful software development. Work experience provides a deeper understanding of software development methodologies and industry standards. |
| Marketing and Sales | Hands-on experience in marketing campaigns, customer interactions, and sales strategies is essential for effective performance in marketing and sales roles. Work experience allows candidates to build relationships, refine communication skills, and master sales techniques. |
| Healthcare | Practical experience in patient care, medical procedures, and administrative tasks is vital for healthcare professionals. Work experience allows healthcare professionals to develop essential clinical skills and learn to effectively manage patient care. |
| Customer Service | Work experience in customer service provides invaluable insights into handling diverse customer interactions, resolving complaints, and providing excellent service. This experience allows candidates to develop communication skills, conflict resolution abilities, and a deeper understanding of customer needs. |
Future Trends and Solutions
The future of work is rapidly evolving, demanding a proactive approach to skills development and workforce preparedness. The traditional career path is morphing, with roles becoming more specialized and demanding a broader range of skills. Work experience, therefore, becomes an increasingly crucial tool for bridging the gap between education and employment.Adapting work experience programs to meet these future needs requires a nuanced understanding of emerging trends and a commitment to fostering a diverse and skilled workforce.
This includes encouraging young people to engage in practical learning, equipping existing employees with the skills of tomorrow, and recognizing the value of transferable skills developed through real-world applications.
Future Skills Demands and Work Experience Adaptation
The increasing automation of tasks and the rise of new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming industries. These changes demand a workforce proficient in digital literacy, critical thinking, and problem-solving. Work experience programs must adapt to provide opportunities for young people to gain practical experience in these areas. For instance, internships in data analysis or AI development are becoming increasingly relevant.
This necessitates a shift in curricula and partnerships with businesses to ensure that practical experience mirrors the needs of the evolving job market.
Strategies to Encourage Young People in Work Experience
Encouraging participation in work experience programs requires innovative strategies that appeal to today’s young people. These strategies should address the perceived barriers to entry, such as the cost of participation, lack of awareness, and concerns about potential impact on academic performance. A successful approach may involve subsidized programs, partnerships with schools to integrate work experience into curriculum, and showcasing successful work experience stories through mentorship programs.
Offering flexible work arrangements and diverse opportunities for engagement can further encourage participation.
Innovative Solutions to Upskill Existing Workers
Upskilling existing workers is crucial for maintaining a competitive workforce. Organizations can implement internal training programs focused on emerging technologies. These programs could include micro-credentials, online courses, and workshops to enhance employees’ skills in areas like data analysis, digital marketing, and project management. Additionally, companies should consider creating mentorship programs to share expertise and foster a culture of continuous learning.
Mentorship programs facilitate the transfer of knowledge and experience, leading to the upskilling of the workforce.
Importance of Transferable Skills and Work Experience
Work experience fosters the development of essential transferable skills that are valuable across various roles and industries. These skills include communication, teamwork, problem-solving, time management, and adaptability. These skills are highly sought after by employers and are crucial for success in today’s dynamic work environment. The practical application of these skills in real-world scenarios is key to enhancing their value and facilitating the career progression of individuals.
Table Summarizing Solutions for Addressing Future Skills Needs
| Area of Focus | Solution | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Encouraging Participation | Subsidized programs | Financial assistance to offset costs of participation |
| Encouraging Participation | School partnerships | Integration of work experience into curriculum |
| Upskilling Existing Workers | Internal training programs | Micro-credentials, online courses, and workshops |
| Upskilling Existing Workers | Mentorship programs | Knowledge sharing and fostering continuous learning |
| Transferable Skills | Real-world application | Developing and enhancing skills through practical experience |
Illustrative Examples of Work Experience: Work Experience Key To Tackling Skills Shortages
Gaining practical experience is crucial for bridging the skills gap. Real-world exposure through various work experiences provides invaluable opportunities to develop and apply knowledge, refine existing skills, and discover new passions. This section explores diverse examples of work experience, highlighting their impact on skill development and future career paths.
Volunteer Work: Cultivating Essential Skills
Volunteer work, often overlooked, is a powerful catalyst for skill development. It provides opportunities to apply learned knowledge in a real-world setting and build a range of crucial skills. Beyond practical skills, volunteering fosters essential soft skills like teamwork, communication, and problem-solving.
- Teamwork: Working with a diverse group on a community project, such as organizing a food drive or fundraising event, develops collaborative skills and the ability to effectively contribute to a shared goal. The experience of coordinating tasks and responsibilities amongst team members improves interpersonal skills and builds a sense of shared responsibility.
- Communication: Volunteer roles often require clear communication to interact with clients, stakeholders, or other volunteers. For instance, presenting information at a fundraising event, or assisting individuals with tasks, necessitates strong communication skills, which are directly applicable in professional settings.
- Problem-solving: Volunteers often face unexpected challenges and need to adapt and improvise. Addressing logistical issues, resolving conflicts, or overcoming obstacles in a volunteer capacity strengthens problem-solving abilities, which are highly valued in any career.
Part-Time Jobs: Building Foundational Skills
Part-time jobs, especially those in related fields, provide a tangible bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application. These experiences provide opportunities to learn specific skills, understand industry dynamics, and develop professional habits.
- Customer service roles: Handling customer inquiries, resolving complaints, and providing assistance build essential communication and interpersonal skills. Working in fast-paced environments teaches adaptability and the importance of efficient problem-solving.
- Retail or service roles: These positions often involve teamwork, handling cash transactions, and providing excellent customer service, which are crucial skills in many industries. Learning to manage time effectively and prioritize tasks are also critical skills gained from part-time employment.
Short-Term Projects: Enhancing Work Experience
Short-term projects offer concentrated learning experiences. They provide a focused opportunity to learn and apply specific skills in a limited time frame, fostering valuable experience that can be leveraged for future job applications.
- Internships: Internships are short-term projects often focused on gaining practical experience in a specific field. They provide valuable exposure to industry practices, professional networks, and allow for the development of industry-specific skills.
- Freelancing: Taking on small projects or tasks as a freelancer exposes individuals to client management, project planning, and time management skills. These skills are transferable and valuable for various roles.
Different Types of Work Experience and Benefits
| Type of Work Experience | Specific Benefits |
|---|---|
| Volunteer Work | Develops teamwork, communication, and problem-solving skills; enhances soft skills; and provides opportunities to apply knowledge in a real-world setting. |
| Part-Time Jobs | Provides practical experience in a specific field; builds industry knowledge and professional habits; and enhances time management and prioritization skills. |
| Short-Term Projects (e.g., internships) | Offers focused learning experiences in a specific field; provides exposure to industry practices; develops industry-specific skills; and fosters networking opportunities. |
Overcoming Challenges in Implementation
Successfully implementing work experience programs requires careful planning and proactive strategies to address potential obstacles. This crucial step ensures the program’s effectiveness and positive impact on both participants and employers. The challenges are often multifaceted, ranging from securing placements to managing participant expectations. By anticipating and addressing these issues, programs can maximize their contribution to bridging the skills gap.
Potential Obstacles in Implementing Work Experience Programs
Many factors can hinder the smooth execution of work experience initiatives. Insufficient employer engagement is a common issue. Recruiting suitable placements, especially for diverse roles and sectors, can prove challenging. Moreover, inadequate support systems for participants, including mentorship and guidance, can negatively impact their experience. Addressing these obstacles is critical to fostering a positive and productive experience for all involved.
Strategies to Overcome Implementation Challenges
Implementing effective strategies to overcome these challenges is vital for the success of work experience programs. Building strong relationships with potential employers is key. This includes active outreach, highlighting the benefits of hosting participants, and demonstrating the value of work experience for both the organization and the student. Furthermore, developing clear communication channels and providing robust support systems for participants is crucial.
This may involve offering tailored training, mentorship programs, and access to experienced professionals. The establishment of clear guidelines and expectations for both employers and participants helps to mitigate misunderstandings and ensure a smooth process.
Ensuring Diverse Representation in Work Experience Opportunities
Promoting diversity in work experience programs is not just ethically important, but also essential for creating a representative pool of talent and reflecting the workforce. This requires proactive outreach to diverse communities and organizations. Targeting underrepresented groups, offering support for potential participants from these backgrounds, and actively seeking placements in diverse industries are vital. This proactive approach, combined with clear communication and ongoing monitoring, can significantly increase diversity in work experience opportunities.
The Importance of Providing Constructive Feedback During Work Experience
Constructive feedback is essential for participants to learn and develop. Regular feedback sessions, delivered in a supportive and constructive manner, can help participants identify strengths and areas for improvement. This fosters a culture of learning and development, maximizing the benefit of the work experience. By focusing on specific examples and offering suggestions for improvement, participants can gain valuable insights into their performance.
Feedback sessions should be well-structured, ensuring that participants feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and perspectives.
Table: Potential Barriers and Strategies to Overcome Them
| Potential Barrier | Strategies to Overcome |
|---|---|
| Insufficient Employer Engagement | Develop a strong employer outreach strategy, highlighting benefits, and offering incentives for hosting participants. Showcase success stories from previous placements. |
| Lack of Diverse Placements | Proactively target underrepresented groups and sectors. Collaborate with diverse organizations and community groups. Offer incentives for employers to host diverse participants. |
| Inadequate Participant Support | Establish robust support systems, including mentorship programs, guidance from experienced professionals, and clear communication channels. Provide tailored training and resources to enhance participants’ skill development. |
| Misaligned Expectations | Develop clear guidelines and expectations for both employers and participants. Provide detailed information about the program’s objectives and requirements. Ensure consistent communication and follow-up throughout the placement. |
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Programs
Assessing the success of work experience programs requires a multifaceted approach. Simply counting participants isn’t enough; we need to understand the genuine impact on both the individuals gaining experience and the organizations offering it. This involves measuring tangible outcomes, tracking skills development, and analyzing the long-term benefits for all stakeholders.A robust evaluation process helps refine program design, identify areas for improvement, and demonstrate the value of work experience in addressing skills gaps.
It provides critical data for future program development and for advocating for the importance of work experience within the broader educational and employment landscape.
Metrics for Evaluating Program Success
Understanding the effectiveness of work experience programs necessitates defining clear metrics. These metrics should encompass the perspectives of both participants and host organizations. Focusing on quantifiable data allows for objective assessment and comparison across different programs. Key areas to consider include participant engagement, skill acquisition, and the long-term impact on employment outcomes.
Assessing the Impact on Participant Skills
Assessing the impact on participant skills requires a structured approach that goes beyond subjective observations. Pre- and post-program assessments are essential for measuring skill development. These assessments should be aligned with the specific skills targeted by the program. For instance, if the program focuses on communication skills, the assessments should specifically evaluate communication competencies.
Tracking Outcomes of Work Experience Initiatives
Tracking the outcomes of work experience initiatives is crucial for demonstrating the program’s value. This involves collecting data on various aspects, such as participants’ performance reviews, feedback from supervisors, and the number of participants who secure employment after the program. By systematically collecting this data, a clear picture of the program’s impact emerges.
Measuring Long-Term Benefits of Work Experience Programs
Measuring the long-term benefits necessitates a longitudinal approach. This involves following participants after their work experience to assess their career progression, salary increases, and overall job satisfaction. This data provides valuable insight into the lasting contributions of the program and justifies the investment in work experience initiatives.
Table of Metrics for Measuring Program Effectiveness
| Metric Category | Specific Metric | Example of Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Participant Engagement | Number of hours worked | Track the total hours of work experience each participant completes. |
| Skill Acquisition | Pre- and post-program skill assessments | Administer standardized tests or assessments to measure skills like teamwork, communication, and problem-solving before and after the program. |
| Participant Satisfaction | Surveys and feedback forms | Collect feedback from participants on their experience through surveys or structured feedback forms, evaluating aspects like learning, support, and overall satisfaction. |
| Employer Satisfaction | Supervisor feedback and performance reviews | Gather feedback from supervisors regarding participant performance and contributions. |
| Employment Outcomes | Number of participants securing employment | Track the number of participants who secure employment after completing the program, considering timeframes for follow-up. |
| Long-Term Career Progression | Salary increases and promotions | Monitor participants’ career progression over time, collecting data on salary increases, promotions, and job advancements after the program. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, work experience is not just a valuable stepping stone; it’s a fundamental component in addressing the pressing skills shortages across various industries. By integrating practical experience into education and training, and by fostering a culture of continuous learning, we can equip individuals with the necessary skills to thrive in the modern economy. This comprehensive approach to skill development will ultimately benefit both individuals and businesses alike.






