Kicking off with OKR and lean roadmap, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to effectively align your objectives with a lean methodology. We’ll explore defining OKRs, aligning them with your lean roadmap, and implementing the strategy for maximum impact. The goal is to provide actionable steps and real-world examples, ensuring a clear understanding of the practical application of OKRs and lean principles.
This detailed guide covers everything from defining objectives and key results (OKRs) and understanding lean principles to implementing your plan and measuring progress. Expect actionable insights, practical examples, and a clear understanding of how to adapt this strategy to your unique organizational needs.
Defining OKRs and Lean Roadmaps
Setting clear goals and effectively executing plans are crucial for any organization. This involves understanding the tools and methodologies that support strategic alignment and efficient workflows. Two such powerful tools are Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Lean Roadmaps. This exploration delves into their definitions, characteristics, and core principles, highlighting their similarities and differences.A well-defined strategy needs both a guiding vision and a structured approach for achieving it.
OKRs and Lean Roadmaps, while serving distinct purposes, often work hand-in-hand to create a cohesive framework for success.
Defining Objectives and Key Results (OKRs)
OKRs, or Objectives and Key Results, are a goal-setting framework that helps teams and organizations define ambitious objectives and track progress toward achieving them. They focus on ambitious, yet measurable goals, with a clear timeframe for completion. The framework encourages transparency and accountability across the organization, allowing teams to track progress and adapt strategies as needed.
“OKRs are a goal-setting framework designed to help organizations and teams focus on ambitious objectives and track progress towards achieving them.”
Characteristics of a Well-Defined Lean Roadmap
A well-defined Lean Roadmap is characterized by its focus on continuous improvement, iterative development, and customer value. It Artikels a clear path toward achieving strategic goals by focusing on eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and streamlining workflows. This iterative approach ensures flexibility and adaptability to changing circumstances and market demands. It’s crucial for maintaining momentum and efficiently allocating resources.
Core Principles Behind Lean Methodologies
Lean methodologies are grounded in the principle of eliminating waste and maximizing value for the customer. Key principles include:
- Value Creation: Identifying and focusing on activities that directly add value to the customer.
- Value Stream Mapping: Visualizing the entire process to identify and eliminate non-value-added steps.
- Flow: Creating a smooth and uninterrupted flow of work to minimize delays and bottlenecks.
- Pull Systems: Ensuring that work is only initiated when needed, based on customer demand.
- Perfection: Continuously striving for improvement and eliminating waste in all areas of the process.
These principles, when applied effectively, lead to significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and overall performance.
Comparing and Contrasting OKRs and Lean Roadmaps
OKRs and Lean Roadmaps, while distinct, can be complementary. OKRs focus on the
- what* and
- why* of strategic goals, while Lean Roadmaps focus on the
- how* of achieving them. OKRs provide the overarching strategic direction, while Lean Roadmaps Artikel the specific steps and processes for achieving those objectives.
Key Differences Between OKRs and Lean Roadmaps
The table below highlights the key differences between OKRs and Lean Roadmaps, emphasizing their distinct roles in strategic planning and execution.
| Feature | OKRs | Lean Roadmap | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Strategic Objectives and Measurable Results | Process Optimization and Value Stream Mapping | OKRs define the desired outcomes, while Lean Roadmaps focus on the process improvements needed to achieve them. |
| Scope | High-level organizational goals | Detailed operational steps and timelines | OKRs provide the big picture, while Lean Roadmaps zoom in on specific processes and activities. |
| Time Horizon | Long-term, often quarterly or annually | Short-term, iterative sprints | OKRs are usually defined for longer periods, while Lean Roadmaps focus on shorter, iterative cycles. |
| Goal | Define and track progress towards ambitious targets | Streamline processes and optimize workflows | OKRs aim for overall success, while Lean Roadmaps focus on improving efficiency within specific processes. |
Aligning OKRs with Lean Roadmaps
Connecting your Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) with your Lean Roadmap is crucial for maintaining focus and driving measurable progress. A well-aligned approach ensures that every step taken on the roadmap directly contributes to achieving your overarching business goals. This process is not just about creating a to-do list; it’s about strategically mapping out the path to success.Effective alignment between OKRs and Lean Roadmaps fosters a clear understanding of the desired outcomes and the specific actions needed to reach them.
This clarity allows teams to work collaboratively, track progress accurately, and adapt to changing circumstances while staying on course towards their strategic objectives.
Breaking Down OKRs into Actionable Steps
The first step in aligning OKRs with a Lean Roadmap is to break down your overarching objectives into smaller, actionable steps. This decomposition process allows you to visualize the individual tasks and milestones needed to achieve each key result. By creating this granular level of detail, you ensure that every piece of the puzzle contributes to the larger picture.
This breakdown allows for better allocation of resources, improved tracking, and increased accountability.For example, an OKR of “Increase website traffic by 20% in Q3” can be broken down into specific actions like “Optimize website content for ,” “Launch a social media campaign,” and “Implement a paid advertising strategy.” Each of these actions can then be further decomposed into smaller, manageable tasks, creating a clear path to achieving the overall key result.
Prioritizing Tasks and Milestones
Prioritizing tasks and milestones on the Lean Roadmap is critical to ensure that you are focusing on the most impactful actions first. This prioritization should be based on factors such as the impact on achieving the OKR, the dependencies between tasks, and the potential risks involved.Prioritization frameworks, like the Eisenhower Matrix (urgent/important), can be used to effectively categorize tasks and allocate resources accordingly.
This helps avoid wasting time on less impactful activities, allowing your team to focus on those with the highest potential for contributing to OKR success. For instance, a task that directly impacts a key metric should likely be prioritized higher than a task with a less tangible impact.
Monitoring Progress Towards OKRs
Monitoring progress towards OKRs within the Lean Roadmap is a continuous process. Regular check-ins, progress reports, and data analysis are essential to track how well you’re performing against your targets. Use dashboards, spreadsheets, or project management tools to visualize progress and identify any roadblocks.These tools provide a clear overview of where your team stands in relation to the OKR targets and allow for proactive adjustments to the roadmap as needed.
This proactive approach ensures that your team remains on track and makes necessary course corrections to stay on schedule and within budget.
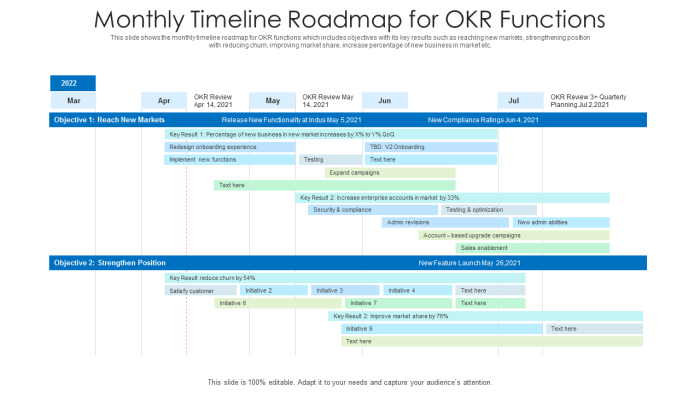
Translating OKRs into Actionable Items
The following table illustrates how specific OKRs translate into actionable items on the Lean Roadmap:
| OKR | Description | Actionable Items on Roadmap | Milestones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increase website traffic by 20% in Q3 | Drive more users to the website. | Optimize website content for , Launch social media campaign, Implement paid advertising strategy | Content optimization complete, Social media campaign launched, Paid ads campaign live |
| Improve customer satisfaction scores by 15% | Enhance customer experience. | Implement customer feedback surveys, Enhance customer service response time, Develop new customer support resources | Surveys implemented, Average response time reduced, New resources available |
| Increase sales by 10% | Boost revenue. | Run targeted marketing campaigns, Develop new product features, Implement sales training | Campaigns launched, New features released, Training completed |
Creating Effective OKRs for Lean Roadmaps
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) are powerful tools for aligning teams and driving progress towards strategic goals. When integrated with a Lean Roadmap, they provide a structured framework for iteratively improving products and processes. This article delves into creating effective OKRs to support your Lean Roadmap, focusing on common pitfalls, measurable Key Results, time-bound specifics, feedback loops, and practical examples.Effective OKRs are more than just ambitious targets; they are actionable steps designed to be tracked and adjusted based on ongoing progress.
By clearly defining measurable objectives and results, organizations can ensure that efforts remain focused and aligned with their overall strategic roadmap.
Common Pitfalls in Defining Ineffective OKRs
Ambiguous objectives and poorly defined Key Results lead to wasted effort and inaccurate progress tracking. Unclear goals often result in teams working in different directions, hindering overall progress. Key Results that lack quantifiable metrics make it difficult to assess actual performance. For example, a vague objective like “Improve customer satisfaction” lacks the specificity needed to drive meaningful action.
A Key Result of “Increase customer satisfaction scores by 15% in Q3” is more actionable.
OKRs and lean roadmaps are crucial for strategic alignment, but consider the potential implications for data privacy. Law enforcement’s increasing access to cellphone data, as highlighted in this article on law enforcement feasts on cellphone data , raises significant questions about the ethical use of such information. This underscores the need for robust privacy protocols within our OKR and lean roadmap development processes, ensuring data security and responsible technology integration.
Creating Measurable Key Results for OKRs
Key Results should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Vague or subjective measures can lead to inaccurate progress tracking. For example, a Key Result like “Increase user engagement” lacks the necessary metrics. Instead, a measurable Key Result could be “Increase daily active users by 20% in the next quarter.” Using concrete metrics like numbers, percentages, or specific milestones ensures that progress can be objectively evaluated.
Importance of Time-Bound and Specific OKRs within the Lean Roadmap
Lean Roadmaps are iterative and often require adjustments based on learning and feedback. Time-bound OKRs ensure that teams maintain focus and momentum. Specific OKRs help ensure alignment with the Lean Roadmap, ensuring that every action supports the larger strategic vision. By establishing clear timelines and metrics, teams can track progress and make necessary adjustments to maintain focus on the roadmap’s key priorities.
For instance, if a Key Result isn’t on track, the team can pivot their efforts and re-evaluate the strategy for the current sprint.
Role of Feedback Loops in Refining OKRs Based on Progress on the Lean Roadmap
Regular feedback loops are crucial for adapting OKRs to changing circumstances. Monitoring progress against Key Results allows teams to identify areas needing improvement or adjustment. Data gathered during the execution phase informs necessary changes and helps teams iterate effectively. Weekly or bi-weekly progress meetings can serve as effective feedback loops, providing insights into challenges and opportunities. This iterative approach helps ensure that OKRs remain relevant and aligned with the evolving Lean Roadmap.
Examples of Well-Defined OKRs Supporting a Lean Roadmap
- Objective: Enhance user onboarding experience. Key Result: Reduce user abandonment rate during onboarding by 10% in Q
4. Key Result: Increase user engagement measured by the average time spent on the platform by 15% in Q4. This example demonstrates a clear objective with measurable Key Results directly tied to the Lean Roadmap’s user experience improvement initiatives. - Objective: Improve conversion rates on the e-commerce platform. Key Result: Increase the conversion rate by 12% in Q4 by optimizing the checkout process. Key Result: Increase the number of returning customers by 15% in Q4. This example demonstrates how OKRs can be used to measure and improve specific aspects of a Lean Roadmap related to e-commerce conversion.
- Objective: Streamline the internal approval process. Key Result: Reduce the average time taken for internal approvals by 20% in Q4 by automating key steps. Key Result: Increase employee satisfaction scores related to the approval process by 10% in Q4. This illustrates how OKRs can be used to improve internal processes and workflows, which often form a crucial part of a Lean Roadmap.
Implementing OKRs and Lean Roadmaps
Putting your OKRs and Lean Roadmap into action requires a structured approach. This involves more than just defining goals; it necessitates a systematic implementation process that ensures alignment, consistent progress, and adaptation to changing circumstances. Successful execution hinges on effective communication, collaborative efforts, and regular reviews to maintain momentum and address any deviations.The practical application of OKRs and Lean Roadmaps is a dynamic process.
It demands a proactive approach that allows for flexibility and adaptation, ensuring that the strategy remains relevant and effective in the face of evolving market dynamics and internal insights. By establishing clear implementation steps and fostering a culture of open communication and continuous improvement, organizations can maximize the benefits of these powerful tools.
Step-by-Step Implementation Procedure
A structured approach to implementation is crucial for achieving desired outcomes. This involves a series of clearly defined steps that guide the organization through the process, from initial planning to ongoing review and adjustment. Each step builds upon the previous one, ensuring a seamless and efficient transition.
- Define clear roles and responsibilities: Assign specific tasks and responsibilities to individuals or teams. This ensures accountability and prevents confusion regarding who is responsible for what. This crucial step clarifies expectations and promotes ownership.
- Develop a detailed action plan: Break down overarching OKRs into smaller, actionable tasks. This provides a clear roadmap for achieving objectives within the allocated timeframes. This granular approach facilitates progress tracking and allows for more focused effort.
- Establish regular communication channels: Establish clear communication channels for teams to share updates, challenges, and successes. This fosters collaboration and ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding progress. Transparent communication builds trust and shared understanding.
- Implement a system for progress tracking: Develop a method for tracking progress towards OKRs. This allows for regular monitoring and adjustments to the plan as needed. Regular progress updates keep stakeholders informed and enable timely course correction.
- Conduct regular reviews and make adjustments: Schedule regular meetings to assess progress against the roadmap. This provides an opportunity to identify areas needing improvement and make necessary adjustments to the plan. Continuous evaluation is crucial for maintaining alignment and achieving goals.
Role of Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are essential for successful implementation. Open dialogue facilitates the sharing of ideas, concerns, and solutions, fostering a supportive environment for teams to work together effectively.
- Foster open communication: Encourage teams to share information freely and address concerns promptly. Transparent communication fosters a collaborative environment where teams can openly discuss challenges and solutions.
- Promote cross-functional collaboration: Encourage collaboration across different teams to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals. This integrated approach ensures alignment and maximizes collective impact.
- Establish feedback mechanisms: Implement regular feedback loops to gather input from team members and stakeholders. This valuable input enables continuous improvement and ensures that the implementation process remains aligned with organizational needs.
Importance of Regular Reviews and Adjustments
Regular reviews and adjustments are vital for maintaining momentum and achieving desired outcomes. These reviews allow for course correction, ensuring that the implementation process remains relevant and effective. Proactive adaptation ensures that the strategy remains aligned with changing circumstances and emerging insights.
- Schedule regular check-ins: Establish a schedule for reviewing progress against OKRs and the Lean Roadmap. These scheduled check-ins facilitate a systematic review of performance and progress.
- Identify areas for improvement: Regular reviews provide opportunities to identify areas where the implementation process can be improved. This enables proactive adjustments to optimize the process and maximize results.
- Adapt to changing circumstances: Be prepared to adjust the Lean Roadmap based on evolving market conditions or internal insights. This adaptability ensures that the strategy remains effective and aligned with changing priorities.
Adapting the Lean Roadmap
Adaptability is key to successful implementation. The Lean Roadmap should be flexible enough to accommodate changing circumstances and emerging insights. Organizations should be prepared to modify the roadmap in response to market shifts, technological advancements, or new competitive pressures.
- Monitor external factors: Stay informed about external factors that might impact the implementation process. Understanding the context enables proactive adjustments to the Lean Roadmap.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders: Solicit feedback from stakeholders on the effectiveness of the Lean Roadmap. This input provides valuable insights for necessary adjustments.
- Re-evaluate priorities: Be prepared to re-evaluate priorities and reallocate resources as needed. This agility allows for rapid response to changing market conditions.
Implementation Phases
| Phase | Key Activities | Timeline | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | Defining OKRs, creating Lean Roadmap, assigning roles, developing action plan | 1-2 weeks | Clear OKRs, comprehensive roadmap, defined roles and responsibilities |
| Execution | Implementing tasks, tracking progress, monitoring KPIs, fostering communication | Ongoing | Consistent progress towards OKRs, improved communication, identified roadblocks |
| Review and Adjustment | Regular check-ins, identifying areas for improvement, adapting the Lean Roadmap | Ongoing | Identified areas for improvement, adjusted roadmap, sustained momentum |
| Optimization | Fine-tuning the process, leveraging insights, continuous improvement | Ongoing | Increased efficiency, improved resource allocation, maximum impact |
Measuring and Reporting OKR Progress on Lean Roadmaps
Tracking OKR progress on a Lean Roadmap is crucial for maintaining alignment, adapting to changes, and ensuring the team stays on track. Effective measurement and reporting systems provide transparency, allowing stakeholders to understand the current status and identify potential roadblocks early on. Regular reporting also helps teams refine their strategies and make data-driven decisions.
Methods for Measuring OKR Progress
Different methods can be used to measure progress toward OKRs within a Lean Roadmap. Quantitative metrics, like the number of users acquired or sales generated, offer concrete evidence of progress. Qualitative metrics, such as customer satisfaction scores or product feedback, provide valuable insights into user experience and product development effectiveness. Combining both types of metrics provides a comprehensive view of OKR achievement.
Importance of Consistent Reporting and Data Visualization
Consistent reporting is paramount for effective OKR management. Regular updates on progress allow teams to proactively address issues and make necessary adjustments. Visualizing data through charts and graphs enhances understanding and facilitates quick identification of trends, outliers, and areas needing attention. This transparency fosters collaboration and accountability, driving better performance and more efficient resource allocation.
Visual Representations for Tracking OKR Progress
Visual representations are critical for quickly grasping OKR progress. Line graphs can illustrate the trajectory of key metrics over time, revealing trends and potential deviations from the planned path. Bar charts effectively compare progress across different OKRs or teams. Progress indicators (e.g., a traffic light system: green for on track, yellow for caution, red for intervention needed) can provide an at-a-glance summary of OKR status.
Scatter plots can show correlations between different metrics and highlight potential relationships. Choosing the right visual representation depends on the specific data and the message you want to convey.
OKRs and lean roadmaps are crucial for focusing efforts, but sometimes a radical idea like the new ASUS desktop that transforms into a massive tablet, as seen in this article , can inspire a fresh perspective on how we approach problem-solving. Thinking outside the box, as demonstrated by this innovative device, can lead to breakthroughs that help us refine our OKR and lean roadmap strategies for better results.
Creating Reports for Clear Communication
Reports should clearly communicate OKR progress and roadmap status. They should include a concise overview of the current state, highlighting key achievements and areas requiring attention. Data visualization should be used to illustrate progress clearly and effectively. A detailed explanation of the reasons behind any deviations from the planned path is essential for understanding and addressing potential roadblocks.
OKRs and lean roadmaps are crucial for any tech team, especially when tackling the complexities of modern IT security. For example, understanding the ever-evolving threats to mobile enterprise IT security, like the ones discussed in the ghost haunting mobile enterprise IT security , is paramount. Clearly defined OKRs, combined with a lean approach to problem-solving, can help prioritize the right security measures and streamline the implementation process, ultimately making your team more effective.
The report should conclude with a summary of next steps and planned actions.
Data Visualization Techniques for OKR Progress Reporting
| Visualization Technique | Description | When to Use | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line Graph | Shows trends over time. | Tracking progress of a key metric like user growth or sales over quarters. | User Acquisition over Time |
| Bar Chart | Compares values across categories. | Comparing progress of different OKRs or teams. | Sales Performance by Team |
| Progress Indicator (Traffic Light) | Provides an at-a-glance status. | Summarizing overall OKR status across the roadmap. | OKR Status: Green, Yellow, Red |
| Scatter Plot | Shows correlation between two variables. | Identifying potential relationships between customer satisfaction and feature adoption. | Customer Satisfaction vs. Feature Usage |
Case Studies of OKRs and Lean Roadmaps: Okr And Lean Roadmap
Diving deep into real-world applications of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and Lean Roadmaps is crucial for understanding their effectiveness. This section explores successful implementations across various industries, highlighting key lessons, challenges, and the tangible impact on organizational performance. Analyzing these case studies allows us to glean practical insights for implementing these frameworks within our own organizations.Understanding how other companies have successfully navigated the complexities of integrating OKRs and Lean Roadmaps provides invaluable lessons and inspiration.
This allows for a more practical understanding of how to implement these frameworks within one’s own organizational structure.
Successful Implementations in Different Industries
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented OKRs and Lean Roadmaps, driving significant improvements in their operational efficiency and strategic alignment. A common thread in these successes is the careful consideration of the organization’s unique needs and culture.
- Software Development Company: A software development company transitioned from a project-based approach to an OKR-driven model, aligning individual and team goals with the company’s overall objectives. This resulted in a 25% increase in productivity and a 15% reduction in development time for new features, demonstrating the effectiveness of the OKR methodology in improving development processes.
- E-commerce Retailer: An e-commerce retailer implemented Lean Roadmaps to streamline their product development cycle. By focusing on value streams and eliminating waste, they reduced product development time by 30% and improved customer satisfaction, highlighting the efficiency improvements Lean Roadmaps can deliver.
- Manufacturing Company: A manufacturing company used OKRs to drive improvements in production efficiency and quality. By defining clear objectives and measurable key results, they reduced production defects by 10% and increased output by 15%, showcasing the power of OKRs in driving operational excellence.
Key Lessons Learned from Successful Implementations
Analyzing successful deployments reveals several crucial lessons. Effective implementation often involves strong leadership support, clear communication, and continuous feedback loops.
- Leadership Buy-in: Strong leadership support is essential for successful OKR and Lean Roadmap integration. Leaders must actively participate in setting objectives, monitoring progress, and providing resources to teams. Without active leadership, teams are less likely to embrace these methodologies.
- Clear Communication: Transparent communication of OKRs and the Lean Roadmap to all stakeholders is vital. This fosters understanding and ensures everyone is working towards shared goals. This includes not only the objectives but also the methods for achieving them.
- Continuous Feedback: Regular feedback mechanisms are critical for identifying areas for improvement and adapting the framework as needed. This includes both formal and informal feedback loops to ensure the methodology remains relevant and effective.
Challenges Faced and How They Were Overcome
While the benefits of OKRs and Lean Roadmaps are significant, challenges can arise. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for long-term success.
- Resistance to Change: Resistance to change from employees is a common challenge. Addressing concerns, fostering open dialogue, and demonstrating the value of the new methodology are essential for overcoming resistance.
- Lack of Resources: Implementing these frameworks often requires additional resources. Identifying and allocating necessary resources to support the implementation is crucial.
- Defining Measurable Objectives: Developing measurable key results that align with the organizational strategy can be difficult. Utilizing data analysis and clear communication with teams can help.
Impact on Organizational Performance
The impact of implementing OKRs and Lean Roadmaps on organizational performance can be substantial. These frameworks can lead to increased efficiency, improved strategic alignment, and enhanced employee engagement.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlining processes and eliminating waste through Lean Roadmaps leads to greater efficiency. This is often reflected in reduced costs and faster turnaround times.
- Improved Strategic Alignment: OKRs force alignment between individual and team goals with the company’s overall objectives. This creates a more focused and strategic approach.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Employees are more engaged when they understand their role in achieving larger objectives. This increased engagement often translates into higher morale and productivity.
Comparative Analysis of Case Studies
| Company | Industry | Key Success Factors | Challenges Faced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Company A | Software Development | Strong leadership support, clear communication, continuous feedback loops | Resistance to change, initial lack of understanding of the methodology |
| E-commerce Retailer B | E-commerce | Focus on value streams, waste elimination, strong data analysis | Complexity of integrating new tools, lack of initial data |
| Manufacturing Company C | Manufacturing | Clear definition of measurable objectives, effective communication across teams | Resistance to change from production staff, challenges in measuring quality metrics |
Adapting OKRs and Lean Roadmaps for Different Scenarios

OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) and Lean Roadmaps are powerful tools for setting strategic goals and achieving them efficiently. However, their effectiveness hinges on tailoring them to specific project types, industry sectors, and organizational structures. This adaptability ensures alignment with the unique characteristics and challenges of each context, leading to better outcomes.Effective OKR and Lean Roadmap implementation necessitates understanding how these frameworks can be adjusted to fit various scenarios.
This involves recognizing the specific needs and constraints of different project types, industries, and organizational structures. By making appropriate adjustments, teams can maximize the benefits of these frameworks and achieve greater success.
Adapting for Different Project Types
Understanding the unique nature of different project types is crucial for tailoring OKRs and Lean Roadmaps. Projects can range from simple, well-defined tasks to complex, multifaceted endeavors with numerous moving parts. This requires a flexible approach that accounts for the different levels of uncertainty and required detail. For instance, a simple marketing campaign might need simpler, more focused OKRs and a lean roadmap compared to a product development project requiring more granular breakdowns and potential pivots.
Adapting for Specific Industry Sectors
Different industries have unique challenges and opportunities. Adapting OKRs and Lean Roadmaps to industry-specific contexts is essential for relevance and effectiveness. For example, in the fast-paced tech industry, OKRs might focus on rapid iteration and innovation, while in a more regulated healthcare sector, the focus might be on compliance and patient outcomes. This necessitates adjusting the measurement metrics and timelines to reflect the specific constraints and priorities of each industry.
Tailoring to Organizational Structures
Organizational structure significantly impacts how OKRs and Lean Roadmaps are implemented. A hierarchical structure might require more formal approval processes, while a flat, agile structure might prioritize collaboration and rapid decision-making. This means adjusting the communication channels, review cycles, and decision-making authority levels to align with the organizational setup.
Scenarios Requiring Lean Roadmap Modification, Okr and lean roadmap
There are scenarios where the Lean Roadmap itself might require modification. For instance, unforeseen market shifts, unexpected technological advancements, or major changes in customer behavior can necessitate adjustments to the roadmap. This adaptation might involve adding new features, eliminating outdated ones, or reprioritizing tasks to remain relevant to evolving circumstances. The flexibility built into the Lean Roadmap is crucial in such situations.
Table of Scenarios and Adaptations
| Scenario | Project Type | Industry Sector | Organizational Structure | Recommended Adaptations for OKRs and Lean Roadmaps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex Product Development | Large, multifaceted | Tech | Hierarchical | Break down OKRs into smaller, more manageable sub-objectives. Use more detailed iterations within the Lean Roadmap to accommodate evolving requirements. Establish clear communication channels and decision-making processes. |
| Rapid Marketing Campaign | Short-term, focused | Retail | Flat, agile | Define concise OKRs focused on key metrics like conversions and brand awareness. Prioritize sprints and iterative improvements within the Lean Roadmap. Encourage quick decision-making and collaboration. |
| Regulatory Compliance Project | Long-term, methodical | Healthcare | Hierarchical | Focus OKRs on achieving specific compliance milestones. Incorporate thorough documentation and rigorous testing phases within the Lean Roadmap. Ensure alignment with regulatory requirements and protocols. |
Final Review
In conclusion, mastering OKR and lean roadmap integration unlocks significant potential for organizational success. By understanding how to define effective OKRs, align them with a lean roadmap, and consistently measure progress, you can drive targeted results and achieve significant milestones. This guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to navigate this process, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and enhanced performance.