
Consumers want sustainable products, and that desire is driving a major shift in the market. This trend isn’t just a passing fad; it reflects a fundamental change in consumer values and priorities. From eco-conscious packaging to ethically sourced materials, sustainability is now a key factor in purchasing decisions across various demographics and product categories. We’ll explore the motivations behind this shift, examine the available sustainable products, and analyze the strategies companies are using to meet this demand.
This in-depth look at consumer preferences for sustainable products will examine the driving forces behind this growing trend. We’ll explore various factors influencing consumer choices, including price, convenience, brand reputation, and social media’s impact. Understanding the motivations of different consumer segments (like millennials and Gen Z) will be key to unlocking the secrets behind this evolving market.
Understanding Consumer Motivations: Consumers Want Sustainable Products
Consumers are increasingly seeking out sustainable products, driven by a multitude of factors. This shift reflects a growing awareness of environmental concerns and a desire for ethical consumption. Understanding these motivations is crucial for businesses looking to tap into this market and create products that resonate with modern values.
Sustainable Product Features Appealing to Consumers
Consumers are drawn to a variety of features in sustainable products. These features often encompass environmental benefits, ethical sourcing, and innovative design. Examples include products made from recycled materials, using renewable energy in manufacturing, or featuring eco-friendly packaging. Consumers also appreciate transparency regarding the product’s lifecycle and origin. For instance, certifications like Fair Trade or organic farming labels signal ethical sourcing and resonate strongly with environmentally conscious consumers.
Values and Beliefs Driving Consumer Interest in Sustainability
A variety of values and beliefs underpin consumer interest in sustainability. Environmental consciousness is a key driver, with consumers increasingly concerned about climate change and pollution. Ethical considerations, such as fair labor practices and animal welfare, also play a significant role. Furthermore, some consumers are motivated by a desire for personal well-being and a connection to nature.
The belief that sustainable products are better for the environment and contribute to a healthier future is a powerful motivator.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choices
Consumer choices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Price is a significant factor, though consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for sustainable options, particularly if they perceive a strong value proposition. Convenience is also important, and brands can gain an advantage by streamlining the purchase process for sustainable products. Finally, brand reputation plays a crucial role; consumers often trust brands that have a strong commitment to sustainability.
Consumer Perceptions of Sustainability Across Demographics
Consumer perceptions of sustainability vary across demographics. Millennials and Gen Z are often more engaged with sustainability than older generations, driven by their stronger environmental awareness and greater access to information. However, interest in sustainability is growing across all age groups. For example, parents often prioritize sustainable products for their children, considering factors like safety and health.
Motivations of Different Consumer Segments
Millennials and Gen Z often prioritize ethical sourcing and transparency in product information, while older generations may focus more on tangible benefits like reduced environmental impact. Millennials are often more likely to seek out products with specific certifications and detailed information about their origin. Gen Z frequently seeks out products that reflect their values, often through brands that advocate for social responsibility.
Social Media and Influencers
Social media and influencers play a significant role in shaping consumer attitudes towards sustainable products. Consumers are increasingly relying on online reviews and recommendations from influencers. The ability of social media platforms to disseminate information rapidly about sustainable products and brands creates a strong impetus for engagement and purchases.
Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products, and this shift is impacting various industries. For example, Microsoft’s recent announcement to Windows Phone 7 developers, urging them to build CDMA carriers to wait ( microsoft tells winpho7 devs to build cdma carriers to wait ), highlights the evolving landscape of technology and the need for companies to adapt to consumer preferences.
This trend ultimately emphasizes the importance of sustainability in product development, pushing companies to create products with a reduced environmental footprint.
Comparison of Consumer Motivations
| Product Type | Motivation | Demographic | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Product | Environmental consciousness, ethical sourcing, desire for a healthier future | Millennials, Gen Z, environmentally aware consumers | Studies show that consumers are willing to pay a premium for sustainable products if they believe in the value proposition. |
| Conventional Product | Price, convenience, brand recognition | Broad consumer base, including those less focused on sustainability | Historically, affordability and ease of access have been major factors influencing product choices. |
Sustainable Product Offerings
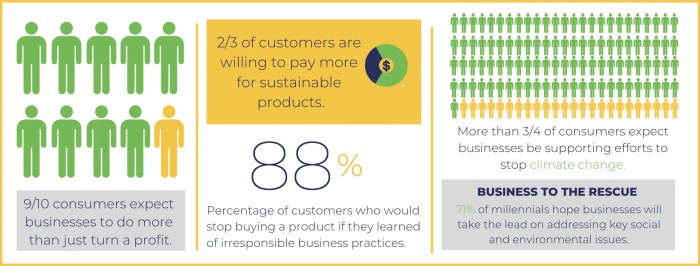
The demand for sustainable products is soaring as consumers increasingly prioritize environmental responsibility. This shift in consumer behavior is driving innovation in product design, manufacturing, and packaging. Businesses are responding by offering a wider range of sustainable alternatives, from clothing made from recycled materials to electronics with extended lifespans. This evolution is essential for mitigating environmental impact and fostering a more sustainable future.
Consumers are increasingly craving sustainable products, prioritizing ethical sourcing and eco-friendly practices. However, even the most conscientious shoppers can fall victim to poor security measures, leading to unforeseen financial or personal issues. This can happen to anyone, regardless of their values or intentions, as explained in this insightful piece on why bad security can happen to good people: why bad security can happen to good people.
Ultimately, the drive for sustainable products requires a comprehensive approach, encompassing not just the product itself, but also the security measures protecting the entire supply chain.
Range of Sustainable Products, Consumers want sustainable products
A diverse range of sustainable products is available across various sectors. This includes clothing made from organic cotton, recycled polyester, or innovative plant-based fibers. Food items with sustainable sourcing practices, reduced packaging, or locally-sourced ingredients are also gaining popularity. Electronics featuring longer lifecycles, repairability, and the use of recycled components represent another important area.
Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Innovative packaging solutions are crucial for reducing waste and promoting sustainability. Examples include compostable or biodegradable packaging materials derived from plant-based sources. Reusable packaging, such as refillable containers and durable bags, further minimize environmental impact. Minimizing packaging overall and using lighter, more efficient materials are also key approaches.
Innovative Approaches to Sustainable Products
Innovative approaches are transforming sustainable product creation. These include designing products for durability and repairability, encouraging consumers to extend the lifespan of items, and developing closed-loop systems for material recovery and reuse. This approach not only reduces waste but also enhances product longevity and consumer value.
Role of Recycled Materials
Recycled materials play a significant role in sustainable product design. Using recycled materials reduces the demand for virgin resources, lessening the environmental impact associated with extraction and processing. This includes incorporating recycled plastics, metals, and textiles into various products. Examples include using recycled PET bottles to create new fabrics or utilizing scrap metals for electronics manufacturing.
Environmental Impact of Materials
The environmental impact of different sustainable product materials varies. Factors like the energy required for production, the carbon footprint of transportation, and the material’s biodegradability all influence the overall environmental impact. For instance, while bamboo is a fast-growing material with a relatively low carbon footprint, its production may still require significant water resources. Comparatively, recycled materials generally have a lower environmental impact than virgin materials, but the specific impact depends on the recycling process and the material’s inherent properties.
Sustainable Product Categories
| Category | Product Example | Key Feature | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clothing | Organic cotton t-shirt | Made from sustainably grown cotton | Reduces pesticide use and conserves water resources |
| Food | Locally sourced produce | Minimizes transportation emissions | Supports local farmers and reduces carbon footprint |
| Electronics | Refurbished laptop | Extends product lifespan | Reduces electronic waste and conserves resources |
| Packaging | Compostable food containers | Biodegradable and compostable | Reduces landfill waste and promotes circularity |
Consumer Behavior and Purchasing Decisions
Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions. This heightened awareness has led to a growing demand for sustainable products, but understanding the complexities of consumer behavior is crucial for businesses aiming to tap into this market. Factors like price, perceived value, and readily available information all play a significant role in shaping consumer choices.
Influencing Factors in Sustainable Product Decisions
Consumer decisions regarding sustainable products are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Price sensitivity, perceived value, environmental consciousness, and readily available information all contribute to the decision-making process. For example, a consumer might prioritize a sustainable product if its perceived value aligns with their personal values, even if the price is slightly higher than a conventional alternative.
Conversely, if the price difference is significant, consumers may opt for the more affordable option, regardless of sustainability claims.
Price Sensitivity in Sustainable Purchases
Price sensitivity is a key factor in the adoption of sustainable products. While many consumers are willing to pay a premium for sustainable options, the price difference often acts as a significant barrier. A higher price point can deter consumers, especially those with limited budgets. This is where strategies like highlighting the long-term cost savings or offering sustainable products at competitive price points become crucial.
For instance, a company might offer a durable, long-lasting product made from recycled materials, which, despite an initial higher price, could ultimately reduce the total cost of ownership over its lifespan.
Impact of Consumer Education
Consumer education plays a critical role in shaping purchasing behavior towards sustainable products. Increased knowledge about the environmental and social benefits of sustainable choices can motivate consumers to make informed decisions. For example, educational campaigns highlighting the lifecycle impact of different materials or the benefits of supporting ethical sourcing can encourage more sustainable purchases. Furthermore, transparent labeling and clear communication about sustainability claims are crucial for fostering consumer trust and understanding.
Barriers to Adopting Sustainable Products
Several barriers hinder the widespread adoption of sustainable products. One key obstacle is a lack of readily available information about product sustainability. Consumers may be uncertain about the authenticity and credibility of sustainability claims, making it difficult to differentiate genuine sustainable options from misleading marketing. Furthermore, the perceived lack of readily available choices in the market can also serve as a barrier.
Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products, and that’s a trend that’s pushing innovation across many sectors. But is Google Drive, with its massive user base, ready to embrace this trend and become a truly sustainable platform? The question of whether Google Drive is ready for a sustainable makeover is a crucial one. The article is gdrive ready to come out of its shell delves into the complexities of this issue, highlighting the challenges and opportunities.
Ultimately, consumer demand for sustainable products will likely drive Google to re-evaluate its processes and embrace more eco-friendly practices.
A perceived lack of comparable, attractive options can deter consumers from making sustainable purchases.
Transparency and Credibility of Sustainability Claims
Transparency and credibility in sustainability claims are paramount. Consumers are increasingly skeptical of unsubstantiated or misleading claims. This necessitates a focus on clear, verifiable information regarding the sustainability of products. Authenticity in sustainability claims fosters consumer trust and builds brand loyalty. A commitment to transparent and traceable supply chains, along with verified certifications, can help enhance credibility.
Successful Sustainable Marketing Campaigns
Successful sustainable marketing campaigns leverage consumer values and address their concerns. Companies that successfully communicate their sustainability efforts and transparently highlight the environmental or social benefits of their products tend to perform better. For example, Patagonia’s focus on environmental activism and their commitment to recycled materials resonates strongly with environmentally conscious consumers.
Trust and Transparency in Brand Communication
Trust and transparency are essential elements in brand communication regarding sustainability. Consumers are more likely to support brands that are genuine and transparent in their sustainability efforts. This requires demonstrating a commitment to continuous improvement and addressing any shortcomings transparently. Consistent, genuine communication regarding sustainability, including setbacks and challenges, is crucial to building long-term consumer trust.
| Product Type | Consumer Behavior | Motivation | Barriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Product | Researching product certifications, seeking out transparency in sourcing, considering long-term value, and potentially paying a premium | Environmental consciousness, ethical considerations, health concerns, and a desire for positive social impact | Lack of readily available information, higher prices compared to conventional alternatives, limited choices, and concerns about the authenticity of sustainability claims |
| Non-Sustainable Product | Prioritizing affordability, convenience, and immediate gratification. Less research into product origins or environmental impact | Price, convenience, and familiarity with the product | Limited awareness of environmental and social consequences, lack of perceived long-term value, and potential health concerns |
Marketing and Communication Strategies
Consumers are increasingly seeking sustainable products, driven by a desire to minimize their environmental impact. Effective marketing strategies are crucial to connect with this conscious consumer base and promote sustainable offerings. These strategies must go beyond simply stating a product is “eco-friendly” and instead resonate with the values and motivations of these consumers.Sustainable products require tailored marketing strategies to highlight their unique value proposition.
This involves understanding not just the environmental benefits, but also the social and economic aspects that appeal to the target audience. Communication should focus on transparency, authenticity, and the overall customer experience.
Effective Communication Strategies for Sustainable Products
Communicating the benefits of sustainability effectively is crucial to attracting consumers. This involves more than just labeling a product as “green.” Clear, concise, and compelling messaging is key.
- Highlighting the environmental impact reduction: Quantify the positive environmental impact of the product. For example, a clothing company could state that using recycled materials reduced water consumption by X% compared to conventional production. This quantitative data builds trust and demonstrates the tangible benefits of the sustainable choice.
- Storytelling for Emotional Connection: Consumers connect with brands that share their values. Using storytelling, brands can convey the story behind the product, including the materials used, the ethical sourcing practices, and the positive impact on communities or the environment. A brand could share the journey of a farmer who practices sustainable agriculture to illustrate the values of the product.
- Visual Elements for Engagement: High-quality images and videos can effectively communicate the sustainable aspects of a product. Images showcasing the manufacturing process using recycled materials or the product’s impact on the environment can create a powerful connection with the consumer.
- Showcasing the Environmental Impact: Use clear visuals to demonstrate the reduced environmental impact of the product. This could include infographics showing the carbon footprint reduction, water usage decrease, or waste material reduction. The visual aids should be simple, yet compelling, making the environmental benefits easily understandable for the average consumer.
Importance of Clear and Concise Labeling
Transparency and clear communication are essential for building consumer trust in sustainable products. Consumers want to know exactly what they’re buying and how it aligns with their values.
- Accurate and easily understandable labeling: Avoid jargon and complex terms. Clearly state the sustainable materials used, the manufacturing processes, and any certifications or standards met. Labels should highlight the specific environmental benefits and explain them in simple terms.
Examples of Successful Marketing Campaigns
Several brands have successfully integrated sustainability into their marketing strategies, creating positive consumer engagement.
- Patagonia’s focus on environmental activism: Patagonia’s campaigns have consistently highlighted environmental issues and encouraged consumers to take action. This aligns with consumer values and fosters a sense of shared responsibility.
- Seventh Generation’s emphasis on transparency and natural ingredients: Seventh Generation’s marketing showcases the natural ingredients and ethical sourcing of their products, resonating with consumers seeking natural and sustainable options.
Value Proposition of Sustainable Products
Communicating the value proposition effectively is critical. It’s not just about environmental benefits; it’s about the overall experience and how the product aligns with consumer values.
- Beyond the Environmental Impact: Highlight the social and economic benefits. For example, products made by employing fair trade practices could emphasize the positive impact on workers’ lives. Consumers appreciate a holistic view of sustainability.
Marketing Strategies Table
| Strategy | Target Audience | Key Message | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Campaigns | Eco-conscious millennials and Gen Z | Highlighting the ethical and environmental benefits of the product. | Engagement rate, reach, website traffic |
| Influencer Marketing | Trendsetters and early adopters | Showcase the product’s unique features and sustainability credentials. | Sales conversions, brand mentions |
| Partnerships with Environmental Organizations | Eco-conscious consumers | Demonstrating commitment to environmental protection. | Brand awareness, media coverage |
Challenges and Opportunities
The journey towards a more sustainable future in product development and marketing presents both significant hurdles and exciting prospects. Companies are facing increasing pressure to adopt environmentally friendly practices, yet navigating this transition can be complex. Consumers, too, are becoming more discerning, demanding transparency and accountability in the products they buy. This dynamic environment requires careful consideration of both the challenges and opportunities to ensure long-term success and sustainability.
Challenges in Producing Sustainable Products
Producing sustainable products often entails higher upfront costs. Finding eco-friendly materials, implementing sustainable manufacturing processes, and adhering to stringent environmental regulations can significantly increase production expenses. Furthermore, the availability of these materials might be limited, posing supply chain challenges. This can make sustainable products less competitive in the short term compared to conventional alternatives.
Challenges in Marketing Sustainable Products
Marketing sustainable products presents its own set of difficulties. Consumers are often skeptical about greenwashing, which is the practice of misleading consumers about the environmental benefits of a product. Building trust and credibility takes time and substantial effort. Communicating the true environmental impact of a product, often complex and multifaceted, requires clear and compelling messaging that resonates with the target audience.
Misinformation and a lack of standardized labeling can further complicate marketing efforts.
Potential Solutions to Address Production and Marketing Challenges
Addressing the production challenges involves exploring innovative sourcing strategies, investing in eco-friendly technologies, and optimizing production processes to minimize waste. Collaborating with suppliers committed to sustainability is also crucial. Regarding marketing, transparent communication, highlighting specific sustainable features, and utilizing certifications and labels can build consumer trust.
Innovation in Sustainable Product Development
Innovation in sustainable product development focuses on creating products that are both environmentally friendly and economically viable. This involves using recycled materials, developing bio-based alternatives, and designing products for recyclability and durability. For example, companies are experimenting with 3D printing using recycled plastics, reducing material waste and creating customized products. Another example involves designing products with a longer lifespan and enhanced repairability.
Examples of Successful Sustainable Business Models
Several companies have successfully implemented sustainable business models. Patagonia, known for its commitment to environmental conservation, promotes repairs and reuses materials. Other companies, like TOMS Shoes, implement a “one for one” model, donating a pair of shoes to a child in need for every pair purchased. These models demonstrate that sustainable practices can be profitable and create a positive social impact.
Opportunities Presented by Growing Consumer Demand
The increasing demand for sustainable products creates substantial opportunities for companies. This demand allows companies to differentiate themselves, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and command premium prices for their products. Consumers are willing to pay a premium for products they perceive as having a lower environmental footprint.
Long-Term Sustainability of the Industry
The long-term sustainability of the industry hinges on a collaborative effort. Governments need to support sustainable practices through regulations and incentives. Companies must commit to long-term environmental goals, investing in research and development of innovative sustainable products. Consumers play a vital role by demanding transparency and supporting businesses with sustainable practices.
Table: Key Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Products
| Challenge | Potential Solution | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| High upfront costs of sustainable materials | Explore innovative sourcing strategies, invest in eco-friendly technologies, optimize production processes | Reduced production costs, increased efficiency, improved supply chain resilience | Using recycled plastic in packaging, optimizing energy use in manufacturing |
| Consumer skepticism about greenwashing | Transparent communication, highlight specific sustainable features, utilize certifications and labels | Increased consumer trust, brand differentiation, improved market positioning | Clearly labeling products’ recycled content or carbon footprint |
| Limited availability of sustainable materials | Diversify sourcing strategies, develop partnerships with sustainable material providers, explore alternative materials | Improved material access, enhanced resilience, reduced supply chain vulnerabilities | Partnering with farms using sustainable agricultural practices |
| Complexity in communicating environmental impact | Develop clear, concise, and easily understood messaging that highlights key benefits | Improved consumer understanding, increased brand credibility, enhanced consumer engagement | Use infographics and storytelling to explain product life cycle |
Epilogue

In conclusion, the demand for sustainable products is undeniable and presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses. Understanding consumer motivations, offering a wide range of sustainable options, and employing effective marketing strategies are crucial for success in this evolving market. Ultimately, the future of consumerism hinges on our ability to balance economic growth with environmental responsibility.

